Abstract
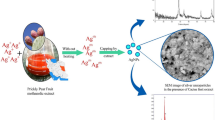
Aegle marmelos (L.) or bael commonly known as wood apple, is rich in bioactive compounds has diverse pharmacological importance and is widely employed for the synthesis of green nanoparticles. The current study aims to evaluate the phytochemical components of A. marmelos (L.) by biochemical assays and its antioxidant activity. Further, silver nanoparticles synthesized from A. marmelos (L.) fruit extract exhibited antibacterial effect against pathogens such as Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterococcus faecalis. The phytochemical screening revealed the phytochemicals such as saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids, phenols, and tannins. UV–Vis spectrophotometry confirms silver ions in the biosynthesized nanoparticles. Further, FT-IR revealed the chemical bonds of alkanes, amines, alcohols, and alkenes. Bioderived silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) showed the highest inhibitory activity against Staphylococcus aureus (29.33 ± 1.59 mm) followed by Enterococcus faecalis (20.14 ± 1.5 mm), Micrococcus luteus (19.33 ± 1.3 mm), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (16.23 ± 1.2 mm), and Escherichia coli (16.13 ± 1.5 mm) at the concentration of 100 µl the highest. The antioxidant activity of different concentrations (25, 50, 100, and 200 µl) of biosynthesized AgNPs were 40%, 46%, 57%, and 61%, respectively. The cytotoxic effect of bioderived nanoparticles on VERO cell lines by MTT assay showed increased cytotoxicity with an increase in concentration and the highest IC50 value recorded at 1000 µg/ml. These results indicate that the bioactive components of A. marmelos (L.) fruit extract exhibited potential antioxidant activity. Bioactive silver nanoparticles showed the highest antibacterial prospects that can be exploited in new drug and antiseptic lotion formulations of herbal origin with sustainable synthesis and application.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri S, Mukherji S, Mukherji S (2014) Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv 4:3974–3983. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra44507k
Ali ZA, Yahya R, Sekaran SD, Puteh R (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using apple extract and its antibacterial properties. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng, 2016.
Athawale A, Bokare A, Singh H et al (2020) Synthesis of Ag2O Coated TiO2 nanoparticles by sonochemically activated methods for enhanced photocatalytic activities. Top Catal 63:1056–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-020-01374-0
Banu AS, Thirumurugan V, Amudha M (2018) Green Biosynthesis of Silver Nano Particles from Aegle Marmelos Aqueous Leaf Extract. Mater Res Bull 11:6–11. https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-1107010611
Bapat MS, Singh H, Shukla SK et al (2022) Evaluating green silver nanoparticles as prospective biopesticides: An environmental standpoint. Chemosphere 286:131761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131761
Behera P, Raj VJ, Basavaraju R (2014) Phytochemical and antimicrobial activity of fruit pulp of Aegle marmelos. J Chem Pharm Res 6(8):319–326
Christopher JG, Saswati B, Ezilrani P (2015) Optimization of Parameters for Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Aegle Marmelos. Braz Arch Biol Technol 58:702–710
Devi M, Devi S, Sharma V et al (2020a) Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using methanolic fruit extract of Aegle marmelos and their antimicrobial potential against human bacterial pathogens. J Tradit Chinese Med Sci 10:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2019.04.007
Devi M, Devi S, Sharma V et al (2020b) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using methanolic fruit extract of Aegle marmelos and their antimicrobial potential against human bacterial pathogens. J Tradit Complement Med 10:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2019.04.007
Dimkpa CO, McLean JE, Martineau N et al (2013) Silver nanoparticles disrupt wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth in a sand matrix. Environ Sci Technol 47:1082–1090. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302973y
Edris AE (2007) Pharmaceutical and therapeutic potentials of essential oils and their individual volatile constituents: a review. Phytother Res 21(4):308–323
Ghoreishi SM, Behpour M, Khayatkashani M (2011) Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Rosa damascena and its primary application in electrochemistry. Phys E Low-Dimensional Syst Nanostructures 44:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2011.07.008
Gudimella K, kanthi, Gedda G, Kumar PS, et al (2022) Novel synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from bio-based Carica Papaya Leaves: Optical and structural properties with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Environ Res 204:111854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111854
Gurjar PS, Bhattacherjee AK, Singh A, Dikshit A, Singh VK (2019) Characterization of nutraceuticals in bael powder prepared from fruits harvested at different developmental stages. Indian J Tradit Know 18(4):724–730
Hernández P, Santiago-Cuevas A, Palacios-Cabrera C et al (2022) Development and applications of Ru and Ce based iron oxides as photocatalysts. Mater Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.131720
Ibrahim E, Fouad H, Zhang M et al (2019) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using endophytic bacteria and their role in inhibition of rice pathogenic bacteria and plant growth promotion. RSC Adv 9:29293–29299. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra04246f
Jeeva K, Thiyagarajan M, Elangovan V et al (2014) Caesalpinia coriaria leaf extracts mediated biosynthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity against clinically isolated pathogens. Ind Crops Prod 52:714–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.11.037
Kanmani P, Lim ST (2013) Synthesis and structural characterization of silver nanoparticles using bacterial exopolysaccharide and its antimicrobial activity against food and multidrug resistant pathogens. Process Biochem 48:1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.05.011
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, et al (2014) Corrigendum to Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles [Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2007;1:95–101]. Nanomedicine Nanotechnology, Biol Med 10:e1119. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2014.04.007
Kora AJ, Sashidhar RB, Arunachalam J (2012) Aqueous extract of gum olibanum (Boswellia serrata): A reductant and stabilizer for the biosynthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles. Process Biochem 47:1516–1520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.06.004
Korukonda JR, Paria S (2012) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from aqueous Aegle Marmelos leaf extract. Mater Res Bull. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.11.035
Krupa NDA, Raghavan V (2014) Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aegle marmelos ( Bael ) Fruit Extract and Its Application to Prevent Adhesion of Bacteria : A Strategy to Control Microfouling. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/949538
Kumar CG, Poornachandra Y (2015) Biodirected synthesis of Miconazole-conjugated bacterial silver nanoparticles and their application as antifungal agents and drug delivery vehicles. Colloids Surf B; COLLOID 125:110–119
Kumar A, Kumar AA, Nayak AP, Mishra P, Panigrahy M, Sahoo PK, Panigrahi K (2019) Carbohydrates and polyphenolics of extracts from genetically altered plant acts as catalysts for in vitro synthesis of silver nanoparticle. J Biosci 44(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-018-9826-6(012345
Kushwah M, Bhadauria S, Singh KP, Gaur MS (2019) Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Aegle marmelos Fruit Peel Extract. Anal Chem Lett 9:329–344. https://doi.org/10.1080/22297928.2019.1626279
Madhumithra SK, Balashanmugam P, Mosachristas K et al (2018) In vitro cytotoxicity of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles from shells of pistacia vera L. Int J Appl Pharm 10:162–167. https://doi.org/10.22159/ijap.2018v10i4.27154
Minhas H, Kumar D, Kumar A (2019) Preparation, characterization and electromagnetic interference shielding effect of Ni-doped ZnO thin films. Mater Res Express. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab381e
Nalvothula R, Nagati VB, Koyyati R, Merugu R, Padigya PRM (2014) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Tectona grandis leaf extract and evaluation of their antibacterial potential. Int J ChemTech Res 6(1):293–298
Nguyen NTT, Nguyen LM, Nguyen TTT, et al (2022) Formation, antimicrobial activity, and biomedical performance of plant-based nanoparticles: a review. Springer International Publishing
Okafor F, Janen A, Kukhtareva T et al (2013) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, their characterization, application and antibacterial activity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:5221–5238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10105221
Ovais M, Khalil AT, Islam NU et al (2018a) Role of plant phytochemicals and microbial enzymes in biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:6799–6814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9146-7
Ovais M, Khalil AT, Raza A et al (2018b) Multifunctional theranostic applications of biocompatible green-synthesized colloidal nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:4393–4408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8928-2
Pathirana C K, Madhujith T, Eeswara J (2020) Bael (Aegle marmelos L. Corrêa), a medicinal tree with immense economic potentials. Advances in Agriculture, 2020. doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8814018
Patil S, Sivaraj R, Rajiv P, Venckatesh R, Seenivasan R (2015) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle from leaf extract of Aegle marmelos and evaluation of its antibacterial activity. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 7(6):169–173
Peddi SP, Sadeh BA (2015) Structural studies of silver nanoparticles obtained through single-step green synthesis. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 92:8. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/92/1/012004
Priyadarshini S, Gopinath V, Meera Priyadharsshini N et al (2013) Synthesis of anisotropic silver nanoparticles using novel strain, Bacillus flexus and its biomedical application. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 102:232–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.08.018
Rajaram A, Vanaja GR, Vyakaranam P, Rachamallu A, Reddy GV, Anilkumar K, Reddanna P (2018) Anti-inflammatory profile of Aegle marmelos (L) Correa (Bilva) with special reference to young roots grown in different parts of India. J Ayurveda Integr Med 9(2):90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaim.2017.03.006
Rout A, Jena PK, Parida UK, Bindhani BK (2013) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves extract of Centella Asiatica L. for studies against human pathogens. Int J Pharma Bio Sci 4
Rupiasih NN, Aher A, Gosavi S, Vidyasagar PB (2013) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex extract of Thevetia peruviana: A novel approach towards poisonous plant utilization. J Phys Conf Ser 423:8. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/423/1/012032
Sampath G, Govarthanan M, Rameshkumar N, Viet D (2021) Eco - friendly biosynthesis metallic silver nanoparticles using Aegle marmelos ( Indian bael ) and its clinical and environmental applications. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01883-8
Samrot AV, Silky IVC et al (2019) Bioactivity studies of datura metel, aegle marmelos, annona reticulata and saraca indica and their green synthesized silver nanoparticle. J Pure Appl Microbiol 13:329–338. https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.13.1.36
Saravanan C, Rajesh R, Kaviarasan T et al (2017) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using bacterial exopolysaccharide and its application for degradation of azo-dyes. Biotechnol Reports 15:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.02.006
Sarvamangala D, Kondala K, Murthy USN, Rao BN, Sharma GVR, Satyanarayana R (2013) Biogenic synthesis of AGNP’s using Pomelo fruit—characterization and antimicrobial activity against Gram+ Ve and Gram− Ve bacteria. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 19(2), 30–35. www.globalresearchonline.net
Subasri S, Abilasha S, Poovizhi A, et al (2019) Molecular docking and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Aegle marmelos and it ’ s anti - bacterial activity. 1–9
Suman TY, Radhika Rajasree SR, Kanchana A, Elizabeth SB (2013) Biosynthesis, characterization and cytotoxic effect of plant mediated silver nanoparticles using Morinda citrifolia root extract. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 106:74–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.01.037
Sunita P, Palaniswamy M (2017) Size dependent application of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles against bacterial skin pathogens. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 10:192–195. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2017.v10i10.19718
Swamy VS, Prasad R (2012) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Santalum album and its antimicrobial activity. J Optoelectron Biomed Mater 4(3):53–59
Tamuly C, Hazarika M, Borah SC et al (2013) In situ biosynthesis of Ag, Au and bimetallic nanoparticles using Piper pedicellatum C.DC: Green chemistry approach. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 102:627–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.09.007
Thirunavoukkarasu M, Balaji U, Behera S et al (2013) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticle from leaf extract of Desmodium gangeticum (L.) DC. and its biomedical potential. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 116:424–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.07.033
Tran TV, Nguyen DTC, Kumar PS et al (2022) Green synthesis of ZrO2 nanoparticles and nanocomposites for biomedical and environmental applications: a review. Environ Chem Lett 20:1309–1331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01367-9
Venthodika A, Chhikara N, Mann S, Garg MK, Sofi SA, Panghal A (2021) Bioactive compounds of Aegle marmelos L., medicinal values and its food applications: a critical review. Phytother Res 35(4):1887–1907. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6934
Zhou Y, Lin W, Huang J et al (2010) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by foliar broths: roles of biocompounds and other attributes of the extracts. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:1351–1359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-010-9652-8
Zuas O, Hamim N, Sampora Y (2014) Bio-synthesis of silver nanoparticles using water extract of Myrmecodia pendan (Sarang Semut plant). Mater Lett 123:156–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.03.026
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the facility rendered by Department of Biomedical Engineering, SSN College of Engineering, Chennai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors express no conflict of interests.
Ethical statement
The manuscript is the author’s original work which has not been published anywhere or being considered for publication elsewhere.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Priya, M.S.R., Subashini, R., Kumar, P.S. et al. Assessment of in vitro biopotency of bioderived silver nanoparticles from Aegle marmelos (L.) fruit extract. Appl Nanosci 13, 3875–3885 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02619-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02619-y