Abstract
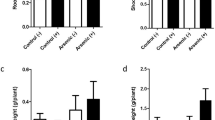
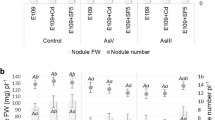
Arsenic (As) is a toxic metalloid that has gained special interest in the past years as a global environmental problem. Groundwater in Córdoba province (Argentina) presents high As concentrations which can be absorbed by plants or be used for artificial irrigation. The aim of this research was to elucidate the differential responses of symbiotic interactions established with three bacterial strains and soybean plants to realistic doses of arsenic. The reference strain Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110 and the native isolate Bradyrhizobium sp. Per 3.64 were able to grow up to 13 mM As(V) whereas the native strain Bradyrhizobium sp. Per 3.61 grew up to 9.5 mM As(V). Metalloid addition did not modify the soybean plant growth at 6 μM As(V). Nevertheless, it was enough to induce oxidative stress as observed by an increase on lipid peroxidation. The soybean-Bradyrhizobium sp. assay at 6 μM As(V) showed no changes in growth variables (shoot and root dry weight) in plants inoculated with the reference microsymbiont or Bradyrhizobium sp. Per 3.61. Regarding As uptake by plants, metalloid accumulation followed the same distribution pattern among strains. Remarkably, at 6 μM As(V), soybean inoculation with Bradyrhizobium sp. Per 3.61 revealed a significantly lower translocation factor (TF) in comparison to other inoculated strains promoting As phytostabilization. At the highest As(V) concentration tested, only Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110 was able to nodulate the legume, however, a significant decrease in the number and dry weight of nodules and nitrogen content was observed. In conclusion, the inoculation of soybean plants with the reference strain Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110 exposed to high As(V) concentration represents an effective and promising symbiotic interaction that allows the development of the legume due to the minimal effects on plant growth. However, in low As(V) concentration environments, the native isolate Bradyrhizobium sp. Per 3.61, is shown to be the best inoculant among the tested strains, owing to the limitation of metalloid translocation and accumulation to edible parts of the legume, avoiding fruit contamination and human poisoning.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abril A, Zurdo-Piñeiro JL, Peix A, Rivas R, Velázquez E (2007) Solubilization of phosphate by a strain of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. Trifolii isolated from Phaseolus vulgaris in el Chaco Arido soil (Argentina). In: Velázquez E, Rodríguez-Barrueco C (eds) First inter- national meeting on microbial phosphate solubilization, vol 102, Developments in plant and soil sciences, vol 102. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 135–138
Angle JS, McGrath SP, Chaudri AM, Chaney RL, Giller KE (1993) Inoculation effects on legumes grown in soil previously treated with sewage sludge. Soil Biol Biochem 2:575–580
Balestrasse KB, Gardey L, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2001) Response of antioxidant defence system in soybean nodules and roots subjected to cadmium stress. Aust J Plant Physiol 28:497–504
Balestrasse KB, Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2003) Effect of cadmium stress on nitrogen metabolism in nodule and roots of soybean plants. Funct Plant Biol 30:57–64
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro M (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34
Bhattacharjee H, Rosen BP (2007) Arsenic metabolism in prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes in: Nies DH, Silver S (ed) molecular microbiology of heavy metals, pp 372-405
Bianucci E, Sobrino-Plata J, Carpena-Ruiz RO, Tordable MC, Fabra A, Hernández LE, Castro S (2012) Contribution of phytochelatins to cadmium tolerance in peanut plants. Metallomics 4:1119–1124
Bianucci E, Furlan A, Rivadeneira J, Sobrino-Plata J, Carpena-Ruiz RO, Tordable MC, Fabra A, Hernández LE, Castro S (2013) Influence of cadmium on the symbiotic interaction established between peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and sensitive or tolerant bradyrhizobial strains. J Environ Manag 130:126–134
Bianucci E, Furlan A, Tordable MDC, Hernández LE, Carpena-Ruiz RO, Castro S (2017) Antioxidant responses of peanut roots exposed to realistic groundwater doses of arsenate: identification of glutathione S-transferase as a suitable biomarker for metalloid toxicity. Chemosphere 181:551–561
Blarasin M, Cabrera A, Matteoda E, Aguirre M, Giuliano Albo J, Becher Quinodoz F, Maldonado L, Felizzia J, Palacio D, Echevarría K, Frontera H (2014) Aspectos geoquímicos, isotópicos, contaminación y aptitudes de uso In: Aguas Subterráneas De La Provincia De Córdoba. Ed: UniRío, pp 83–148
Cabrera A, Blarasin M, Matteoda E, Villalba G, Gomez ML (2005) Composición química del agua subterránea en el sur de córdoba: línea de base hidroquímica o fondo natural en referencia a arsénico y flúor. http://www.produccion-animal.com.ar. Accessed 1 March 2016
Cargnelutti D, Tabaldi LA, Spanevello RM, Jucoski GO, Battisti V, Redin M, Linares CEB, Dressler VL, Flores MM, Nicoloso FT, Morsch VM, Schetinger MRC (2006) Mercury toxicity induces oxidative stress in growing cucumber seedlings. Chemosphere 65:999–1006
Carpena RO, Vázquez S, Esteban E, Fernández-Pascual M, de Felipe MR, Zornoza P (2003) Cadmium-stress inwhite lupin: effects on nodule structure and functioning. Plant Physiol Biochem 41:911–919
Cho UH, Park JO (2000) Mercury-induced oxidative stress in tomato seedlings. Plant Sci 156:1–9
Dary M, Chamber-Perez MA, Palomares AJ, Pajuelo E (2010) “in situ” phytostabilisation of heavy metal polluted soils using Lupinus luteus inoculated with metal resistant plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria. J Hazard Mater 177:323–330
Delamuta JR, Ribeiro RA, Ormeño-Orrillo E, Melo IS, Martínez-Romero E, Hungria M (2013) Polyphasic evidence supporting the reclassification of Bradyrhizobium japonicum group Ia strains as Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3342–3351
Dhankher OP, Rosen BP, McKinney EC, Meagher RB (2006) Hyperaccumulation of arsenic in the shoots of Arabidopsis silenced for arsenate reductase (ACR2). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:5413–5418
Duan GL, Zhou Y, Tong YP, Mukhopadhyay R, Rosen BP, Zhu YG (2007) A CDC25 homologue from rice functions as an arsenate reductase. New Phytol 174:311–321
Fernández LA, Perotti EB, Sagardoy MA, Gómez MA (2008) Desnitrification activity of Bradyrhizobium sp. isolated from argentine soybean cultivated soils. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:2577–2585
Finnegan P, Chen W (2012) Arsenic effects on plant metabolism. Front Physiol 3:182
Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2016) http://faostat.fao.org. Accessed July 2015
Francisca FM, Celollada-Verdaguer MP, Carro-Pérez ME (2006) Presented in part at Conference VIII Congreso Latinoamericano de hidrología subterránea. Distribución espacial del arsénico en las aguas subterráneas de la provincia de Córdoba, Argentina. Asunción
Gothberg A, Greger M, Holm K, Bengtson BE (2004) Influence level on uptake and effects of mercury, cadmium and lead in water spinach. J Environ Qual 33:1247–1255
Hartley-Whitaker J, Ainsworth G, Meharg AA (2001) Copper and arsenate induced oxidative stress in Holcus lanatus L. clones with differential sensitivity. Plant Cell Environ 24:713–722
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 25:189–198
Herouart D, Baudoiun E, Frendo P, Harrison J, Santos R, Jamet A, Van de Sype G, Touati D, Puppo A (2002) Reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide and glutathione: a key role in the establishment of the legume-rhizobium symbiosis? Plant Physiol Biochem 40:619–624
Hoagland D, Arnon D (1950) The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Station California 347:1–39
Hughes MF (2002) Arsenic toxicity and potential mechanisms of action. Toxicol Lett 133:1–16
Ibáñez F, Angelini J, Taurian T, Tonelli ML, Fabra A (2009) Endophytic occupation of peanut root nodules by opportunistic Gammaproteobacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 32:49–55
Lafuente A, Pajuelo E, Caviedes MA, Rodriguez-Llorente ID (2010) Reduced nodulation in alfalfa induced by arsenic correlates with altered expression of early nodulins. Plant Physiol 167:286–291
Lafuente A, Pérez-Palacios P, Doukkali B, Molina-Sánchez M, Jiménez-Zurdo JI, Caviedes MA, Rodríguez-Llorente ID, Pajuelo E (2015) Unraveling the effect of arsenic on the model Medicago–Ensifer interaction: a transcriptomic meta-analysis. New Phytol 205:255–272
Liu Y, Zhu YG, Chen BD, Christie P, Li XL (2005) Yield and arsenate uptake of arbuscular mycorrhizal tomato colonized by Glomus mosseae BEG167 in as spiked soil under glasshouse conditions. Environ Int 31:867–873
Mandal SM, Pati B, Das R, Amit K, Ghosh KA (2008) Characterization of a symbiotically effective Rhizobium resistant to arsenic: isolated from root nodules of Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper grown in arsenic-contaminated field. J Gen Appl Microbiol 54:93–99
Mandon K, Pauly N, Boscari A, Brouquisse R, Frendo P, Demple B, Puppo A (2009) ROS in the legume- rhizobium Symbiosis. In: del Río LA, Puppo A (eds) Reactive oxygen species in plant signaling. Signaling and Communication in Plants. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 135–147
Mascher R, Lippmann B, Holzinger S, Bergmann H (2002) Arsenate toxicity: effects on oxidative stress response molecules and enzymes in red clover plants. Plant Sci. 163:961–969
Molina AS, Nievas C, Chaca MVP, Garibotto F, González U, Marsa SM, Luna C, Giménez MS, Zirulnik F (2008) Cadmium induced oxidative damage and antioxidative defense mechanisms in Vigna mungo L. Plant Growth Regul 56:285–295
Moreno-Jiménez E, Peñalosa JM, Esteban E, Carpena RO (2007) Mercury accumulation and resistance to mercury stress in Rumex induratus and Marrubium vulgare grown on perlite. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 170:485–494
Moreno-Jiménez E, Peñalosa JM, Carpena-Ruiz RO, Esteban E (2008) Comparison of arsenic resistance in Mediterranean woody shrubs used in restoration activities. Chem 71:466–473
Nelson D, Sommers L (1973) Determination of total nitrogen in plant material. Agron J 65:109–112
Neumann H, Bode-Kirchhoff A, Madeheim A, Wetzel A (1998) Toxicity testing of heavy metals with the Rhizobium-legume symbiosis: high sensitivity to cadmium and arsenic compounds. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 5:28–36
Ortega-Villasante C, Rellán-Álvarez R, Del Campo FF, Carpena-Ruiz RO, Hernández LE (2005) Cellular damage induced by cadmium and mercury in Medicago sativa. J Exp Bot 56:2239–2251
Ortega-Villasante C, Hernández LE, Rellán-Álvarez R, Del Campo FF, Carpena-Ruiz RO (2007) Rapid alteration of cellular redox homeostasis upon exposure to cadmium and mercury in alfalfa seedlings. New Phytol 176:96–107
Ott T, van Dongen JT, Gunther C, Krusell L, Desbrosses G, Vigeolas H, Bock V, Czechowski T, Geigenberger P, Udvardi MK (2005) Symbolic leghemoglobins are crucial for nitrogen fixation in legume root nodules but not for general plant growth and development. Curr Biol 15:531–535
Päivöke A, Simola S (2001) Arsenate toxicity to Pisum sativum: mineral nutrients, chlorophyll content, and phytase activity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 49:111–121
Pajuelo E, Rodríguez-Llorente ID, Dary M, Palomares AJ (2008) Toxic effects of arsenic on Sinorhizobium-Medicago sativa symbiotic interaction. Environ Pollut 154:203–211
Pajuelo E, Rodríguez-Llorente ID, Lafuente A, Caviedes MÁ (2011) Legume-Rhizobium symbioses as a tool for bioremediation of heavy metal polluted soils. In: Khan MS, Zaidi A, Goel R, Musarrat J (eds) Biomanagement of metal-contaminated soils, vol 20. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 95–123
Panigrahi DP, Randhawa GS (2010) A novel method to alleviate arsenic toxicity in alfalfa plants using a deletion mutant strain of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Plant Soil 336:459–467
Panigrahi DP, Sagar A, Dalal S, Randhawa GS (2013) Arsenic resistence and symbiotic efficiencies of alfalfa and cowpea rhizobil strain isolated from arsenic agricultural fields. J Exp Biol 3:322–333
Pauly N, Pucciariello C, Mandon K, Innocenti G, Jamet A, Boudouin E, Herouart D, Frendo P, Puppo A (2006) Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and glutathione: key players in the legume-Rhizobium simbiosis. J Exp Bot 57:1769–1776
Poschenrieder C, Gunsé B, Barceló J (1989) Influence of cadmium on water relations, stomatal resistance, and abscisic acid content in expanding bean leaves. Plant Physiol 90:1365–1371
Reichman SM (2007) The potential use of the legume-rhizobium symbiosis for the remediation of arsenic contaminated sites. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2587–2593
Reimann C, de Caritat P (1998) Chemical elements in the environment. Springer, Berlin, p 398
Sanitá di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Sharma I (2012) Arsenic induced oxidative stress in plants. Biologia (Bratisl) 67:447–453
Sharp RE, LeNoble ME (2002) ABA, ethylene and the control of shoot and root growth under water stress. J Exp Bot 53:33–37
Shri M, Kumar S, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Mallick S, Misra P, Shukla D, Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Tuli R (2009) Effect of arsenic on growth, oxidative stress, and antioxidant system in rice seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1102–1110
Singh RP, Agrawal M (2007) Effects of sewage sludge amendment on heavy metal accumulation and consequent responses of Beta vulgaris plants. Chemosphere 67:2229–2240
Srivastava M, Ma LQ, Singh N, Singh S (2005) Antioxidant responses of hyper-accumulator and sensitive fern species to arsenic. J. Exp. Bot. 56:1335–1342
Singh N, Ma LQ, Srivastava M, Rathinasabapathi B (2006) Metabolic adaptations to arsenic induced oxidative stress in Pteris vittata L. and Pteris ensiformis L. Plant Sci 170:274–282
Sobrino-Plata J, Ortega-Villasante C, Flores-Cáceres ML, Escobar C, Del Campo FF, Hernández LE (2009) Differential alterations of antioxidant defenses as bioindicators of mercury and cadmium toxicity in alfalfa. Chemosphere 77:946–954
Sobrino-Plata J, Herrero J, Carrasco-Gil S, Pérez-Sanz A, Lobo C, Escobar C, Millán R, Hernández LE (2013) Specific stress responses to cadmium, arsenic and mercury appear in the metallophyte Silene vulgaris when grown hydroponically. RSC Adv 3:4736–4744
Somasegaran P, Hoben H (1994a) Quantifying the growth of Rhizobia, handbook for Rhizobia: methods in legume-Rhizobium technology. New York: Springer, Verlag, pp 47–57
Somasegaran P, Hoben H (1994b) Screening effective strains of Rhizobia in potted field soil, handbook for Rhizobia: methods in legume-Rhizobium technology. New York: Springer, Verlag, pp 182–188
Stoeva N, Berova M, Zlatev Z (2005) Effect of arsenic on some physiological parameters in bean plant. Biol Plant 49:293–296
Talano M, Cejas RB, González PS, Agostini E (2013) Arsenic effect on the model crop symbiosis Bradyrhizobium-soybean. Plant Physiol Biochem 63:8–14
Talukdar D (2013) Arsenic-induced oxidative stress in the common bean legume, Phaseolus vulgaris L. seedlings and its amelioration by exogenous nitric oxide. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 19:69–79
Tripathi RD, Srivastava S, Mishra S, Singh N, Tuli R, Gupta DK, Maathuis FJM (2007) Arsenic hazards: strategies for tolerance and remediation by plants. Trends Biotechnol 25:158–165
Trueb LF (1998) Die chemischen Elemente. Ein Streifzug durch das Periodensystem. Cryst Res Technol 33:26
Vázquez S, Goldsbrough P, Carpena RO (2009) Comparative analysis of the contribution of phytochelatins to cadmium and arsenic tolerance in soybean and white lupin. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:63–67
Vázquez-Reina S, Esteban E, Goldsbrough P (2005) Arsenate-induced phytochelatins in white lupin: influence of phosphate status. Physiol Plant 124:41–49
Verbruggen N, Hermans C, Schat H (2009) Mechanisms to cope with arsenic or cadmium excess in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:1–9
Vincent J (1970) A manual for the practical study of root nodule bacteria. IBP Handbook. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications Ltd, pp 73–97
Wang ZH, Li SX (2003) Effects of N forms and rates on vegetable growth and nitrate accumulation. Pedosphere 13:309–316
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2008) Effect of metal-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobium on the performance of pea grown in metal-amended soil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55:33–42
Wittenberg JB, Bergersen FJ, Appleby CA, Turne GL (1974) Facilitated oxygen diffusion. The role of leghemoglobin in nitrogen fixation by bacteroids isolated from soybean root nodules. J Biol Chem 249:4057–4066
Yang HC, Rosen BP (2016) New mechanisms of bacterial arsenic resistance. Biom J 39:5–13
Zahran HH (1999) Rhizobium-legume symbiosis and nitrogen fixation under severe conditions and in an arid climate. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:968–989
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica de la Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto (SECYT-UNRC), Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), This work was also funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Awarded to L.E. Hernández projects AGL2010-15151, AGL2014-53771-R). Special thanks are also given to Andrés Bianucci for his assistance with the images presented and Josh Taylor for his English editing assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bianucci, E., Godoy, A., Furlan, A. et al. Arsenic toxicity in soybean alleviated by a symbiotic species of Bradyrhizobium . Symbiosis 74, 167–176 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-017-0499-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-017-0499-y