Abstract
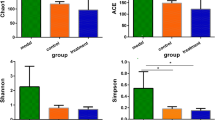
The current investigation is trying to study the impact of the mixture of Chinese herbs Qi Wei Bai Zhu San (QWBZS) on bacterial lactase gene from antibiotics-induced diarrhea (AAD) mice, as the good curative effect of QWBZS on diarrhea. Mice (6 mice per group) were randomly selected as control, model and treatment groups. To induce diarrhea, mice in both model and treatment groups were intragastrically injected with mixture of gentamycin sulfate and cefradine (23.33 mL kg−1 day−1) twice per day and continuously for totally 5 days. After the success of establishing diarrhea model, the mice in treatment group were gavaged with QWBZS for 3 days. Intestinal contents in all three groups were then collected and DNA was extracted in aseptic environment for the following sequencing. The results showed that mice from QWBZS treatment group had obviously detectable levels of intestinal bacteria, such as Actinobacteria, Firmicutes and Proteobacteria, which produce phyla lactase specifically. In comparison with other groups, the mice in treatment group had more abundant expression of lactase gene from Acidovorax sp. KKs102, Stenotrophomonas sp. LMG11000, Pseudomonas oleovorans, Eggerthella and Burkholderia. Interestingly, the Shannon index decreased significantly after the treatment with QWBZS (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05). 63.1% of lactase genes detected in the mice in treatment group were unclassified, and 32.8% of them were non-homologous to any fragments in the gene bank, which means that most of lactase-producing bacteria are novel. Our results indicate that treatment with QWBZS did not increase the diversity of bacterial lactase gene. Its curative effect on diarrhea may be relevant to its role in facilitating the growth of novel or some key lactase-producing strains.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandre V, Even PC, Larue-Achagiotis C, Blouin JM, Blachier F, Benamouzig R, Tomé D, Davila AM (2013) Lactose malabsorption and colonic fermentations alter host metabolism in rats. Br J Nutr 110:625–631
Cai GX, Zeng A, Xiao NQ, Zhou SN, Guo KX, Tan ZJ (2013) Effects of Jianwei Qiweibaizhusan on the intestinal microorganisms and enzyme activities. J Pharm Technol Drug Res 2(1):6. https://doi.org/10.7243/2050-120X-2-6
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Elguezabal N, Chamorro S, Molina E, Garrido JM, Izeta A, Rodrigo L, Juste RA (2012) Lactase persistence, NOD2 status and Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection associations to Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut Pathog 4(1):6
Guo KX, Zhou SN, Tan ZJ, Cai Y, She Y, Cai GX (2013) Study on inhibition and boosting action of Qiweibaishusan to intestinal yeast. Prog Mod Biomed 13(27):5259–5263
Guo KX, Xiao XY, Liu YJ, Long CX, Tan ZJ (2015a) Effect of Qiweibaizhusan on the intestinal lactobacilli diversity in dysbacteria diarrheal mice. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 21:1071–1075
Guo KX, Tan ZJ, Xie MZ, She Y, Wang XH (2015b) The synergic effect of ultra-micro powder Qiweibaizhusan combined with yeast on dysbacteriotic diarrhea mice. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 21:61–67
Hammer HF, Hammer J (2012) Diarrhea caused by carbohydrate malabsorption. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 41(3):611–627
He L, Long CX, Liu YJ, Guo YF, Xiao NQ, Tan ZJ (2017) Effects of Debaryomyces hansenii treatment on intestinal microorganisms in mice with antibiotics-induced diarrhea. 3 Biotech 7:347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0953-9
Jiang XD, Guo GG, Zhang J (2014) Association of genetic diversity for Amy6-4 gene activity in germplasm of barley. Acta Agron Sin 40(2):205–213
Liu QS, Xu XH, Liu H, Liu YF, Tan ZJ (2014) Effect on intestinal villi and crypts in flora diarrhea mice by Qiweibaizhu powder. Chin Med Mod Distance Educ China 12(23):154–155
Long CX, He L, Guo YF, Liu YW, Xiao NQ, Tan ZJ (2017a) Diversity of bacterial lactase genes in intestinal contents of mice with antibiotics-induced diarrhea. World J Gastroenterol 23(42):7584–7593
Long CX, He L, Liu YW, Hui HY, Tan ZJ, Li DD (2017b) Universal primer for analysis of the diversity of intestinal bacterial lactase gene. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 23(4):758–763
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8228–8235
Mahaffee WF, Kloepper JW (1997) Temporal changes in the bacterial communities of soil, rhizosphere, and endorhiza associated with Field-Grown Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L). Microb Ecol 34(3):210–223
Ojetti V, Gigante G, Gabrielli M, Ainora ME, Mannocci A, Lauritano EC, Gasbarrini G, Gasbarrini A (2010) The effect of oral supplementation with Lactobacillus reuteri or tilactase in lactose intolerant patients: randomized trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 14(3):163–170
Peng HZ, Ren LH (2011) Relationship between antibiotic associated diarrhea and lactose intolerance. Chin Gen Pract 14(26):2999–3000
Pitta DW, Pinchak E, Dowd SE, Osterstock J, Gontcharova V, Youn E, Dorton K, Yoon I, Min BR, Fulford JD, Wickersham TA, Malinowski DP (2010) Rumen bacterial diversity dynamics associated with changing from bermudagrass hay to grazed winter wheat diets. Microb Ecol 59(3):511–512
Pitta DW, Parmar N, Patel AK, Indugu N, Kumar S, Prajapathi KB, Patel AB, Reddy B, Joshi C (2014) Bacterial diversity dynamics associated with different diets and different primer pairs in the rumen of Kankrej cattle. PLoS ONE 9(11):e111710
Qiao WH (2014) 30 Cases of dysbacteriosis-related diarrhea treated with flavored Shenling Baizhu powder. Shanxi J Tradit Chin Med 35(1):17–19
Shannon CE (1997) The mathematical theory of communication. 1963. MD Comput 14:306–317
Strati F, Cavalieri D, Albanese D, De Felice C, Donati C, Hayek J, Jousson O, Leoncini S, Pindo M, Renzi D, Rizzetto L, Stefanini I, Calabrò A, De Filippo C (2016) Altered gut microbiota in Rett syndrome. Microbiome 4(1):41
Tan CC, Shi L (2008) Diversity of Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates by the method of polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism. Mod Dig Interv 13(1):18–21
Tan ZJ, Wu H, Liu FL, Cai Y, Cai GX, Zhang HL, Zeng A (2012) Effect of ultra-micro powder Qiweibaizhusan on the intestinal microbiota and enzyme activities in mice. Acta Ecol Sin 32(21):6856–6863
Wang G, Luo H, Meng K, Wang Y, Huang H, Shi P, Pan X, Yang P, Diao Q, Zhang H, Yao B (2011) High genetic diversity and different distributions of glycosyl hydrolase family 10 and 11 xylanases in the goat rumen. PLoS ONE 6(2):e16731
Wang Y, Yu LK, Han XH, Yuan LY, Cui Y, Ma N (2013) Curative effect of Qiweibaizhusan on antibiotics-associated diarrhea. Lishizhen Med Mater Medica Res 24(10):2451–2452
Wang H, Zeng A, Cao R, Guo ZH, He YS, Tan ZJ (2014) The material base of Qiweibaizhusan regulating intestinal microecology. World Chin J Digestol 22(13):1773–1777
Wang Y, Yu F, Liu MY, Zhao YK, Wang DM, Hao QH, Wang XL (2017) Isolation and characterization of a human intestinal bacterium Eggerthella sp. AUH-JLD49s for the conversion of (−)-3′-desmethylarctigenin. J Agric Food Chem 65(20):4051–4056
Wu H, Zhou SN, Guo C, Tan ZJ, Cai GX, Zeng A, Zhang HL (2012) A metagenome DNA extracting method of intestinal flora in mice for molecular diversity analysis based on PCR technology. Chin J Microecol 24(7):648–651
Yang ZH, Yang WH (2010) 23 Cases of infantile spleen deficiency diarrhea treated with Qiweibaizhusan. Gansu J TCM 23(12):36–37
Yuan P (2012) Gene cloning and expression of pectinases and their diversity analysis in the rumen of Small Tail Han sheep. Dissertation, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
Zeng A, Zhang HL, Tan ZJ, Cai Y, Cai GX, Zhou SN (2012) The construction of mice diarrhea model due to dysbacteriosis and curative effect of ultra-micro Qiweibaizhusan. Microbiol China 39(9):1341–1348
Zhang XL, Xu QQ, Wang LY, Huo XQ, Cao LZ, Chen LG, Ren YH, Dong SS (2009) The influence of Sijunzi decoction on the lactase activity in diarrheal mice intestinal mucosa. The 16th Veterinary Pathology Branch in Chinese Association of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine and the 15th Seminar of Animal Pathophysiology Professional Committee in Chinese Association of Pathophysiology
Zhang XL, Wang YC, Xu QQ, Wang LY, Huo XQ, Cao LZ, Zhang YH, Dong SS (2010) The influence of decoction of compound Radix pulsatillae on the lactase activity in diarrheal mice intestinal mucosa. J Agric Univ Hebei 33(2):99–102
Zhang YY, Zhou LL, Yang SF (2014) The basic research of primary lactase deficiency. Int J Pediatr 41(3):302–304
Zhou XY (2004) Pathogenesis of antibiotics-induced diarrhea. Chin J Microbiol 16(6):376–377
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81573951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest was declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Liu, Y., Guo, Y. et al. Diversity of intestinal bacterial lactase gene in antibiotics-induced diarrhea mice treated with Chinese herbs compound Qi Wei Bai Zhu San. 3 Biotech 8, 4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1024-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1024-y