Abstract
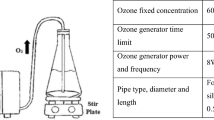
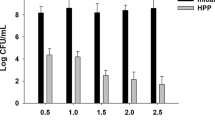
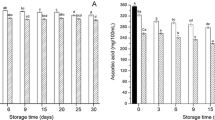
The increasing consumer demand for higher quality fruit juices has encouraged the use of non-thermal processing to extend the shelf life of perishable juice, watermelon juice. Ozone with its high oxidizing effect serve as an effective non-thermal processing treatment. The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of ozone treatment on the physico-chemical, bioactive compounds, pectin methylesterase (PME) activity and microbiological properties of unclarified and clarified watermelon juice. The ozone gas was pumped into watermelon juice for up to 25 min in a closed chamber. The microorganism inactivation in unclarified and clarified watermelon juices improved across the increasing processing time. Among these juices, the microorganism inactivation efficiency of ozone was found higher on clarified juice (3.466 log) than unclarified juice (3.150 log). It was found that °Brix value and PME activity were not altered by ozone treatment. The other physico-chemical properties (titratable acidity, pH, total colour difference, non-enzymatic browning, cloudiness) and bioactive compounds reduced across processing time. This study demonstrated that ozone treatment is an effective non-thermal processing technique to reduce the microorganism in watermelon juice. Further study is required to optimise the processing parameters of ozone treatment to maintain the overall quality of the watermelon juice.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Ascorbic acid
- DHA:
-
Dehydroascorbic acid
- MEA:
-
Malt extract agar
- NA:
-
Nutrient agar
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- NEB:
-
Non-enzymatic browning
- OWJ:
-
Ozonated watermelon juices
- PG:
-
Polygalacturonase
- PME:
-
Pectin methylesterase
- TA:
-
Titratable acidity
- TCD:
-
Total colour difference
- TPC:
-
Total phenolic content
- USFDA:
-
United States Food and Drug Administration
References
Aguiló-Aguayo I, Soliva-Fortuny R, Martín-Belloso O (2010) Color and viscosity of watermelon juice treated by high-intensity pulsed electric fields or heat. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 11:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2009.12.004
Bharate SS, Bharate SB (2014) Non-enzymatic browning in citrus juice: chemical markers, their detection and ways to improve product quality. J Food Sci Technol 51:2271–2288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0718-8
Botondi R, Sanctis FD, Moscatelli N, Vettraino AM, Catelli C, Mencarelli F (2015) Ozone fumigation for safety and quality of wine grapes in postharvest dehydration. Food Chem 188:641–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.029
Collins JK, Wu G, Perkins-Veazie P, Spears K, Claypool PL, Baker RA, Clevidence BA (2007) Watermelon consumption increases plasma arginine concentrations in adults. Nutrition 23:261–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2007.01.005
Criegee R (1975) Mechanism of ozonolysis. Angew Chem-Int Edit Engl 14:745–752. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.197507451
Cullen PJ, Valdramidis V, Tiwari BK, Patil S, Bourke P, O’Donnell CP (2010) Ozone processing for food preservation: an overview on fruit juice treatments. Ozone-Sci Eng 32:166–179. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919511003785361
Dewhirst RA, Fry SC (2018) The oxidation of dehydroascorbic acid and 2,3-diketogulonate by distinct reactive oxygen species. Biochem J 475:3451–3470. https://doi.org/10.1042/bcj20180688
Edwards AJ, Vinyard BT, Wiley ER, Brown ED, Collins JK, Perkins-Veazie P, Baker RA, Clevidence BA (2003) Consumption of watermelon juice increases plasma concentrations of lycopene and β-carotene in humans. J Nutr 133:1043–1050. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/133.4.1043
Eissa HA, Shaheen MS, Botros HW (2014) Impact of γ-irradiation on aroma flavour, bio-active constituents and quality attributes of water melon juice. J Plant Pathol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7471.1000227
Feng L, Zhang K, Gao M, Shi C, Ge C, Qu D, Zhu J, Shi Y, Han J (2018) Inactivation of vibrio parahaemolyticus by aqueous ozone. J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:1233–1246. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1801.01056
Guzel-Seydim ZB, Greene AK, Seydim A (2004) Use of ozone in the food industry. LWT 37:453–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2003.10.014
Henry LK, Puspitasari-Nienaber NL, Jarén-Galán M, Breemen RB, Catignani GL, Schwartz SJ (2000) Effects of ozone and oxygen on the degradation of carotenoids in an aqueous model system. J Agric Food Chem 48:5008–5013. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf000503o
Jaramillo-Sánchez GM, Loredo AB, Gómez PL, Alzamora SM (2017) Ozone processing of peach juice: impact on physico-chemical parameters, color, and viscosity. Ozone Sci Eng 40:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2017.1417111
Kim C, Park M, Kim S, Cho Y (2014) Antioxidant capacity and anti-inflammatory activity of lycopene in watermelon. Int J Food Sci Technol 49:2083–2091. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12517
Kim J, Yousef AE, Dave S (1999) Application of ozone for enhancing the microbiological safety and quality of foods: a review. J Food Prot 62:1071–1087. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028x-62.9.1071
Lee SK, Kader AA (2000) Preharvest and postharvest factors influencing vitamin c content of horticultural crops. Postharvest Biol Technol 20:207–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-5214(00)00133-2
Mosqueda-Melgar J, Raybaudi-Massilia RM, Martín-Belloso O (2008) Combination of high-intensity pulsed electric fields with natural antimicrobials to inactivate pathogenic microorganisms and extend the shelf-life of melon and watermelon juices. Food Microbiol 25:479–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2008.01.002
Naz AS, Butt MST, Sultan MTM, Qayyum MMN, Niaz RS (2014) Watermelon lycopene and allied health claims. EXCLI J 13:650–666. https://doi.org/10.17877/DE290R-6561
Nielsen SS (2010) Food analysis laboratory manual. Springer, Cham
Oliveira AFA, Mar JM, Santos SF, da Silva Júnior JL, Kluczkovski AM, Bakry AM, Bezerra JA, Numomura RCS, Sanches EA, Campelo PH (2018) Non-thermal combined treatments in the processing of açai (Euterpe oleracea) juice. Food Chem 265:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.05.081
Santos MD, Queirós RP, Fidalgo LG, Inácio RS, Lopes RP, Mota MJ, Sousa SG, Delgadillo I, Saraiva JA (2015) Preservation of a highly perishable food, watermelon juice, at and above room temperature under mild pressure (hyperbaric storage) as an alternative to refrigeration. LWT 62:901–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.06.055
Shah NNAK, Sulaiman A, Sidek NSM, Supian NAM (2019a) Quality assessment of ozone-treated citrus fruit juices. Int Food Res J 26:1405–1415
Shah NNAK, Supian NAM, Hussein NA (2019b) Disinfectant of pummelo (Citrus Grandis L. Osbeck) fruit juice using gaseous ozone. J Food Sci Technol 56:262–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3486-2
Tiwari BK, O’Donnell CP, Brunton NP, Cullen PJ (2009a) Degradation kinetics of tomato juice quality parameters by ozonation. Int J Food Sci Technol 44:1199–1205. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2009.01946.x
Tiwari BK, O’Donnell CP, Muthukumarappan K, Cullen PJ (2009b) Anthocyanin and colour degradation in ozone treated blackberry juice. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 10:70–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2008.08.002
Torres B, Tiwari BK, Patras A, Wijngaard HH, Brunton N, Cullen PJ, O’Donnell CP (2011) Effect of ozone processing on the colour, rheological properties and phenolic content of apple juice. Food Chem 124:721–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.06.050
Walsh KA, Bennett SD, Mahovic M, Gould LH (2014) Outbreaks associated with cantaloupe, watermelon, and honeydew in the United States, 1973–2011. Foodborne Pathog Dis 11:945–952. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2014.1812
Woodall AA, Lee SW, Weesie RJ, Jackson MJ, Britton G (1997) Oxidation of carotenoids by free radicals: relationship between structure and reactivity. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1336:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4165(97)00006-8
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Medklinn International Sdn. Bhd for providing ozone generator used in this work. This work was supported by School of Science, Monash University Malaysia.
Funding
This work was supported by School of Science, Monash University Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lee BJ and Thoo YY conceived of the presented idea. Lee BJ carried out the experiments. Thoo YY and Ting ASY supervised the project. Lee BJ wrote the manuscript with support from Thoo YY and Ting ASY.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The Authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, B.J., Ting, A.S.Y. & Thoo, Y.Y. Impact of ozone treatment on the physico-chemical properties, bioactive compounds, pectin methylesterase activity and microbiological properties of watermelon juice. J Food Sci Technol 59, 979–989 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05102-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05102-8