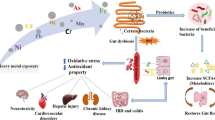
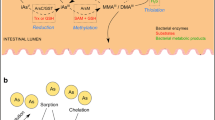
Abstract
Organisms are exposed to multiple toxicants in their surroundings in the increasingly contaminated complex environment. Such toxic exposures are observed to trigger complex biological responses that might or might not be identical to the responses elicited by individual exposures of the same toxicants. Two notable water contaminants, fluoride (F) and arsenic (As) are present worldwide and pose threat to organisms. These contaminants are consumed via contaminated water, drugs, toothpastes, cosmetics etc. Symbiotic microbiota dwelling in the gastrointestinal tract, are the key modulators of host health. Number of reports have concluded that F and As can alter the gut bacterial homeostasis, leading to the deterioration of host health. All the vital bodily systems including digestive, cardiovascular, nervous, reproductive and renal, are getting affected due to the alteration of gut bacteria. This scenario surely hints towards a complex association between toxicants, gut microbiota and host health. Taking into consideration, the present review intends to focus on individual and combined effects of F and As on the perturbation of gut bacteria of different organisms with special emphasis on the effect on human health.
Graphical Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- As2O3 :
-
Arsenic trioxide
- As:
-
Arsenic
- c-AMP:
-
Cyclic-adenosine monophosphate
- DMA:
-
Dimethyl arsinic acid
- F:
-
Fluoride
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- HF:
-
Hydrogen fluoride
- MGBB:
-
Microbiota-gut-blood barrier
- MMA:
-
Monomethyl arsonic acid
- MVA:
-
Mevalonic acid
- NaAsO2 :
-
Sodium arsenite
- NaF:
-
Sodium fluoride
- OTUs:
-
Operative taxonomical groups
- SCFAs:
-
Short chain fatty acids
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- ZO:
-
Zonula occludens
References
Alarcón-Herrera MT, Bundschuh J, Nath B, Nicolli HB, Gutierrez M, Reyes-Gomez VM, Nunez D, Martín-Dominguez IR, Sracek O. Co-occurrence of arsenic and fluoride in groundwater of semi-arid regions in Latin America: Genesis, mobility and remediation. J Hazard Mater. 2013;262:960–9.
Baldelli V, Scaldaferri F, Putignani L, Del Chierico F. The role of Enterobacteriaceae in gut microbiota dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel diseases. Microorganisms. 2021;9(4):697.
Belotserkovsky I, Sansonetti PJ. Shigella and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Escherichia coli a Versat Pathog. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/82_2018_104.
Bist P, Choudhary S. Impact of heavy metal toxicity on the gut microbiota and its relationship with metabolites and future probiotics strategy: a review. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022;200(12):5328–50.
Brabec JL, Wright J, Ly T, Wong HT, McClimans CJ, Tokarev V, Sherchan SP. Arsenic disturbs the gut microbiome of individuals in a disadvantaged community in Nepal. Heliyon. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03313.
Brennan CA, Garrett WS. Fusobacterium nucleatum—symbiont, opportunist and oncobacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2019;17(3):156–66.
Brouwer S, Rivera-Hernandez T, Curren BF, Harbison-Price N, De Oliveira DM, Jespersen MG, Davies MR, Walker MJ. Pathogenesis, epidemiology and control of group A Streptococcus infection. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023;9:1–7.
Büttner FM, Zoll S, Nega M, Götz F, Stehle T. Structure-function analysis of Staphylococcus aureus amidase reveals the determinants of peptidoglycan recognition and cleavage. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(16):11083–94.
Calatayud M, Barrios JA, Velez D, Devesa V. In vitro study of transporters involved in intestinal absorption of inorganic arsenic. Chem Res Toxicol. 2012;25(2):446–53.
Chakraborti D, Mukherjee SC, Pati S, Sengupta MK, Rahman MM, Chowdhury UK, Lodh D, Chanda CR, Chakraborti AK, Basu GK. Arsenic groundwater contamination in middle Ganga plain, Bihar, India: a future danger? Environ Health Perspect. 2003;111(9):1194–201.
Chattopadhyay A, Podder S, Agarwal S, Bhattacharya S. Fluoride-induced histopathology and synthesis of stress protein in liver and kidney of mice. Arch Toxicol. 2011;85:327–35.
Chen F, Luo Y, Li C, Wang J, Chen L, Zhong X, Guo L. Sub-chronic low-dose arsenic in rice exposure induces gut microbiome perturbations in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety. 2021;227:112934.
Chen G, Hu P, Xu Z, Peng C, Wang Y, Wan X, Cai H. The beneficial or detrimental fluoride to gut microbiota depends on its dosages. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;209:111732.
Chi L, Bian X, Gao B, Ru H, Tu P, Lu K. Sex-specific effects of arsenic exposure on the trajectory and function of the gut microbiome. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016;29:949–51.
Choiniere J, Wang L. Exposure to inorganic arsenic can lead to gut microbe perturbations and hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016;6(5):426–9.
Czarnowski W, Wrześniowska K, Krechniak J. Fluoride in drinking water and human urine in Northern and Central Poland. Sci Total Environ. 1996;191(1–2):177–84.
Das N, Das A, Sarma KP, Kumar M. Provenance, prevalence and health perspective of co-occurrences of arsenic, fluoride and uranium in the aquifers of the Brahmaputra River floodplain. Chemosphere. 2018;194:755–72.
De A, Mridha D, Joardar M, Das A, Chowdhury NR, Roychowdhury T. Distribution, prevalence and health risk assessment of fluoride and arsenic in groundwater from lower Gangetic plain in West Bengal India. Groundw Sustain Dev. 2022;16:100722.
Dheer R, Patterson J, Dudash M, Stachler EN, Bibby KJ, Stolz DB, Shiva S, Wang Z, Hazen SL, Barchowsky A, Stolz JF. Arsenic induces structural and compositional colonic microbiome change and promotes host nitrogen and amino acid metabolism. Toxicol Appl Pharm. 2015;289(3):397–408.
Ding YH, Qian LY, Pang J, Lin JY, Xu Q, Wang LH, Huang DS, Zou H. The regulation of immune cells by Lactobacilli: a potential therapeutic target for anti-atherosclerosis therapy. Oncotarget. 2017;8(35):59915.
Dionizio A, Uyghurturk DA, Melo CG, Sabino-Arias IT, Araujo TT, Ventura TM, Perles JV, Zanoni JN, Den Besten P, Buzalaf MA. Intestinal changes associated with fluoride exposure in rats: Integrative morphological, proteomic and microbiome analyses. Chemosphere. 2021;1(273):129607.
Dong X, Shulzhenko N, Lemaitre J, Greer RL, Peremyslova K, Quamruzzaman Q, Rahman M, Hasan OS, Joya SA, Golam M, et al. Arsenic exposure and intestinal microbiota in children from Sirajdikhan. Bangladesh PLoS One. 2017;12:e0188487.
Dutta J. Fluoride, arsenic and other heavy metals contamination of drinking water in the tea garden belt of Sonitpur district, Assam. India Int J ChemTech Res. 2013;5(5):2614–22.
Fan P, Liu P, Song P, Chen X, Ma X. Moderate dietary protein restriction alters the composition of gut microbiota and improves ileal barrier function in adult pig model. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):43412.
Farooqi A, Masuda H, Firdous N. Toxic fluoride and arsenic contaminated groundwater in the Lahore and Kasur districts, Punjab, Pakistan and possible contaminant sources. Environ Pollut. 2007;145(3):839–49.
Ferreira-Halder CV, de Sousa Faria AV, Andrade SS. Action and function of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in health and disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;31(6):643–8.
Fu R, Niu R, Li R, Yue B, Zhang X, Cao Q, Wang J, Sun Z. Fluoride-induced alteration in the diversity and composition of bacterial microbiota in mice colon. Biol Trace Element Res. 2020;196(2):537–44.
Gerritsen J, Hornung B, Renckens B, van Hijum SA, Dos Santos VA, Rijkers GT, Schaap PJ, de Vos WM, Smidt H. Genomic and functional analysis of Romboutsia ilealis CRIBT reveals adaptation to the small intestine. PeerJ. 2017;5:e3698.
Ghosh S, Mukherjee M, Roychowdhury T. Bacterial bio-mobilization and-sequestration of arsenic in contaminated paddy fields of West Bengal, India. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2022;1(43):102420.
Government of India, “Bhu-Jal News”, Quarterly Journal Volume No.24, Number 1, Jan-March 2009
Gu X, Sim JX, Lee WL, Cui L, Chan YF, Chang ED, Teh YE, Zhang AN, Armas F, Chandra F, Chen H. Gut Ruminococcaceae levels at baseline correlate with risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Iscience. 2022;25(1):103644.
Guo H, Zhang Y, Xing L, Jia Y. Spatial variation in arsenic and fluoride concentrations of shallow groundwater from the town of Shahai in the Hetao basin. Inner Mongolia Appl Geochem. 2012;27(11):2187–96.
Guo P, Zhang K, Ma X, He P. Clostridium species as probiotics: potentials and challenges. J Animal Sci Biotechnol. 2020;11(1):1.
Hall LL, George SE, Kohan MJ, Styblo M, Thomas DJ. In vitro methylation of inorganic arsenic in mouse intestinal cecum. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997;147(1):101–9.
Hall MN, Gamble MV. Nutritional manipulation of one-carbon metabolism: effects on arsenic methylation and toxicity. J Toxicol. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/595307.
Hoen AG, Madan JC, Li Z, Coker M, Lundgren SN, Morrison HG, Palys T, Jackson BP, Sogin ML, Cottingham KL, et al. Sex-specific associations of infants’ gut microbiome with arsenic exposure in a US population. Sci Rep. 2018;8:12627.
Hosokawa S, Kuroda K, Narihiro T, Aoi Y, Ozaki N, Ohashi A, Kindaichi T. Cometabolism of the superphylum Patescibacteria with anammox bacteria in a long-term freshwater anammox column reactor. Water. 2021;13(2):208.
Hughes MF, Beck BD, Chen Y, Lewis AS, Thomas DJ. Arsenic exposure and toxicology: a historical perspective. Toxicol Sci. 2011;123(2):305–32.
Jha SK, Singh RK, Damodaran T, Mishra VK, Sharma DK, Rai D. Fluoride in groundwater: toxicological exposure and remedies. J Toxicol Environ Health, Part B. 2013;16(1):52–66.
Joardar M, Das A, Chowdhury NR, Mridha D, Das J, De A, Majumder S, Majumdar KK, Roychowdhury T. Impact of treated drinking water on arsenicosis patients with continuous consumption of contaminated dietary foodstuffs: a longitudinal health effect study from arsenic prone area, West Bengal India. Groundw Sustain Dev. 2022;18:100786.
Kabir H, Gupta AK, Tripathy S. Fluoride and human health: Systematic appraisal of sources, exposures, metabolism, and toxicity. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. 2020;50(11):1116–93.
Kadowaki R, Tanno H, Maeno S, Endo A. Spore-forming properties and enhanced oxygen tolerance of butyrate-producing Anaerostipes spp. Anaerobe. 2023;8:102752.
Kim SH, Kim K, Ko KS, Kim Y, Lee KS. Co-contamination of arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater of unconsolidated aquifers under reducing environments. Chemosphere. 2012;87(8):851–6.
Kitchin KT. Recent advances in arsenic carcinogenesis: modes of action, animal model systems, and methylated arsenic metabolites. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2001;172(3):249–61.
Komuroglu AU, Seckin H, Ertaş M, Meydan I. Metagenomic Analysis of intestinal microbiota in florated rats. Biol Trace Element Res. 2022;200(7):3275–83.
Kumar M, Das A, Das N, Goswami R, Singh UK. Co-occurrence perspective of arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater of Diphu, Assam, Northeastern India. Chemosphere. 2016;150:227–38.
La Reau AJ, Suen G. The Ruminococci: key symbionts of the gut ecosystem. J Microbiol. 2018;56:199–208.
Lee KC, Webb RI, Janssen PH, Sangwan P, Romeo T, Staley JT, Fuerst JA. Phylum Verrucomicrobia representatives share a compartmentalized cell plan with members of bacterial phylum Planctomycetes. BMC Microbiol. 2009;9:1.
Leylabadlo HE, Ghotaslou R, Feizabadi MM, Farajnia S, Moaddab SY, Ganbarov K, Khodadadi E, Tanomand A, Sheykhsaran E, Yousefi B, Kafil HS. The critical role of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in human health: an overview. Microb Pathog. 2020;1(149):104344.
Li A, Wang Y, He Y, Liu B, Iqbal M, Mehmood K, Jamil T, Chang YF, Hu L, Li Y, Guo J. Environmental fluoride exposure disrupts the intestinal structure and gut microbial composition in ducks. Chemosphere. 2021;1(277):130222.
Li G, Zheng X, Zhu Y, Long Y, Xia X. In-depth insights into the disruption of the microbiota-gut-blood barrier of model organism (Bombyx mori) by fluoride. Sci Total Environ. 2022;10(838):156220.
Liu J, Wang HW, Lin L, Miao CY, Zhang Y, Zhou BH. Intestinal barrier damage involved in intestinal microflora changes in fluoride-induced mice. Chemosphere. 2019;234:409–18.
Liu P, Li R, Tian X, Zhao Y, Li M, Wang M, Ying X, Yuan J, Xie J, Yan X, Lyu Y. Co-exposure to fluoride and arsenic disrupts intestinal flora balance and induces testicular autophagy in offspring rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe. 2021;222:112506.
Lu K, Abo RP, Schlieper KA, Graffam ME, Levine S, Wishnok JS, Swenberg JA, Tannenbaum SR, Fox JG. Arsenic exposure perturbs the gut microbiome and its metabolic profile in mice: an integrated metagenomics and metabolomics analysis. Environ Health Perspect. 2014;122(3):284–91.
Lu K, Cable PH, Abo RP, Ru H, Graffam ME, Schlieper KA, Parry NM, Levine S, Bodnar WM, Wishnok JS, Styblo M. Gut microbiome perturbations induced by bacterial infection affect arsenic biotransformation. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013;26(12):1893–903.
Lu K, Mahbub R, Fox JG. Xenobiotics: interaction with the intestinal microflora. ILAR J. 2015;56(2):218–27.
Luo Q, Cui H, Peng X, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Liu J, Deng Y. Dietary high fluorine alters intestinal microbiota in broiler chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;173:483–91.
Mahlangu O, Mamba B, Momba M. Efficiency of silver impregnated porous pot (SIPP) filters for production of clean potable water. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2012;9(9):3014–29.
Miao L, Gong Y, Li H, Xie C, Xu Q, Dong X, Elwan HA, Zou X. Alterations in cecal microbiota and intestinal barrier function of laying hens fed on fluoride supplemented diets. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe. 2020;193:110372.
Mondal P, Shaw P, Bandyopadhyay A, Bhowmik AD, Chakraborty A, Sudarshan M, Chattopadhyay A. Mixture effect of arsenic and fluoride at environmentally relevant concentrations in zebrafish (Danio rerio) liver: expression pattern of Nrf2 and related xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes. Aquat Toxicol. 2019;1(213):105219.
Mondal P, Shaw P, Bhowmik AD, Bandyopadhyay A, Sudarshan M, Chakraborty A, Chattopadhyay A. Combined effect of arsenic and fluoride at environmentally relevant concentrations in zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain: alterations in stress marker and apoptotic gene expression. Chemosphere. 2021;1(269):128678.
Moran GP, Zgaga L, Daly B, Harding M, Montgomery T. Does fluoride exposure impact on the human microbiome? Toxicol Lett. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2023.03.001.
Narsimha A, Sudarshan V. Contamination of fluoride in groundwater and its effect on human health: a case study in hard rock aquifers of Siddipet, Telangana State, India. Appl Water Sci. 2017;7:2501–12.
Navas-Acien A, Silbergeld EK, Streeter RA, Clark JM, Burke TA, Guallar E. Arsenic exposure and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of the experimental and epidemiologic evidence. Environ Health Perspect. 2006;114(5):641–8.
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W, Pettersson S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science. 2012;336(6086):1262–7.
Paul DS, Harmon AW, Devesa V, Thomas DJ, Stýblo M. Molecular mechanisms of the diabetogenic effects of arsenic: inhibition of insulin signaling by arsenite and methylarsonous acid. Environ Health Perspect. 2007;115(5):734–42.
Purohit A, Alam MJ, Kandiyal B, Das B, Banerjee SK. Gut microbiome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2022;191(1):187–206.
Qin J, Rosen BP, Zhang Y, Wang G, Franke S, Rensing C. Arsenic detoxification and evolution of trimethylarsine gas by a microbial arsenite S-adenosylmethionine methyltransferase. Proceed Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103(7):2075–80.
Qiu Y, Chen X, Yan X, Wang J, Yu G, Ma W, Xiao B, Quinones S, Tian X, Ren X. Gut microbiota perturbations and neurodevelopmental impacts in offspring rats concurrently exposure to inorganic arsenic and fluoride. Environ Int. 2020;1(140):105763.
Reddy PS, Rani GP, Sainath SB, Meena R, Supriya CH. Protective effects of N-acetylcysteine against arsenic-induced oxidative stress and reprotoxicity in male mice. J Trace Elements Med Biol. 2011;25(4):247–53.
Ribeiro DA, Cardoso CM, Yujra VQ, Viana MD, Aguiar O, Pisani LP, Oshima CT. Fluoride induces apoptosis in mammalian cells: in vitro and in vivo studies. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(9):4767–77.
Richardson JB, Dancy BC, Horton CL, Lee YS, Madejczyk MS, Xu ZZ, Ackermann G, Humphrey G, Palacios G, Knight R, Lewis JA. Exposure to toxic metals triggers unique responses from the rat gut microbiota. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):6578.
Robertson FN. Arsenic in ground-water under oxidizing conditions, south-west United States. Environ Geochem Health. 1989;11:171–85.
Seltenrich N. Arsenic and diabetes: assessing risk at low-to-moderate exposures. Environ Health Perspect. 2018;126(4):044002.
Shahi SK, Freedman SN, Mangalam AK. Gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis: the players involved and the roles they play. Gut Microbes. 2017;8(6):607–15.
Shao M, Zhu Y. Long-term metal exposure changes gut microbiota of residents surrounding a mining and smelting area. Scientific Rep. 2020;10(1):4453.
Shinohara T, Okamoto K, Koyano S, Otani A, Yamashita M, Wakimoto Y, Jubishi D, Hashimoto H, Ikeda M, Harada S, Okugawa S. Plesiomonas shigelloides septic shock following ingestion of Dojo nabe (loach hotpot). InOpen Forum Infectious Diseases 2021 Aug 1 (Vol. 8, No. 8, p. ofab401). US: Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofab401.
Şi̇reli̇ M, Bülbül A. The effect of acute fluoride poisoning on nitric oxide and methemoglobin formation in the guinea pig. Turkish J Vet Anim Sci. 2004;28(3):591–5.
Smedley PL. Arsenic in rural groundwater in Ghana: part special issue: hydrogeochemical studies in sub-Saharan Africa. J Afr Earth Sc. 1996;22(4):459–70.
Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, Michaud M, Gallini CA, Bohlooly-y M, Glickman JN, Garrett WS. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science. 2013;341(6145):569–73.
Stojanov S, Berlec A, Štrukelj B. The influence of probiotics on the firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms. 2020;8(11):1715.
Sun N, Ni X, Wang H, Xin J, Zhao Y, Pan K, Jing B, Zeng D. Probiotic Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 prevents memory dysfunction induced by chronic high-fluorine intake through modulating intestinal environment and improving gut development. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020;12:1420–38.
Theriot CM, Koenigsknecht MJ, Carlson PE Jr, Hatton GE, Nelson AM, Li B, Huffnagle GB, Z. Li J, Young VB. Antibiotic-induced shifts in the mouse gut microbiome and metabolome increase susceptibility to Clostridium difficile infection. Nat Commun. 2014;5(1):3114.
Tian X, Yan X, Chen X, Liu P, Sun Z, Niu R. Identifying serum metabolites and gut bacterial species associated with nephrotoxicity caused by arsenic and fluoride exposure. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023;24:1–2.
Toprak NU, Duman N, Sacak BÜ, Ozkan MC, Sayın E, Mulazimoglu L, Soyletir G. Alloprevotella rava isolated from a mixed infection of an elderly patient with chronic mandibular osteomyelitis mimicking oral squamous cell carcinoma. New Microb New Infect. 2021;42:100880.
Tseng CH. Arsenic methylation, urinary arsenic metabolites and human diseases: current perspective. J Environ Sci Health C. 2007;25(1):1–22.
Vacca M, Celano G, Calabrese FM, Portincasa P, Gobbetti M, De Angelis M. The controversial role of human gut lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms. 2020;8(4):573.
Vitellio P, Celano G, Bonfrate L, Gobbetti M, Portincasa P, De Angelis M. Effects of Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus rhamnosus on gut microbiota in patients with lactose intolerance and persisting functional gastrointestinal symptoms: a randomised, double-blind, cross-over study. Nutrients. 2019;11(4):886.
Wang HT, Ma L, Zhu D, Ding J, Li G, Jin BJ, Shao YH, Zhang WX, Song MY, Fu SL. Responses of earthworm metaphire vulgaris gut microbiota to arsenic and nanoplastics contamination. Sci Total Environ. 2022;1(806):150279.
Wang HT, Zhu D, Li G, Zheng F, Ding J, O’Connor PJ, Zhu YG, Xue XM. Effects of arsenic on gut microbiota and its biotransformation genes in earthworm Metaphire sieboldi. Environ Sci Technol. 2019;53(7):3841–9.
Wang HW, Miao CY, Liu J, Zhang Y, Zhu SQ, Zhou BH. Fluoride-induced rectal barrier damage and microflora disorder in mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020;27:7596–607.
Wang K, Wu W, Wang Q, Yang L, Bian X, Jiang X, Lv L, Yan R, Xia J, Han S, Li L. The negative effect of Akkermansia muciniphila-mediated post-antibiotic reconstitution of the gut microbiota on the development of colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:932047.
Wang SX, Wang ZH, Cheng XT, Li J, Sang ZP, Zhang XD, Han LL, Qiao XY, Wu ZM, Wang ZQ. Arsenic and fluoride exposure in drinking water: children’s IQ and growth in Shanyin county, Shanxi province. China Environ Health Perspect. 2007;115(4):643–7.
Wang Y, Shvartsev SL, Su C. Genesis of arsenic/fluoride-enriched soda water: a case study at Datong, Northern China. Appl Geochem. 2009;24(4):641–9.
Wang YF, Qiao M, Wang HT, Zhu D. Species-specific effects of arsenic on the soil collembolan gut microbiota. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019;15(183):109538.
Wei B, Yu J, Kong C, Li H, Yang L, Xia Y, Wu K. Effects of arsenic methylation and metabolism on the changes of arsenic-related skin lesions. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2512-2.
Whitford GM. Intake and metabolism of fluoride. Adv Dental Res. 1994;8(1):5–14.
WHO, Environmental Health Criteria-224. Arsenic and arsenic compounds, second ed., World Health Organization, Geneva, 2003.
WHO. Fluoride in Drinking-water. Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality. 2004
Wu F, Guo X, Zhang J, Zhang M, Ou Z, Peng Y. Phascolarctobacterium faecium abundant colonization in human gastrointestinal tract. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(4):3122–6.
Wu F, Yang L, Islam MT, Jasmine F, Kibriya MG, Nahar J, Barmon B, Parvez F, Sarwar G, Ahmed A, Eunus M. The role of gut microbiome and its interaction with arsenic exposure in carotid intima-media thickness in a Bangladesh population. Environ Int. 2019;1(123):104–13.
Wu H, Wu R, Chen X, Geng H, Hu Y, Gao L, Fu J, Pi J, Xu Y. Developmental arsenic exposure induces dysbiosis of gut microbiota and disruption of plasma metabolites in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022;1(450):116174.
Wu S, Wang Y, Iqbal M, Mehmood K, Li Y, Tang Z, Zhang H. Challenges of fluoride pollution in environment: mechanisms and pathological significance of toxicity–a review. Environ Pollut. 2022;1(304):119241.
Xin J, Sun N, Wang H, Ma H, Wu B, Li L, Wang Y, Huang H, Zeng D, Bai X, Chen A. Preventive effects of Lactobacillus johnsonii on the renal injury of mice induced by high fluoride exposure: Insights from colonic microbiota and co-occurrence network analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;25(228):113006.
Xin J, Wang H, Sun N, Bughio S, Zeng D, Li L, Wang Y, Khalique A, Zeng Y, Pan K, Jing B. Probiotic alleviate fluoride-induced memory impairment by reconstructing gut microbiota in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;215:112108.
Yadav M, Singh G, Jadeja RN. Fluoride contamination in groundwater, impacts, and their potential remediation techniques. Groundw Geochem: Pollut Remediat Methods. 2021;25:22–41.
Yan X, Chen X, Tian X, Qiu Y, Wang J, Yu G, Dong N, Feng J, Xie J, Nalesnik M, Niu R. Co-exposure to inorganic arsenic and fluoride prominently disrupts gut microbiota equilibrium and induces adverse cardiovascular effects in offspring rats. Sci Total Environ. 2021;1(767):144924.
Yang J, Li Y, Wen Z, Liu W, Meng L, Huang H. Oscillospira-a candidate for the next-generation probiotics. Gut Microbes. 2021;13(1):1987783.
Yasuda K, Hsu T, Gallini CA, Mclver LJ, Schwager E, Shi A, DuLong CR, Schwager RN, Abu-Ali GS, Franzosa EA, Garrett WS. Fluoride depletes acidogenic taxa in oral but not gut microbial communities in mice. Msystems. 2017;2(4):e00047-e117.
Yeoh YK, Sun Y, Ip LY, Wang L, Chan FK, Miao Y, Ng SC. Prevotella species in the human gut is primarily comprised of Prevotella copri, Prevotella stercorea and related lineages. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):9055.
Younan S, Sakita GZ, Albuquerque TR, Keller R, Bremer-Neto H. Chromium (VI) bioremediation by probiotics. J Sci Food Agric. 2016;96(12):3977–82.
Yu H, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Shang X, Lu Y, Fu Y, Li Y. Effects of fluorine on intestinal structural integrity and microbiota composition of common carp. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021;199:3489–96.
Zeng Q, Xu Y, Yu X, Yang J, Hong F, Zhang A. Silencing GSK3β instead of DKK1 can inhibit osteogenic differentiation caused by co-exposure to fluoride and arsenic. Bone. 2019;1(123):196–203.
Zhang C, Zhang M, Wang S, Han R, Cao Y, Hua W, Mao Y, Zhang X, Pang X, Wei C, Zhao G. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J. 2010;4(2):232–41.
Zhang YJ, Li S, Gan RY, Zhou T, Xu DP, Li HB. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(4):7493–519.
Zhong G, Wan F, Lan J, Jiang X, Wu S, Pan J, Tang Z, Hu L. Arsenic exposure induces intestinal barrier damage and consequent activation of gut-liver axis leading to inflammation and pyroptosis of liver in ducks. Sci Total Environ. 2021;20(788):147780.
Zhong N, Ma Y, Meng X, Sowanou A, Wu L, Huang W, Gao Y, Pei J. Effect of fluoride in drinking water on fecal microbial community in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022;1:1–9.
Zhu SQ, Liu J, Han B, Zhao WP, Zhou BH, Zhao J, Wang HW. Fluoride exposure cause colon microbiota dysbiosis by destroyed microenvironment and disturbed antimicrobial peptides expression in colon. Environ Pollut. 2022;1(292):118381.
Zhu YP, Xi SH, Li MY, Ding TT, Liu N, Cao FY, Zeng Y, Liu XJ, Tong JW, Jiang SF. Fluoride and arsenic exposure affects spatial memory and activates the ERK/CREB signaling pathway in offspring rats. Neurotoxicology. 2017;1(59):56–64.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the Department of Zoology, Visva-Bharati for providing infrastructural support. Miss. Sunanda Mukherjee expresses her gratitude to DST-INSPIRE (No.DST/INSPIRE Fellowship/2019/IF190941) fellowship for the financial assistance. Miss Olivia Sarkar is thankful to DST-INSPIRE (No. DST/INSPIRE Fellowship/2021/IF210118) for providing financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.M. wrote the manuscript and designed the diagram. O.S. checked and revised the manuscript. A.C. provided suggestions and revised the manuscript for final submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this review.
Additional information
Corresponding Editor: Umesh C. Lavania; Reviewers: Pallab Shaw, Debasish Bandyopadhyay.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, S., Sarkar, O. & Chattopadhyay, A. Individual and combined effects of fluoride and arsenic on gut bacteria: a recent update. Nucleus (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-023-00460-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-023-00460-4