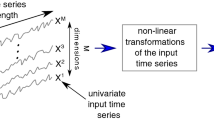
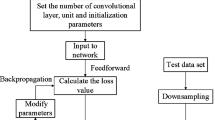
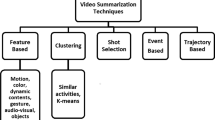
Abstract
With the popularity of sports wearable smart devices, it is no longer difficult to obtain human movement data. A series of running fitness software came into being, leading the nation's running wave and greatly promoting the rapid development of the sports industry. However, a large amount of sports data has not been deeply mined, resulting in a huge waste of its value. In order to make the data collected by smart sports equipment better serve the sports enthusiasts, thereby more effectively improving the degree of informatization of the sports industry, this paper selects the design and implementation of the human motion recognition information processing system as the main research content. This article combs the previous research results of human motion recognition information processing systems related to sports wearable intelligence and proposes a three-layer human motion recognition information processing system architecture, including data collection layer, data calculation layer, and data application layer. In the data calculation layer, different from the traditional classification algorithm, this paper proposes a classifier based on the recurrent neural network algorithm. The mechanical motion capture method mainly uses mechanical devices to track and measure motion. A typical system consists of multiple joints and rigid links. Inertial measurement units are bound to the joints to obtain angles and accelerations, and then analyze the human body motion based on these angles and accelerations. From the perspective of optical motion capture, the Kinect somatosensory camera is researched, and the method of human motion capture based on depth images, and the principle and method of human motion information are analyzed. At the same time, research on the application of Kinect's motion capture data. As a deep learning algorithm, convolutional action recognition model has the characteristics of being good at processing long and interrelated data and automatically learning features in the data. It solves the defect that the traditional recognition method needs to manually extract the motion features from the data, the whole system structure is streamlined, and the recognition efficiency is higher. The overall evaluation is as high as 99.4%. It avoids the manual extraction of time-domain and frequency-domain features of time series data, and at the same time avoids the loss of data information caused by dimensionality reduction.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data sharing does not apply to this article because no data set was generated or analyzed during the current research period.
References
Ali J, Altintas B, Pulatkan A et al (2020) Open versus arthroscopic Latarjet procedure for the treatment of chronic anteriorgleno humeral instability with glenoid bone loss. Arthroscopy 36(4):940–949
Beibei, Hongliu, Qingyun et al (2019) [Study on gait symmetry based on simulation and evaluation system of prosthesis gait]. Sheng wu yi xue gong cheng xue za zhi = Journal of biomedical engineering = Shengwu yixue gongchengxue zazhi 36(6):924–929
Carbone S, Moroder P, Runer A et al (2018) Scapular dyskinesis after Latarjet procedure. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25(3):422–427
Cerciello S, Redler A, Corona K (2018) Regarding, “Revision arthroscopicrepair versus Latarjet procedure in patients with recurrent instability after initial repair attempt: a cost-effectiveness model.” Arthroscopy 34(4):1005–1006
Chi Andrew S, Kim John et al (2017) Non-contrast diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. Clin Imaging 7(44):46–50
Cuéllar A, Cuéllar R, de Heredia PB (2017) Arthroscopic revision surgery for failure of open Latarjet technique. Arthroscopy 33(5):910–917
Ekhtiari S, Horner NS, Bedi A et al (2018) The learning curve for the Latarjet procedure: a systematic review. Orthop J Sports Med 6(7):157–168
Ernstbrunner L, Plachel F, Heuberer P et al (2018) Arthroscopic versus open iliac crest bone grafting in recurrent anterior shoulder instability with glenoid bone loss: a computed tomography—based quantitative assessment. Arthroscopy 34(2):352–359
Fields BKK, Skalski MR, Patel DB et al (2019) Adhesive capsulitis: review of imaging findings, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment options. Skeletal Radiol 48(8):1171–1184
Godenèche A, Merlini L, Roulet S et al (2020) Screw removal can resolve unexplained anterior pain without recurrence of shoulder instability after open Latarjet procedures. Am J Sports Med 48(6):1450–1455
Harris G, Bou-Haidar P, Harris C (2019) Adhesive capsulitis: review of imaging and treatment. Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 57(6):633–643
Homsi C, Bordalo-Rodrigues M, da Silva JJ et al (2020) Ultrasound in adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: Is assessment of the coracohumeral ligament a valuable diagnostic tool? Skeletal Radiol 35(9):673–678
Hsu Jason E, Anakwenze Okechukwu A, Warrender William J, Abboud JA (2019) Current review of adhesive capsulitis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20(3):502–514
Hurley ET, Lim Fat D, Farrington SK et al (2019) Open versus arthroscopic Latarjet procedure for anterior shoulder instability: asystematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med 47(5):1248–1253
Jurkovic IA, Papanikolaou N, Stathakis S et al (2016) Assessment of lung tumour motion and volume size dependencies using various evaluation measures. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci 47(1):30-42.e1
Lafosse T, Amsallem L, Delgrande D et al (2017a) Arthroscopic screw removal after arthroscopic Latarjet procedure. Arthrosc Tech 6(3):559–566
Lafosse L, Lejeune E, Bouchard A et al (2017b) The arthroscopic Latarjet procedure for the treatment of anterior shoulder instability. Arthroscopy 23(11):1–5
Latarjet M (2020) Treatment of recurrent dislocation of the shoulder. Lyon Chir 49(8):994–997
Lee SY, Park J, Song SW (2019) Correlation of MR arthrographic findings and range of shoulder motions in patients with frozen shoulder. Am J Roentgenol 198(1):173–179
Lei F, Li X (2017) The kappa (κ0) model of the Longmenshan region and its application to simulation of strong ground-motion by the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake. Chin J Geophys—Chin Ed 60(8):2935–2947
Makhni EC, Lamba N, Swart E et al (2018) Revision arthroscopic repair versus Latarjet procedure in patients with recurrent instability after initial repair attempt: a cost-effectiveness model. Arthroscopy 32(9):1764–1770
Owling PD, Akhtar MA, Liow RY (2016) What is a Bristow-Latarjet procedure? A review of the described operative techniques and outcomes. Bone Joint J 98(9):1208–1214
Ranalletta M, Bertona A, Tanoira I et al (2018) Modified Latarjet procedure without capsule labral repair for failed previous operative stabilizations. Arthrosc Tech 7(7):711–716
Siqueira JC, Pe Rh Inschi MG, Al-Sinbol G (2017) Simplified atmospheric model for UAV simulation and evaluation. Int J Intell Unmanned Syst 5(2–3):63–82
Suh CH, Yun SJ, Jin W et al (2019) Systematic review and meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging features for diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. Eur Radiol 29(2):566–577
Wang W, Cao J, Zhang N et al (2017) Magnetic-spring based energy harvesting from human motions: design, modeling and experiments. Energy Convers Manage 132(Jan):189–197
Xia S, Gao L, Lai YK et al (2017) A survey on human performance capture and animation. J Comput Sci Technol 32(3):536–554
Xiang L, Pan Y, Gong C et al (2017) Adaptive Human-Robot Interaction Control for Robots Driven by Series Elastic Actuators. IEEE Trans Rob 33(1):169–182
Yang C, Li Z, Cui R et al (2017) Neural network-based motion control of an underactuated wheeled inverted pendulum model. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(11):2004–2016
Zhao W, Zheng X, Liu Y et al (2019) An study of symptomatic adhesive capsulitis. PLoS ONE 7(10):277–278
Zhen-Bin G, Xiao-Li W, Jing SU et al (2018) Ecological compensation of Dongjiang river basin based on evaluation of ecosystem service value. J Ecol Rural Environ 34(6):563–570
Funding
The research was not specifically funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JM Writing—editing data curation. JH Supervision and data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
The picture materials quoted in this article have no copyright requirements, and the source has been indicated.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article is ethical, and this research has been agreed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Han, J. Value evaluation of human motion simulation based on speech recognition control. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 14, 796–806 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01584-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01584-z