Abstract
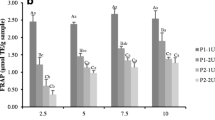
To observe the neuroprotective and antioxidant activities of the grass carp protein hydrolysates (GPH) obtained from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin by enzymatic hydrolysis. GPH prepared using Protamex, at different (5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 %) degrees of hydrolysis (DH) were investigated. The DPPH radial scavenging, reducing power and inhibition of linoleic acid oxidation activities of GPH were significantly improved by a low DH (5 %) compared with those of GPH with a higher DH (p < 0.05). A low degree of enzymatic hydrolysis was appropriate to obtain GPH with improved neuroprotective activities. These results suggest that the control of the DH may be an effective strategy to modify specific neuroprotective and antioxidant activities of GPH, and GPH has potential as a functional food ingredient for related functional and health benefits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler-Nissen J (1986) Methods in food protein hydrolysis. In: Enzymatic hydrolysis of food proteins. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, New York, pp 110–130
Aluko RE, Monu E (2003) Functional and bioactive properties of quinoa seed protein hydrolysates. J Food Sci 68:1254–1258
AOAC (1997) Official methods of analysis. Arlington, VA: American Association of Analytical Chemists (AOAC official method 930.15 for dry matter; 968.06 for protein; 920.39 for fat; 942.05 for ash; 991.43 for carbohydrate)
Canet-Aviles RM, Wilson MA, Miller DW, Ahmad R, McLendon C, Bandyopadhyay S et al (2004) The Parkinson’s disease protein DJ-1 is neuroprotective due to cysteine-sulfinic acid-driven mitochondrial localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9103–9108
Duarte J, Vinderola G, Ritz B, Perdigon G, Matar C (2006) Immunomodulating capacity of commercial fish protein hydrolysate for diet supplementation. Immunobiology 211:341–350
Erickson CA, Barnes CA (2003) The neurobiology of memory changes in normal aging. Exp Gerontol 38:61–69
Gao Y, Dong C, Yin J, Shen J, Tian J, Li C (2012) Neuroprotective effect of fucoidan on H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:523–529
Hu XQ, Huang YY, Dong QF, Song LY, Yuan F, Yu RM (2011) Structure characterization and antioxidant activity of a novel polysaccharide isolated from pulp tissues of litchi chinensis. J Agri Food Chem 59:11548–11552
Jamdar SN, Rajalakshmi V, Pednekar MD, Juan F, Yardi V, Sharma A (2010) Influence of degree of hydrolysis on functional properties, antioxidant activity and ACE inhibitory activity of peanut protein hydrolysate. Food Chem 121:178–184
Kim SK, Mendis E (2006) Bioactive compounds from marine processing byproducts – a review. Food Res Int 39:383–393
Klompong V, Benjakul S, Kantachote D, Shahidi F (2007) Antioxidant activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem 102:1317–1327
Ko S, Kim D, Jeon Y (2012) Protective effect of a novel antioxidative peptide purified from a marine Chlorella ellipsoidea protein against free radical-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem Toxicol 50:2294–2302
Koleva II, Van Beek TA, Linssen JPH, Groot A, Evstatieva LN (2002) Screening of plant extracts for antioxidant activity: a comparative study on three testing methods. Phytochem Analysis 13:8–17
Ladislaus MK, Yan X, Yao WL, Sun DH, Qian H (2007) Optimization of gelatine extraction from grass carp (Catenopharyngodon idella) fish skin by response surface methodology. Bioresource Technol 98:3338–3343
Li B, Chen F, Wang X, Ji B, Wu Y (2007) Isolation and identification of antioxidative peptides from porcine collagen hydrolysate by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Chem 102:1135–1143
Li Y, Jiang B, Zhang T, Mu W, Liu J (2008) Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of chickpea protein hydrolysate (CPH). Food Chem 106:444–450
Lopez J, Uribe E, Vega-Galvez MM, Vergara J, Gonzales E, Di Scala K (2010) Effect of air temperature on drying kinetics, vitamin C, antioxidant activity, total phenolic content, non-enzymatic browning and firmness of blueberries variety O’Neill. Food Bioprocess Tech 3:772–777
Pan M, Jiang TS, Pan JL (2011) Antioxidant activities of rapeseed protein hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Tech 4:1144–1152
Pulido R, Bravo L, Saura-Calixto F (2000) Antioxidant activity of dietary polyphenols as determined by a modified ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay. J Agri Food Chem 48:3396–3402
Reed TT (2011) Lipid peroxidation and neurodegenerative disease. Free Radical Biol Med 51:1302–1319
Slizyte R, Mozuraityte R, Martinez-Alvarez O, Falch E, Fouchereau-Peron M, Rustad T (2009) Functional, bioactive and antioxidant properties of hydrolysates obtained from cod (Gadus morhua) backbones. Process Biochem 44:668–677
Tian L, Zhao Y, Guo C, Yang X (2011) A comparative study on the antioxidant activities of an acidic polysaccharide and various solvent extracts derived from herbal Houttuynia cordata. Carbohydr Polym 83:537–544
Wasswa J, Tang J, Gu XH, Yuan XQ (2007) Influence of the extent of enzymatic hydrolysis on the functional properties of protein hydrolysate from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin. Food Chem 104:1698–1704
Zhu KX, Zhou HM, Qian HF (2006) Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of wheat germ protein hydrolysates (WGPH) prepared with alcalase. Process Biochem 41:1296–1302
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a grant from the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China during the 12th Five-Year Plan Period (2012BAD29B06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, L., Wu, X., Lv, Y. et al. The neuroprotective and antioxidant activities of protein hydrolysates from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin. J Food Sci Technol 52, 3750–3755 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1438-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1438-z