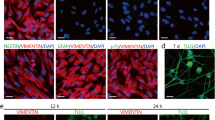
Abstract
The dopaminergic neurons are responsible for the release of dopamine. Several diseases that affect motor function, including Parkinson's disease (PD), are rooted in inadequate dopamine (DA) neurotransmission. The study's goal was to create a quick way to make dopaminergic neuron-like cells from human fibroblasts (hNF) using only two small molecules: hedgehog pathway inhibitor 1 (HPI-1) and neurodazine (NZ). Two small compounds have been shown to induce the transdifferentiation of hNF cells into dopaminergic neuron-like cells. After 10 days of treatment, hNF cells had a big drop in fibroblastic markers (Col1A1, KRT18, and Elastin) and a rise in neuron marker genes (TUJ1, PAX6, and SOX1). Different proteins and factors related to dopaminergic neurons (TH, TUJ1, and dopamine) were significantly increased in cells that behave like dopaminergic neurons after treatment. A study of the autophagy signaling pathway showed that apoptotic genes were downregulated while autophagy genes (LC3, ATG5, and ATG12) were significantly upregulated. Our results showed that treating hNF cells with both HPI-1 and NZ together can quickly change them into mature neurons that have dopaminergic activity. However, the current understanding of the underlying mechanisms involved in nerve guidance remains unstable and complex. Ongoing research in this field must continue to advance for a more in-depth understanding. This is crucial for the safe and highly effective clinical application of the knowledge gained to promote neural regeneration in different neurological diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- PD:
-
Parkinson's disease
- DA:
-
dopamine
- TH:
-
tyrosine hydroxylase
- hNF:
-
human fibroblasts
- HPI-1:
-
hedgehog pathway inhibitor 1
- NZ:
-
neurodazine
References
Adelipour M, Saleth LR, Ghavami S, Alagarsamy KN, Dhingra S, Allameh A (2022) The role of autophagy in the metabolism and differentiation of stem cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Mol Basis Dis 1868(8):166412
Antonellis PJ, Engle SE, Brewer KM, Berbari NF (2021) The hedgehog signaling pathway is expressed in the adult mouse hypothalamus and modulated by fasting. eNeuro 8(5)
Bale AE, Yu K-p (2001) The hedgehog pathway and basal cell carcinomas. Hum Mol Genet 10(7):757–762
Caiazzo M, Dell’Anno MT, Dvoretskova E, Lazarevic D, Taverna S, Leo D, Sotnikova TD, Menegon A, Roncaglia P, Colciago G (2011) Direct generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nature 476(7359):224–227
Connell JP, Kodali S, Cooke JP (2015) Therapeutic transdifferentiation: a novel approach for ischemic syndromes. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc J 11(3):176
Cox AG, Hampton MB (2007) Bcl-2 over-expression promotes genomic instability by inhibiting apoptosis of cells exposed to hydrogen peroxide. Carcinogenesis 28(10):2166–2171
Csordás G, Gábor E, Honti V (2021) There and back again: the mechanisms of differentiation and transdifferentiation in Drosophila blood cells. Dev Biol 469:135–143
Daubner SC, Le T, Wang S (2011) Tyrosine hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 508(1):1–12
De Lau LM, Breteler MM (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5(6):525–535
Driver JA, Logroscino G, Gaziano JM, Kurth T (2009) Incidence and remaining lifetime risk of Parkinson disease in advanced age. Neurology 72(5):432–438
Edsjö A, Lavenius E, Nilsson H, Hoehner JC, Simonsson P, Culp LA, Martinsson T, Larsson C, Påhlman S (2003) Expression of trkB in human neuroblastoma in relation to MYCN expression and retinoic acid treatment. Lab investig 83(6):813–823
Golpich M, Amini E, Mohamed Z, Azman Ali R, Mohamed Ibrahim N, Ahmadiani A (2017) Mitochondrial dysfunction and biogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases: pathogenesis and treatment. CNS Neurosci Therapeutics 23(1):5–22
Gómez-Benito M, Granado N, García-Sanz P, Michel A, Dumoulin M, Moratalla R (2020) Modeling Parkinson’s disease with the alpha-synuclein protein. Front Pharmacol 11:356
Graf T, Enver T (2009) Forcing cells to change lineages. Nature 462(7273):587–594
Halder D, Kim G-H, Shin I (2015) Synthetic small molecules that induce neuronal differentiation in neuroblastoma and fibroblast cells. Mol BioSyst 11(10):2727–2737
Hisahara S, Shimohama S (2011) Dopamine receptors and Parkinson’s disease. Int J Med Chem 2011:403039
Hyman JM, Firestone AJ, Heine VM, Zhao Y, Ocasio CA, Han K, Sun M, Rack PG, Sinha S, Wu JJ (2009) Small-molecule inhibitors reveal multiple strategies for Hedgehog pathway blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(33):14132–14137
Ruiz i Altaba A (2006) How the hedgehog outfoxed the crab. In: Ruiz i Altaba A (ed) Hedgehog-gli signaling in human disease. Springer US, Boston, MA, pp 1–22.
Kalra RS, Dhanjal JK, Das M, Singh B, Naithani R (2021) Cell transdifferentiation and reprogramming in disease modeling: insights into the neuronal and cardiac disease models and current translational strategies. Cells 10(10):2558
Kim J, Su SC, Wang H, Cheng AW, Cassady JP, Lodato MA, Lengner CJ, Chung C-Y, Dawlaty MM, Tsai L-H (2011) Functional integration of dopaminergic neurons directly converted from mouse fibroblasts. Cell stem cell 9(5):413–419
Kim H-J (2011) Stem cell potential in Parkinson's disease and molecular factors for the generation of dopamine neurons. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Mol Basis Dis 1812(1):1-11
Kitazawa M, Wagner JR, Kirby ML, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy AG (2002) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in dopaminergic cells exposed to methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl. J Pharmacol Exp Therapeutics 302(1):26–35
Kordower JH, Olanow CW, Dodiya HB, Chu Y, Beach TG, Adler CH, Halliday GM, Bartus RT (2013) Disease duration and the integrity of the nigrostriatal system in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 136(8):2419–2431
Kou W, Luchtman D, Song C (2008) Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) increases cell viability and expression of neurotrophin receptors in retinoic acid and brain-derived neurotrophic factor differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Eur J Nutr 47:104–113
Liang Z, Chen Y, Gu R, Guo Q, Nie X (2023) Asiaticoside prevents oxidative stress and apoptosis in endothelial cells by activating ROS-dependent p53/Bcl-2/Caspase-3 signaling pathway. Curr Mol Med
Mai S, Muster B, Bereiter-Hahn J, Jendrach M (2012) Autophagy proteins LC3B, ATG5 and ATG12 participate in quality control after mitochondrial damage and influence lifespan. Autophagy 8(1):47–62
Maiti P, Manna J, Dunbar GL (2017) Current understanding of the molecular mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease: targets for potential treatments. Transl Neurodegener 6:1–35
Mizushima N, Levine B (2010) Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 12(9):823–830
Nagatsu T (2006) The catecholamine system in health and disease—relation to tyrosine 3-monooxygenase and other catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B 82(10):388–415
Padilla-Godínez FJ, Ramos-Acevedo R, Martínez-Becerril HA, Bernal-Conde LD, Garrido-Figueroa JF, Hiriart M, Hernández-López A, Argüero-Sánchez R, Callea F, Guerra-Crespo M (2021) Protein misfolding and aggregation: the relatedness between Parkinson’s disease and hepatic endoplasmic reticulum storage disorders. Int J Mol Sci 22(22):12467
Parga J, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Blanco V, Guerra M, Labandeira-Garcia J (2008) Different effects of anti-sonic hedgehog antibodies and the hedgehog pathway inhibitor cyclopamine on generation of dopaminergic neurons from neurospheres of mesencephalic precursors. Dev Dyn 237(4):909–917
Parzych KR, Klionsky DJ (2014) An overview of autophagy: morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxidants Redox Signal 20(3):460–473
Peralta V, Cuesta MJ (2017) Motor abnormalities: from neurodevelopmental to neurodegenerative through “functional”(neuro) psychiatric disorders. Schizophrenia Bull 43(5):956–971
Pfisterer U, Kirkeby A, Torper O, Wood J, Nelander J, Dufour A, Björklund A, Lindvall O, Jakobsson J, Parmar M (2011) Direct conversion of human fibroblasts to dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(25):10343–10348
Qin H, Zhao A, Fu X (2017) Small molecules for reprogramming and transdifferentiation. Cell Mol Life Sci 74:3553–3575
Rai SN, Singh P (2020) Advancement in the modelling and therapeutics of Parkinson’s disease. J Chem Neuroanatomy 104:101752
Ramakrishna K, Nalla LV, Naresh D, Venkateswarlu K, Viswanadh MK, Nalluri BN, Chakravarthy G, Duguluri S, Singh P, Rai SN (2023) WNT-β catenin signaling as a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases: current status and future perspective. Diseases 11(3):89
Rausch W-D, Wang F, Radad K (2022) From the tyrosine hydroxylase hypothesis of Parkinson’s disease to modern strategies: a short historical overview. J Neural Transm 129(5–6):487–495
Rujanapun N, Heebkaew N, Promjantuek W, Sotthibundhu A, Kunhorm P, Chaicharoenaudomrung N, Noisa P (2019) Small molecules re-establish neural cell fate of human fibroblasts via autophagy activation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 55:622–632
Sdek P, Zhang Z, Cao J, Pan H, Chen W, Zheng J (2006) Alteration of cell-cycle regulatory proteins in human oral epithelial cells immortalized by HPV16 E6 and E7. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35(7):653–657
Sheikh A, Alvi AA, Aslam HM, Haseeb A (2012) Hedgehog pathway inhibitors–current status and future prospects. Infect Agents Cancer 7(1):1–2
Shen C-N, Burke ZD, Tosh D (2004) Transdifferentiation, metaplasia and tissue regeneration. Organogenesis 1(2):36–44
Sheng T, Li C, Zhang X, Chi S, He N, Chen K, McCormick F, Gatalica Z, Xie J (2004) Activation of the hedgehog pathway in advanced prostate cancer. Mol Cancer 3(1):1–13
Sisakhtnezhad S, Matin MM (2012) Transdifferentiation: a cell and molecular reprogramming process. Cell Tissue Res 348:379–396
Smith DK, Yang J, Liu M-L, Zhang C-L (2016) Small molecules modulate chromatin accessibility to promote NEUROG2-mediated fibroblast-to-neuron reprogramming. Stem Cell Rep 7(5):955–969
Surmeier DJ (2018) Determinants of dopaminergic neuron loss in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J 285(19):3657–3668
Tabrez S, Jabir N, Shakil S, Greig N, Alam Q, Abuzenadah A, Damanhouri G, Kamal M (2012) A synopsis on the role of tyrosine hydroxylase in Parkinson's disease. CNS Neurol Disord-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders) 11(4):395-409
Unnithan A, Das S, Nadipanna SP (2023) Expression of BAX and Bcl-2 gene in prostate carcinoma and its correlation with gleason score. Adv Hum Biol 13(4):344–349
Valencia M, Kim SR, Jang Y, Lee SH (2021) Neuronal autophagy: Characteristic features and roles in neuronal pathophysiology. Biomol Therapeutics 29(6):605
Wang X, Yang H, Wang X, Du Y (2016) Effect of siRNA-induced silencing of cellular prion protein on tyrosine hydroxylase expression in the substantia nigra of a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Genet Mol Res 15(2):gmr7406
Williams DR, Lee M-R, Song Y-A, Ko S-K, Kim G-H, Shin I (2007) Synthetic small molecules that induce neurogenesis in skeletal muscle. J Am Chem Soc 129(30):9258–9259
Williams DR, Kim G-H, Lee M-R, Shin I (2008) Fluorescent high-throughput screening of chemical inducers of neuronal differentiation in skeletal muscle cells. Nat Protocols 3(5):835–839
Xu Z, Su S, Zhou S, Yang W, Deng X, Sun Y, Li L, Li Y (2020) How to reprogram human fibroblasts to neurons. Cell Biosci 10:1–25
Yadav SK, Rai SN, Singh SP (2017) Mucuna pruriens reduces inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in Parkinsonian mice model. J Chem Neuroanatomy 80:1–10
Yang Y, Chen R, Wu X, Zhao Y, Fan Y, Xiao Z, Han J, Sun L, Wang X, Dai J (2019) Rapid and efficient conversion of human fibroblasts into functional neurons by small molecules. Stem Cell Rep 13(5):862–876
Yoo AS, Sun AX, Li L, Shcheglovitov A, Portmann T, Li Y, Lee-Messer C, Dolmetsch RE, Tsien RW, Crabtree GR (2011) MicroRNA-mediated conversion of human fibroblasts to neurons. Nature 476(7359):228–231
Zentelytė A, Žukauskaitė D, Jacerytė I, Borutinskaitė VV, Navakauskienė R (2021) Small molecule treatments improve differentiation potential of human amniotic fluid stem cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:623886
Zhao D-L, Zou L-B, Lin S, Shi J-G, Zhu H-B (2007) Anti-apoptotic effect of esculin on dopamine-induced cytotoxicity in the human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. Neuropharmacology 53(6):724–732
Zhou J, Li Y, Yan G, Bu Q, Lv L, Yang Y, Zhao J, Shao X, Deng Y, Zhu R (2011) Protective role of taurine against morphine-induced neurotoxicity in C6 cells via inhibition of oxidative stress. Neurotoxicity Res 20:334–342
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Suranaree University of Technology (SUT) Research and Development Fund, Thailand Science Research and Innovation (TSRI), National Science, Research and Innovation Fund (NSRF) (project code 90464), and the NSRF via the Program Management Unit for Human Resources & Institutional Development, Research, and Innovation (PMU-B) (grant number B13F660133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There was no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This work did not involve human participants and/or animals.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not applicable for this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sorraksa, N., Kaokaen, P., Kunhorm, P. et al. Rapid induction of dopaminergic neuron-like cells from human fibroblasts by autophagy activation with only 2-small molecules. 3 Biotech 14, 115 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03957-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03957-0