Abstract
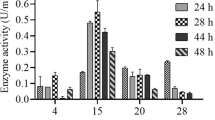
In the present investigation, a soil isolate Pseudomonas aeruginosa CSPS4 was used for retrieving the l-asparaginase encoding gene (Asn_PA) of size 1089 bp. The gene was successfully cloned into the pET28a (+) vector and expressed into E. coli BL21(DE3) for characterization of the protein. The recombinant rAsn_PA enzyme was purified by affinity chromatography using Ni-NTA2+ resins. Molecular weight analysis using SDS-PAGE unveiled rAsn_PA as a monomeric protein of molecular weight ~ 35 kDa. On characterization, the recombinant rAsn_PA showed optimum pH and temperature of 6.0 and 60 °C, respectively, along with significant stability at 50–70 °C, along with 50% residual activity at 80 °C after 3 h of incubation. Similarly, the rAsn_PA exhibited asparaginase activity over a broad pH range between 4 and 8. The enzyme was not significantly inhibited in the presence of detergents. The rAsn_PA was grouped into the asparaginase-glutaminase family II due to the glutaminase activity. The purified rAsn_PA showed antitumor activity by exhibiting a cytotoxic effect on three different cell lines, where IC50 of purified rAsn_PA was 2.3 IU, 3.7 IU, and 20.5 IU for HL-60, MOLM-13, and K-562 cell lines, respectively. Thus, recombinant rAsn_PA of P. aeruginosa CSPS4 may also be explored as an antitumor agent after reducing or minimizing the glutaminase activity. Thermo-acidophilic properties of rAsn_PA make it a novel enzyme that needs to be further investigated.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The full-length gene of l-asparaginase reported here can be retrieved using accession no. OR509736 at NCBI.
References
Alrumman SA, Mostafa YS, Al-Izran KA, Alfaifi MY, Taha TH, Elbehairi SE (2019) Production and anticancer activity of an l-asparaginase from Bacillus licheniformis isolated from the red sea, Saudi Arabia. Sci Rep 6:3756
Amany B, El-Aziz A, Hassanein WA, Mattar ZA, El-Didamony RA (2021) Production of chemotherapeutic agent l-asparaginase from gamma-irradiated Pseudomonas aeruginosa WCHPA075019. Jordan J Biol Sci 14:403–412
Ashok A, Doriya K, Rao JV, Qureshi A, Tiwari AK, Kumar DS (2019) Microbes producing l-asparaginase free of glutaminase and urease isolated from extreme locations of Antarctic soil and Moss. Sci Rep 9:1423
Audipudi AV, Pallavi R, Supriya GNR (2013) Characterization of l-asparaginase producing bacteria from mangrove soil. Chem Tech 1:109–112
Badoei-Dalfard A (2015) Purification and characterization of l-asparaginase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain SN004: production optimization by statistical methods. Biocatal Agri Biotechnol 4:388–397
Cachumba JJ, Antunes FA, Peres GF, Brumano LP, Santos JC, Da Silva SS (2016) Current applications and different approaches for microbial l-asparaginase production. Braz J Microbiol 47:77–85
Darnal S, Patial V, Kumar V, Kumar S, Kumar V, Padwad YS, Singh D (2023) Biochemical characterization of extremozyme l-asparaginase from Pseudomonas sp. PCH199 for therapeutics. AMB Express 13:22
Darvishi F, Jahanafrooz Z, Mokhtarzadeh A (2022) Microbial l-asparaginase as a promising enzyme for treatment of various cancers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106:5335–5347
Davidson L, Brear DR, Wingard P, Hawkins J, Kitto GB (1976) Purification and properties of an l-glutaminase-l-asparaginase from Pseudomonas acidovorans. J Bact 129:1379–1386
Duval M, Suciu S, Ferster A, Rialland X, Nelken B, Lutz P, Philippe N (2002) Comparison of Escherichia coli–asparaginase with Erwinia-asparaginase in the treatment of childhood lymphoid malignancies: results of a randomized European organization for research and treatment of cancer: children’s leukemia group phase 3 trial. Blood J Am Soc Hematol 99:2734–2739
El-Bessoumy AA, Sarhan M, Mansour J (2004) Production, isolation, and purification of l-asparaginase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa 50071 using solid-state fermentation. BMB Rep 37:387–393
El- Naggar NE, El-Ewasy SM, El-Shweihy NM (2014) Microbial l-asparaginase as a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the pros and cons. Int J Pharmacol 10:182–199
El-Naggar NEA, Deraz SF, Soliman HM, El-Deeb NM, El-Ewasy SM (2016) Purification, characterization, cytotoxicity, and anticancer activities of l–asparaginase, anti-colon cancer protein, from the newly isolated alkaliphilic Streptomyces fradiae NEAE-82. Sci Rep 6:32926
El-Sharkawy AS, Farag AM, Embaby AM, Saeed H, El-Shenawy M (2016) Cloning, expression, and characterization of aeruginosa EGYII l-asparaginase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain EGYII DSM 101801 in E. coli BL21 (DE3) pLysS. J Mol Cat B: Enzym 132:16–23
Fatima N, Khan MM, Khan IA (2019) L-asparaginase produced from soil isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa shows potent anti-cancer activity on HeLa cells. Saudi J Biol Sci 26:1146–1153
Gao C, Ma X, Zhang Z, Lu Q, Ashby CR Jr, Wei L, Chen ZS (2022) Asparaginase Erwinia chrysanthemi for acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoblastic lymphoma. Drugs Today (barc) 58:261–271
Goswami R, Hegde K, Veerank VD (2015) Production and characterization of novel glutaminase free recombinant l-asparaginase II of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica SCRI 1043 in E. coli BL21(DE3). Br Microbiol Res J 6:95–112
Husain I, Sharma A, Kumar S, Malik F (2016) Purification and characterization of glutaminase free asparaginase from Pseudomonas otitidis: induce apoptosis in human leukemia MOLT-4 cells. Biochimie 121:38–51
Jia R, Wan X, Geng X, Xue D, Xie Z, Chen C (2021) Microbial l-asparaginase for application in acrylamide mitigation from food: current research status and future perspectives. Microorganisms 9:1659
Kamble KD, Bidwe PR, Muley VY, Kamble LH, Bhadange DG, Musaddiq M (2012) Characterization of l-asparaginase producing bacteria from water, farm, and saline soil. Biosci Disc 3:116–119
Kukurova K, Morales FJ, Bednáriková A, Ciesarová Z (2009) Effect of l-asparaginase on acrylamide mitigation in a fried dough pastry model. Mol Nut Food Res 53:1532–1539
Kumar SS, Haridas M, Abdulhameed S (2020) A novel fibrinolytic enzyme from marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa KU1 and its rapid in vivo thrombolysis with little haemolysis. Int J Biol Macromol 162:470–479
Kumar S, Darnal S, Patial V, Kumar V, Kumar S, Singh D (2022a) Molecular cloning, characterization, and in-silico analysis of l-asparaginase from Himalayan Pseudomonas sp PCH44. 3 Biotech 12:162
Kumar S, Darnal S, Patial V, Kumar V, Singh D (2022b) Molecular characterization of a stable and robust l-asparaginase from Pseudomonas sp. PCH199: evaluation of cytotoxicity and acrylamide mitigation potential. Fermentation 8:568
Mahajan RV, Saran S, Kameswaran K, Kumar V, Saxena RK (2012) Efficient production of l-asparaginase from Bacillus licheniformis with low-glutaminase activity: optimization, scale up and acrylamide degradation studies. Biores Technol 125:11–16
Mahajan RV, Kumar V, Rajendran V, Saran S, Ghosh PC, Saxena RK (2014) Purification and characterization of a novel and robust l-asparaginase having low-glutaminase activity from Bacillus licheniformis: in vitro evaluation of anti-cancerous properties. PLoS ONE 6:99037
Muneer F, Siddique MH, Azeem F, Rasul I, Muzammil S, Zubair M, Afzal M, Nadeem H (2020) Microbial l-asparaginase: purification, characterization, and applications. Arch Microbiol 202:967–981
Nagarethinam S, Naik AN, Udupa N, Rao VJ, Vanathi MB (2012) Microbial l-asparaginase and its future prospects. Asian J Med Res 1:159–160
Prakash O, Nimonkar Y, Desai D (2020) A recent overview of microbes and microbiome preservation. Indian J Microb 60:297–309
Qeshmi IF, Homaei A, Fernandes P, Javadpour S (2018) Marine microbial l- asparaginase: biochemistry, molecular approaches, and applications in tumor therapy and in food industry. Microbiol Res 208:99–112
Qeshmi FI, Homaei A, Khajeh K, Kamrani E, Fernandes P (2022) Production of a novel marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa recombinant l-asparaginase: insight on the structure and biochemical characterization. Mar Biotechnol 24:599–613
Saeed H, Soudan H, El Sharkawy A, Farag A, Embaby A, Ataya F (2018) Expression and functional characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa recombinant l-asparaginase. Protein J 37:461–471
Saeed H, Hemida A, Abdel-Fattah M, Eldoksh A, Shalaby M, Nematalla H, Elkewedi M (2021) Pseudomonas aeruginosa recombinant L-asparaginase: large scale production, purification, and cytotoxicity on THP-1, MDA-MB-231, A549, Caco2 and HCT-116 cell lines. Protein Expr Purif 181:105820
Shakambari G, Ashok Kumar B, Varalakshmi P (2017) L-asparaginase – a promising biocatalyst for industrial and clinical applications. Biocat Agri Biotechnol 17:213–224
Shifrin S, Parrott CL, Luborsky SW (1974) Substrate binding and inter subunit interactions in l-asparaginase. J Biol Chem 249:1335–1340
Shrivastava A, Khan AA, Khurshid M, Kalam MA, Jain SK, Singhal PK (2016) Recent developments in L-asparaginase discovery and its potential as anticancer agent. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 100:1–10
Sindhu R, Manonmani HK (2018) Expression and characterization of recombinant l-asparaginase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Protein Expr Purif 143:83–91
Stadler RH, Blank I, Varga N, Robert F, Hau J, Guy PA, Robert MC, Riediker S (2002) Acrylamide from Maillard reaction products. Nature 3:449–450
Vachhani P, Al Yacoub R, Miller A, Zhang F, Cronin TL, Ontiveros EP, Wang ES (2018) Intensive chemotherapy vs. hypomethylating agents in older adults with newly diagnosed high-risk acute myeloid leukemia: a single center experience. Leuk Res 75:29–35
Vinci RM, Mestdagh F, Meulenaer BD (2012) Acrylamide formation in fried potato products present and future, a critical review on mitigation strategies. Food Chem 133:1138–1154
Yahya S, Jahangir S, Shaukat SS, Sohail M, Khan SA (2016) Production optimization by using Plackett–Burman design and partial characterization of amylase from Aspergillus tubingensis SY 1. Pak J Bot 48:2557–2561
Yuan J, Yang J, Zhuang Z, Yang Y, Lin L, Wang S (2012) Thrombolytic effects of Douchi fibrinolytic enzyme from Bacillus subtilis LD-8547 in vitro and in vivo. BMC Biotechnol 12:1–9
Acknowledgements
VK and DV are grateful to Dr. Shilpa Sharma, NSUT, New Delhi for accessing her laboratory for the cloning experiments. AS and CPC are acknowledged for providing facilities to perform cell line experiments at SGPGI, Lucknow. Besides, DV and VK are thankful to Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Lucknow for providing infrastructure and other useful resources.
Funding
There was no financial support received from any funding agency to carry out the work presented here.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DV conceived the idea and coordinated the complete study. VK performed all the experiments. RK and SS assisted in gene cloning. AS and CPC helped in cell line experiments. VK and DV wrote the manuscript. All the authors read, edited, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, V., Kumar, R., Sharma, S. et al. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a novel thermo-acidophilic l-asparaginase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa CSPS4. 3 Biotech 14, 54 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03916-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03916-9