Abstract
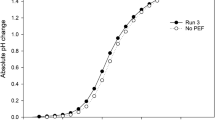
The whole milk spiked with sulfamethazine was treated under thermal and pulsed electric field processing for maximum reduction. The low-temperature long-time (LTLT, 62.5 °C for 30 min), high-temperature short time (HTST, 72 °C for 15 s) pasteurization and ultra-high temperature processing (UHT, 138 °C for 2 s) resulted in the reduction of sulfamethazine 7.3, 5.2 and 4.6% respectively. PEF and combination treatment (thermal + PEF) were found to reduce sulfamethazine content in milk by 67–72% and 73–76% respectively. Combined treatment of milk resulted in a higher percentage of reduction. Similar predicted and actual values proved that they fit the linear regression model and successful application of pulsed electric field technology in reducing antibiotic residues. PEF and mild thermal treatment can be a promising technology to reduce the antibiotic residues with ensuring minimal negative impact on the nutritional quality of food.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- SMZ:
-
Sulfamethazine
- SDM:
-
Sulfadimethoxine
- SMM:
-
Sulfamonomethoxine
- SMR:
-
Sulfamerazine
- SQX:
-
Sulfaquinoxaline
- CAC:
-
Codex alimentarius commission
- PEF:
-
Pulsed electric field
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- LTLT:
-
Low-temperature long time
- HTST:
-
High-temperature short time
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- LOQ:
-
Limit of quantification
References
Armentano A, Summa S, Magro SL, Palermo C, Nardiello D, Centonze D, Muscarella M (2018) Rapid method for the quantification of 13 sulphonamides in milk by conventional high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array ultraviolet detection using a column packed with core-shell particles. J Chromatogr A 1531:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.11.015
Chen F, Zeng L, Zhang Y, Liao X, Ge Y, Hu X, Jiang L (2009) Degradation behaviour of methamidophos and chlorpyrifos in apple juice treated with pulsed electric fields. Food Chem 112(4):956–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.07.016
Delsart C, Grimi N, Boussetta N, MiotSertier C, Ghidossi R, Vorobiev E, MiettonPeuchot M (2016) Impact of pulsed-electric field and high-voltage electrical discharges on red wine microbial stabilization and quality characteristics. J Appl Microbiol 120(1):152–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12981
Fan Y, Ji Y, Kong D, Lu J, Zhou Q (2015) Kinetic and mechanistic investigations of the degradation of sulfamethazine in heat-activated persulfate oxidation process. J Hazard Mater 300:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.058
Granja RH, de Lima AC, Salerno AG, Wanschel AC (2012) Validation of a liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection methodology for the determination of sulfonamides in bovine milk according to 2002/657/EC. Food Control 28(2):304–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.05.018
Ibarra IS, Miranda JM, Rodriguez JA, Nebot C, Cepeda A (2014) Magnetic solid phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of sulphonamides in milk samples. Food Chem 157:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.069
Kumar R, Bawa AS, Kathiravan T, Nadanasabapathi S (2015) Optimization of pulsed electric field parameters for mango nectar processing using response surface methodology. Int Food Res J 22(4):1353–1360
Mamani MC, Reyes FG, Rath S (2009) Multiresidue determination of tetracyclines, sulphonamides and chloramphenicol in bovine milk using HPLC-DAD. Food Chem 117(3):545–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.032
European Union Commission Regulation No 37/2010 of 22nd December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin, Official Journal of the European Communities, L15, 1 (2010)https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/files/eudralex/vol5/reg_2010_37/reg_2010_37_en.pdf
Papapanagiotou EP, Fletouris DJ, Psomas EI (2005) Effect of various heat treatments and cold storage on sulphamethazine residues stability in incurred piglet muscle and cow milk samples. Anal Chim Acta 529:305–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.09.029
Roca M, Althaus RL, Molina MP (2013) Thermodynamic analysis of the thermal stability of sulphonamides in milk using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry detection. Food Chem 136(2):376–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.08.055
Vijayalakshmi S, Nadanasabhapathi S, Kumar R, Kumar SS (2018) Effect of pH and pulsed electric field process parameters on the aflatoxin reduction in model system using response surface methodology. J Agric Food Sci Tech 55(3):868–878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2939-3
Wang L, Wu J, Wang Q, He C, Zhou L, Wang J, Pu Q (2012) Rapid and sensitive determination of sulfonamide residues in milk and chicken muscle by microfluidic chip electrophoresis. J Agric Food Chem 60(7):1613–1618. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2036577
Zhang W, Duan C, Wang M (2011) Analysis of seven sulphonamides in milk by cloud point extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem 126(2):779–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.11.072
Zhang Y, Hou Y, Zhang Y, Chen J, Chen F, Liao X, Hu X (2012) Reduction of diazinon and dimethoate in apple juice by pulsed electric field treatment. J Sci Food Agric 92(4):743–750. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.4636
Zhang Y, Sun J, Hu X, Liao X (2010) Spectral alteration and degradation of cyanidin-3-glucoside exposed to pulsed electric field. J Agric Food Chem 58(6):3524–3531. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9036722
Acknowledgements
Shinde Gokul Pandharinath would like to greatly acknowledge Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) for awarding Senior Research Fellowship (SRF). The authors also express deep gratitude to The Director, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, for his constant support and encouragement.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SGP designed and performed the experiments. SGP wrote the manuscript with support from RR. RK supervised the findings of this work and corrected the manuscript. SN and ADS approved the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinde, .P., Kumar, R., Reddy, K.R. et al. Effect of pulsed electric field processing on reduction of sulfamethazine residue content in milk. J Food Sci Technol 59, 1931–1938 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05207-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05207-0