Abstract
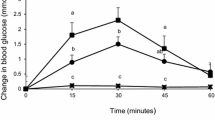
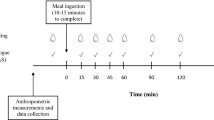
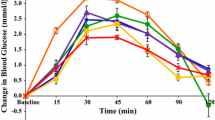
Prevalence of obesity and type-2-diabetes requires dietary manipulation. It was hypothesized that wheat-legume-composite breads will reduce the spike of blood glucose and increase satiety. Four pan bread samples were prepared: White bread (WB) as standard, Whole-wheat bread (WWB), WWB supplemented with chickpea flour at 25 % (25%ChB) and 35 % (35%ChB) levels. These breads were tested in healthy female subjects for acceptability and for effect on appetite, blood glucose, and physical discomfort in digestion. The breads were rated >5.6 on a 9-point hedonic scale with WB significantly higher than all other breads. No difference in area under the curve (AUC) for appetite was found, but blood glucose AUC was reduced as follows: 35%ChB < WB and WWB, WB >25%ChB = WWB or 35%ChB. We conclude that addition of chickpea flour at 35 % to whole wheat produces a bread that is acceptable to eat, causing no physical discomfort and lowers the glycemic response.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (1983) American association of cereal chemists. St. Paul MN: American Association Cereal Chemistry.
Alter EEEJG, Abete I, Astrup A, Martinez JA, van Baak MA (2011) Starches, sugars and obesity. Nutrients 3(3):341–369
Badr HE, Shah NM, Shah MA (2012) Obesity among Kuwaitis aged 50 years or older: prevalence, correlates and comorbidities. Gerantologist. doi:10.1093/geront/gns108
Berrios JDJ, Morales P, Camara M, Sanchez-Mata MC (2010) Carbohydrate composition of raw and extruded pulse flours. Food Res Int 43:531–536
Bojnanska T, FrancaKova H, Liskova M, Tokar M (2012) Legumes - The alternative raw materials for bread production. JMBFS 1(February special issue):876–886
Brownlee M (2003) A radical explanation for glucose-induced beta cell dysfunction. J Clin Invest 112:1788–1790
Chillo S, Monro JA, Mishra S, Henry CJ (2010) Effect of incorporating legume flour into semolina spaghetti on its cooking quality and glycemic impact measured in vitro. Int J Food Sci Nutr 61(2):149–160
Doblado-Maldonado AF, Pike OA, Jess C, Sweley JC, Rose DJ (2012) Key issues and challenges in whole wheat flour milling and storage. J Cereal Sci 56:119–126
FAO/WHO (1998) Expert consultation. FAO Food Nutr Pap 66:1–140
Fenn D, Lukow OM, Humphreys G, Fields PG, Boye JI (2010) Wheat-legume composite flour quality. Int J Food Prop 13:381–393
Flint A, Raben A, Blundell JE, Astrup A (2000) Reproducibility, power and validity of visual analogue scales in assessment of appetite sensations in single test meal studies. Int J Obes 24(1):38–48
Foster-Powell K, Holt S, Brand-Miller J (2002) International table of glycemic index and glycemic load values. Am J Clin Nutr 76:5–56
Guillon F, Champ MM (2002) Carbohydrate fractions of legumes: uses in human nutrition and potential for health. Br J Nutr 88(Suppl 3):S293–S306
Hawkins A, Johnson SK (2005) In vitro carbohydrate digestibility of whole-chickpea and chickpea bread products. Int J Food Sci Nutr 56(3):147–155
Hefnawy TM, El-Shourbagy GA, Ramadan MF (2012) Impact of adding chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) flour to wheat flour on the rheological properties of toast bread. Int Food Res J 19(2):521–525
Idriss M, Ahmed AR, Senge B (2012) Dough rheology and bread quality of wheat–chickpea flour blends. J Food Sci Technol 36:196–202
Johnson SK, Thomas SJ, Hall RS (2005) Palatability and glucose, insulin and satiety responses of chickpea flour and extruded chickpea flour bread eaten as part of a breakfast. Eur J Clin Nutr 59:169–176
Liu S (2002) Intake of refined carbohydrates and whole grain foods in relation to risk of type-2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease. J Am Coll Nutr 21(4):298–306
Liu S, Willet WC, Stampfer MJ, Hu FB, Franz M, Sampson L, Hennekens CH, Manson JE (2000) A prospective study of dietary glycemic load, carbohydrate intake and risk of coronary heart disease in US women. Am J Clin Nutr 71:1455–1461
McCrory MA, Hamaker BR, Lovejoy JC, Eichelsdoerfer PE (2010) Pulse consumption, satiety, and weight management. Adv Nutr 1:17–30
Muir JG, O’Dea K (1992) Measurement of resistant starch: factors affecting the amount of starch escaping digestion in vitro. Am J Clin Nutr 56:123–127
Onoja US, Odo GE, Dibua UME, Eze JI (2011) Physico-chemical properties, energy, mineral, vitamin and sensory evaluation of wheat-based bread supplemented with legume, root, tuber and plantain flour. Glob J Pure Appl Sci 17(3):319–327
Polivy J, Herman CP, Warsh S, Villaume C, Beck B, Rohr R, Pointel JP, Debry G (1978) Internal and external components of emotionality in restrained and unrestrained eaters. J Abnorm Psychol 87:497–504
Radhika G, Sumathi C, Ganesan A, Sudha V, Henry CJK, Mohan V (2010) Glycemic index of Indian flatbreads (rotis) prepared using whole wheat flour and ‘atta mix’-added whole wheat flour. Br J Nutr 103:1642–1647
Ranhotra GS, Loewe RJ (1974) Bread making characteristics of wheat flour fortified with various commercial soy protein products. Cereal Chem 51:629–634
Sidhu JS, Hooti SN, Al-Saqer JM, Al-Amiri HA, Al-Foudari M, Al-Othman A, Hamad A, Al-Haji L, Ahmed N, Mansoor IB, Minal J (2004) Developing functional foods using red palm olein: pilot-scale studies. Int J Food Prop 7(1):1–13
Tosh SM, Yada S (2010) Dietary fibers in seeds and fractions: characterization, functional attributes, and applications. Food Res Int 43:450–460
Tosi P, Gritsch CS, He J, Shewry PR (2011) Distribution of gluten proteins in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) grain. Ann Bot 108(1):23–35
Venn BJ, Green TJ (2007) Glycemic index and glycemic load: measurement issues and their effect on diet-disease relationships. Eur J Clin Nutr 61(1):S122–S131
Wong CL, Mollard RC, Zafar TA, Luhovyy BL, Anderson G (2009) Food intake and satiety following a serving of pulses in young men: effect of processing, recipe, and pulse variety. J Am Coll Nutr 28(5):543–552
Zafar TA, Martin B, Weaver CM (2009) Resistant starches (RS2 and RS3) have variable effects on bone mineral status in rats. Open Nutr J 3:17–22
Zafar TA, Kabir Y, Ghazaii C (2011) Low glycemic index foods suppress glycemic responses, appetite and food intake in young Kuwaiti females. Kuwait J Sci Eng 38(1A):111–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zafar, T.A., Al-Hassawi, F., Al-Khulaifi, F. et al. Organoleptic and glycemic properties of chickpea-wheat composite breads. J Food Sci Technol 52, 2256–2263 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1192-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1192-7