Abstract
This research aims to understand the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG fermentation on egg white powder. In this study, some physico-chemical, functional, textural, and protein structure properties of microwave (MD) and oven dried (OD) egg white powders were determined.
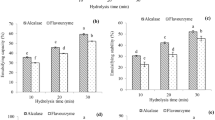
The fermentation process decreased the pH value (5.92, 5.82) and foaming capacity (20.83%, 27.20%) of MD and OD groups. The highest yield (11.61%) and emulsion capacity values (78.17%) were observed in fermented oven dried group. While MD group (703.22 g) had the lowest hardness value, OD group (3301.35 g) exhibited highest hardness value. The denaturation peaks of the samples were ranged between 61.00 °C and 80.43 °C. Scanning electron microscopy images of all sample groups showed broken glass structure. This study suggests that fermentation (L. rhamnosus GG) can effectively improve the quality properties of egg white powder and thus fermented egg white powders could be used in the food industry.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not Applicable
Code availability
Not Applicable
Abbreviations
- mL:
-
Milliliter
- M:
-
Molar
- min:
-
Minute
- g:
-
Gram
- mm:
-
Millimeter
- rpm:
-
Revolutions per minute
- kg:
-
Kilogram
- NaCl:
-
Sodium chloride
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- HCl:
-
Hydrochloric acid
References
AOAC (2000). In: Williams S (ed) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC
Ariyanti D, Hadiyanto H (2013) Ethanol production from whey by Kluyveromyces marxianus in batch fermentation system: kinetics parameters estimation. Bull Chem React Eng Catal 7:179
Arnold JW, Monteagudo-Mera A, Altermann E, Cadenas MB, Thompson AL, Azcarate-Peril MA (2017) Genome sequences of potential probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus isolates from human infants. Genome Announc 5:e00107-00117
Babaei J, Khodaiyan F, Mohammadian M (2019) Effects of enriching with gellan gum on the structural, functional, and degradation properties of egg white heat-induced hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol 128:94–100
Bamidele A, Olusegun O, Folasade J (2019) Influence of different oven drying temperatures on functional properties and amino acid composition of eggs. Am J Food Technol 14:19–27
Chandra M, Shamasundar B (2015) Texture profile analysis and functional properties of gelatin from the skin of three species of fresh water fish. Int J Food Prop 18:572–584
Chang C, Su Y, Gu L, Li J, Yang Y (2021) Microwave induced glycosylation of egg white protein: study on physicochemical properties and baking performance. Food Hydrocolloids 118:106569
Chen C, Chi YJ, Xu W (2012) Comparisons on the functional properties and antioxidant activity of spray-dried and freeze-dried egg white protein hydrolysate. Food Bioprocess Technol 5:2342–2352
Daramola EI (2018) Comparative evaluation of differently processed whole egg powder. Ahmadu Bello University, Department of Animal Science
Doblado R, Frias J, Muñoz R, Vidal-Valverde C (2003) Fermentation of Vigna sinensis var. carilla flours by natural microflora and Lactobacillus species. J Food Prot 66:2313–2320
Dubourg G, Elsawi Z, Raoult D (2015) Assessment of the in vitro antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus species for identifying new potential antibiotics. Int J Antimicrob Agents 46:590–593
Ibanoglu E, Erçelebi EA (2007) Thermal denaturation and functional properties of egg proteins in the presence of hydrocolloid gums. Food Chem 101:626–633
Jiang Y, Jia J, Xiong D, Xu X, Yang Y, Liu X, Duan X (2020) Effects of short-term fermentation with lactic acid bacteria on egg white: characterization, rheological and foaming activities. Food Hydrocolloids 101:105507
Katekhong W, Charoenrein S (2017) Color and gelling properties of dried egg white: effect of drying methods and storage conditions. Int J Food Prop 20:2157–2168
Koç GÇ, Çabuk B (2020) Characterization of the foam-mat dried egg white powder. Gıda 45:150–160
Kudre TG, Bejjanki SK, Kanwate BW, Sakhare PZ (2018) Comparative study on physicochemical and functional properties of egg powders from Japanese quail and white Leghorn chicken. Int J Food Prop 21:957–972
Li P, Jin Y, Sheng L (2020) Impact of microwave assisted phosphorylation on the physicochemistry and rehydration behaviour of egg white powder. Food Hydrocolloids 100:105380
Liu T, Li Y, Yang Y, Yi H, Zhang L, He G (2020) The influence of different lactic acid bacteria on sourdough flavor and a a deep insight into sourdough fermentation through RNA sequencing. Food Chem 307:125529–125529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125529
Ma S, Zhao S, Zhang Y, Yu Y, Liu J, Xu M (2013) Quality characteristic of spray-drying egg white powders. Mol Biol Rep 40:5677–5683
Nahariah N, Hikmah H, Yuliati F (2019) Microbiological activities in fermented egg whites with different level of milk and fermentation times. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science. IOP Publishing, pp 214–221
Orishagbemi C, Ichado I, Sanda M (2017) Physical, functional and sensory properties of foam mat dehydrated whole egg powder. J Sci Res Rep 15:1–7
Pratama A, Putranto WS, Suradi K, Adawiyah R, Risanawati R, Ninda C (2019) The effect of kluyveromyces lactis starter concentration and fermentation time to the physicochemical and functional properties of egg white powder. Jurnal Ilmu Dan Teknologi Hasil Ternak (JITEK) 14:117–125
Preethi R, Shweta D, Moses JA, Anandharamakrishnan C (2020) Conductive hydro drying as an alternative method for egg white powder production. Drying Technol 39(3):324–336
Quan TH, Benjakul S (2018) Gelling properties of duck albumen powder as affected by desugarization and drying conditions. J Texture Stud 49:520–527
Reid G, Burton J (2002) Use of Lactobacillus to prevent infection by pathogenic bacteria. Microbes Infect 4:319–324
Salinas Gonzalez FP (2017) The effect of storage temperature and time on the quality of spray dried egg powder, A Master's Thesis. Louisiana State University
Solval KM, Chouljenko A, Chotiko A, Sathivel S (2019) Growth kinetics and lactic acid production of Lactobacillus plantarum NRRL B-4496, L. acidophilus NRRL B-4495, and L. reuteri B-14171 in media containing egg white hydrolysates. LWT 105:393–399
Tian L, Hu S, Jia J, Tan W, Yang L, Zhang Q, Duan X (2021) Effects of short-term fermentation with lactic acid bacteria on the characterization, rheological and emulsifying properties of egg yolk. Food Chem 341:128163
Wang J, Xu L, Lv Y, Su Y, Gu L, Chang C, Zhang M, Yang Y, Li J (2022) To improve the gel properties of liquid whole egg by short-term lactic acid bacteria fermentation. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 75:102873
Yüceer M, Caner C (2019) Endüstriyel Yumurta Ürünlerinin Helal Gıda Açısından Üretim Şartlarının İncelenmesi ve Değerlendirilmesi. Helal Yaşam Dergisi 1:23–34
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Selcuk University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (SU-BAP, Konya TURKEY) for financial support (Project Number: 19201114).
Funding
This research was funded by Selcuk University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (SU-BAP, Konya TURKEY, Project Number: 19201114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BNG: Investigation, methodology, writing—original draft, formal analysis, data curation. CS: Methodology, data curation, resources, validation, funding acquisition, project administration. KU: Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
There is no ethics.
Consent to participate
All authors have read and approved the MS; and, that all are aware of its submission to JFST.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gundogan, B., Saricoban, C. & Unal, K. The effect of different drying methods on some physico-chemical, functional and protein structure properties of liquid egg white fermented by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J Food Sci Technol 60, 2433–2443 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05766-4
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05766-4