Abstract
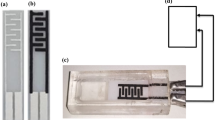
Bioelectrochemical microfluidic devices are developed based on the continuous flow mode of membrane-less, microbial three-electrode cells (M3Cs). These novel devices are the miniaturized microfluidic-based three-electrode cells for the first time, and these are composed of an Ag/AgCl reference electrode, indium tin oxide anode and cathode electrodes. The basic performance of the devices is tested using biofilms grown from wastewater inoculum in an experiment that senses for toxic materials. The toxic materials used are: sodium cyanide, imidazole, and sodium azide in concentrations of 0.02–0.8 mM, with lactate and sodium acetate functioning as substrates. While a constant potential of 0.2 V is applied to the working electrodes of the device, the bioelectrocatalytic oxidation current is monitored at 35°C. When the biocides are introduced, the response current from the cell decreases. The sensor can detect imidazole at the range of 0.02–0.4 mM. The experimental results show the potential of using microfluidic-based microbial electrolysis cells not only as biocide sensors, but also as investigative tools for microbial electrochemical assays.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lovley, D.R. Bug juice: Harvesting electricity with microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Microbial. 4, 497–508 (2006).
Logan, B.E. & Regan, J.M. Microbial challenges and applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 5172–5180 (2006).
Clauwaert, P. et al. Minimizing losses in bio-electrochemical systems: the road to applications. Appl. Microbial Biotechnol. 79, 901–913 (2008).
Wang, H. & Ren, Z.J. A comprehensive review of microbial electrochemical systems as a platform technology. Biotechnol. Adv. 31, 1796–1807 (2013).
Yoon, S.-M. et al. Enrichment of electrochemically active bacteria using a three-electrode electrochemical cell. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17, 110–115 (2007).
Patil, S. et al. Electroactive mixed culture derived biofilms in microbial bioelectrochemical systems: The role of pH on biofilm formation, performance and composition. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 9683–9690 (2011).
Patil, S., Harnish, F. & Schröder, U. Toxicity response of electroactive microbial biofilms-A decisive feature for potential biosensor and power source applications. ChemPhysChem. 11, 2834–2837 (2010).
Dávila, D., Esquivel, J.P. & Sabaté, N. Silicon-based microfabricated microbial fuel cell toxicity sensor. J. Mas, Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 2426–2430 (2011).
Chiao, M., Lam, K.B. & Lin, L. Micromachined microbial and photosynthetic fuel cells. J. Micromech. Microeng. 16, 2547–2553 (2006).
Choi, S. et al. A μL-scale micromachined microbial fuel cell having high power density. Lab Chip 11, 1110–1117 (2011).
Chen, Y.-P. et al. An innovative miniature microbial fuel cell fabricated using photolithography. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 2841–2846 (2011).
Qian, F., He, Z., Thelen, M.P. & Li, Y. A microfluidic microbial fuel cell fabricated by soft lithography. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 5836–5840 (2011).
Hou, H. et al. A microfluidic microbial fuel cell array that support long-term multiplexed analyses of electricigens. Lab Chip 12, 4151–4159 (2012).
Li, Z., Venkataraman, A., Rosenbaum, M.A. & Angenent, L.T. A laminar-flow microfluidic device for quantitative analysis of microbial electrochemical activity. ChemSusChem. 5, 1119–1123 (2012).
Patil, S., Harnish, F., Kapadnis, B. & Schröder, U. Electroactive mixed culture biofilms in microbial bioelectrochemical systems: The role of temperature for biofilm formation and performance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 803–808 (2010).
Jain, A., Connolly, J.O., Woolley, R., Krishnamurthy, S. & Marsili, E. Extracellular electron transfer mechanism in shewanella loihica PV-4 biofilms formed at indium tin oxide and graphite electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 8, 1778–1793 (2013).
Giller, K.E., Witter, E. & Mcgrath, S.P. Toxicity of heavy metals t microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural solils: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 30, 1389–1414 (1998).
Gadd, G.M. & Griffiths, A.J. Microorganisms and heavy-metal toxicity. Microb. Ecol. 4, 303–317 (1978).
Cho, C.-H., Cho, W., Ahn, Y. & Hwan, S.-Y. PDMS-glass serpentine microchannel chip for time domain PCR with bubble suppression in sample injection. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 1810–1817 (2007).
Polk, B.J., Stelzenmuller, A., Mijares, G., MacCrehan, W. & Gaitan, M. Ag/AgCl microelctrodes with improved stability for microfluidics. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 114, 239–247 (2006).
Ko, Y.-J. et al. Real-time immunoassay with a PDMS-glass hybrid microfilter electro-immunosensing chip using nanogold particles and silver enhancement. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 132, 327–333 (2008).
Liu, Y., Harnisch, F., Fricke, K., Sietmann, R. & Schröder, U. Improvement of the anodic bioelectrocatalytic activity of mixed culture biofilms by simple consecutive electrochemical selection procedure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 24, 1012–1017 (2008).
Balch, W.E., Fox, G.E., Magrum, L.J., Woese, C.R. & Wolfe, R.S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol. Rev. 43, 260–296 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, Y., Schröder, U. Microfabricated, continuous-flow, microbial three-electrode cell for potential toxicity detection. BioChip J 9, 27–34 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-014-9104-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-014-9104-0