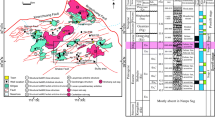
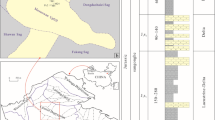
Abstract
Zhen 11 block is located in the deep sag of Gaoyou Sag, North Jiangsu basin, China. It is the main oil-bearing block in the Zhenwu oilfield, which contains multiple types of faults with complex tectonic structures. The Sanduo formation is the target horizon of the study area that has been divided into two members. The purpose of the current study is to evaluate the sedimentology and diagenetic impact on reservoir characteristics. To fulfill the main objective of the study, the core data analysis, thin-section analysis, SEM, CL, and MICP techniques have been used to evaluate the sedimentary facies, reservoir characteristics, and diagenesis of E2s1 in the Zhen 11 block. The reservoir rock of E2s1 in the Zhen 11 block is mainly lithic arkoses and feldspathic litharenite. The grain sorting and rounding are poor, with low composition and structural maturity, reflecting the characteristics of near provenance. The formation comprises primary pores, secondary pores, and microfractures. The porosity and permeability range from 10 to 31% and 0.4 × 10−3μm2 to 8000 × 10−3μm2, respectively. The diagenesis includes compaction, cementation, alteration of clay minerals, and feldspar dissolution. The dissolution of feldspar developed in the early and late burial stages. The mechanical compaction increases by increasing burial depth, due to that mechanism the reservoir characteristics have been reduced. The dissolution of feldspar and the fracturing mechanism is common that enhance the reservoir quality. Carbonate cement and clay contents block pores and pore throats and significantly reduces reservoir quality. E2s1 sandstone is commonly deposited in the braided river and meandering stream depositional environment. It consists of an abundance of quartz and feldspar grains with minor calcite cement. Grains are mostly sub-angular to angular, sub-rounded, and moderate sorting, with primary intergranular porosity that increases the reservoir quality. The meandering channel sandstone is comprised of coarse gravel, sandstone, and siltstone from bottom to top with fair reservoir characteristics. Overall the studied formation consists of moderate to good porosity and permeability that is why it can be acting as a good reservoir.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author Data is transparent and available to the first author.
References
Abay T. B (2017) Diversity of Petroleum in terms of Source Rock Properties and Secondary Alteration Processes. A study of source rocks, migrated petroleum, oils and condensates from the Norwegian Continental Shelf. Oslo: University of Oslo
Ärlebrand A, Augustsson C, Escalona A, Grundvåg SA, Marín D (2021) Provenance, depositional setting and diagenesis as keys to reservoir quality of the Lower Cretaceous in the SW Barents Sea. Mar Pet Geol 132:105217
Baiyegunhi TL, Liu K, Gwavava O, Baiyegunhi C (2020) Impact of diagenesis on the reservoir properties of the cretaceous sandstones in the Southern Bredasdorp Basin. Offshore South Africa Minerals 10(9):757
Bukar M, Worden RH, Bukar S, Shell P (2021) Diagenesis and its controls on reservoir quality of the Tambar oil field. Norwegian North Sea Energy Geosci 2(1):10–31
Chen QH, Wu L, Zhou YC (2015) Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and modes in the area around Shaobo sub-sag, Gaoyou Sag. J China Univ Min Technol 44:282–291
Cheng Q, Zhang M, Li H (2019) Anomalous distribution of steranes in deep lacustrine facies low maturity-maturity source rocks and oil of Funing formation in Subei Basin. J Petrol Sci Eng 181:106–190
Folk RL, Andrews PB, Lewis D (1970) Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand. NZ J Geol Geophys 13(4):937–968
Gao G, Kang G, BaiC Li G (2013) Distribution of the crustal magnetic anomaly and geological structure in Xinjiang, China. J Asian Earth Sci 77:12–20
Gu Y, Dai J (2015) Fault growth and main controlling factors in deep area of Gaoyou Sag. Geotecton Metallog 39(1):53–61
Hao YT, Bonadiman C, Coltorti M (2019) Fragments of asthenosphere incorporated in the lithospheric mantle underneath the Subei Basin, eastern China: constraints from Geothermobarometric results and water contents of peridotite xenoliths in cenozoic basalts. J Asian Earth Sci 1:1–15
Hyodo A, Kozdon R, Pollington AD (2014) Evolution of quartz cementation and burial history of the eau claire formation based on in situ oxygen isotope analysis of quartz overgrowths. Chem Geol 384:168–180
Ibrahem Y, Morozov VP, Sudakov V, Idrisov I, Kolchugin AN (2022) Sedimentary diagenesis and pore characteristics for the reservoir evaluation of domanik formations (Semiluksk And Mendymsk) In the central part of volga-ural petroleum province. Petrol Res 7(1):32–46
Ji YL, Li QS, Wang Y (2012) Fan delta sedimentary system and facies models of Dainan formation of Paleogene In Gaoyou Sag. J Earth Sci Environ 34(1):9–19
Kashif M, Cao Y, Yuan G, Asif M, Jian W, Zhukhun W, Naz AF (2019a) Sedimentological impact on reservoir quality of Es1 sandstone of Shahejie formation, Nanpu Sag. East China Arabian J Geosci 12(17):1–21
Kashif M, Cao Y, Yuan G, Asif M, Javed K, Mendez JN, Miruo L (2019b) Pore size distribution, their geometry and connectivity in deeply buried Paleogene Es1 sandstone reservoir, Nanpu Sag. East China Petrol Sci 16(5):981–1000
Kashif M, Cao Y, Yuan G, Jian W, Cheng X, Sun P, Hassan S (2019c) Diagenesis impact on a deeply buried sandstone reservoir (Es1 Member) of the Shahejie Formation, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Aust J Earth Sci 66(1):133–151
Li J, Zhang X, Tian J, Liang Q, Cao T (2021) Effects of deposition and diagenesis on sandstone reservoir quality: a case study of Permian sandstones formed in a braided river sedimentary system, northern Ordos Basin, Northern China. J Asian Earth Sci 213:104745
Loucks RG, Reed R, M, Ruppel S. C, Hammes U, (2012) Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores. AAPG Bull 96(6):1071–1098
Mei L, Zhanghua L, Aimin J, Rong Z, Changjian S, Ying Y, Zhenhong Z (2013) Origin, flow of formation water and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Zhenwu Area of the North Jiangsu Basin. China Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition 87(3):819–829
Mondol NH, Bjørlykke K, Jahren J, Høeg K (2007) Experimental mechanical compaction of clay mineral aggregates—Changes in physical properties of mudstones during burial. Mar Pet Geol 24(5):289–311
Nabawy BS, Abudeif AM, Masoud MM, Radwan AE (2022) An integrated workflow for petrophysical characterization, microfacies analysis, and diagenetic attributes of the Lower Jurassic type section in northeastern Africa margin: Implications for subsurface gas prospection. Mar Pet Geol 140:105678
Qian W, Sun Q, Jones SJ, Yin T, Zhang C, Xu G, Zhang B (2022) Diagenesis and controlling factors of Oligocene Huagang Formation tight sandstone reservoir in the south of Xihu sag, the East China Sea Shelf Basin. J Petrol Sci Eng 215:110579
Radwan AE (2022) Provenance, depositional facies, and diagenesis controls on reservoir characteristics of the middle Miocene Tidal sandstones, Gulf of Suez Rift Basin: Integration of petrographic analysis and gamma-ray log patterns. Environ Earth Sci 81(15):1–15
Rexer TF, Mathia EJ, Aplin AC, Thomas KM (2014) High-pressure methane adsorption and characterization of pores in Posidonia shales and isolated kerogens. Energy Fuels 28(5):2886–2901
Schmid S, Worden RH, Fisher QJ (2004) Diagenesis and reservoir quality of the Sherwood Sandstone (Triassic), Corrib field, Slyne basin, west of Ireland. Mar Petrol Geol 21(3):299–315
Song N, Wang TG, Chen LQ, Xin R (2010) Comprehensive analysis on hydrocarbon accumulation period of Upper Cretaceous Taizhou formation in Subei Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica 31(2):180–186
Thota ST, Islam MA, Shalaby MR (2023) Reservoir quality evaluation using sedimentological and petrophysical characterization of deep-water turbidites: a case study of Tariki Sandstone Member, Taranaki Basin. New Zealand Energy Geosci 4(1):13–32
Wang J, Cao Y, Liu K, Liu J, Xue X, Xu Q (2016) Pore fluid evolution, distribution and water-rock interactions of carbonate cements in red-bed sandstone reservoirs in the Dongying Depression, China. Mar Pet Geol 72:279–294
Wang GW, Chang XC, Yin W, Li Y, Song TT (2017) Impact of diagenesis on reservoir quality and heterogeneity of the Upper Triassic Chang 8 tight oil sandstones in the Zhenjing area, Ordos Basin. China Mar Petrol Geol 83:84–96
Xi K, Cao Y, Jahren J, Zhu R, Bjørlykke K, Zhang X, Hellevang H (2015) Quartz cement and its origin in tight sandstone reservoirs of the Cretaceous Quantou formation in the southern Songliao basin, China. Mar Pet Geol 66:748–763
Xuming QIU, Shiyou QIAN, Wenquan YU, Qidong L (2016) Main achievements, new understanding and technological progress for oil and gas exploration in North Jiangsu Basin during the 12th Five-Year Plan. China Petrol Explor 21(3):62
Yu Y, Lin L, Zhai C, Chen H, Wang Y, Li Y, Deng X (2019) Impacts of lithologic characteristics and diagenesis on reservoir quality of the 4th member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation tight gas sandstones in the western Sichuan Basin, southwest China. Mar Pet Geol 107:1–19
Zhang X, Lin CM, Yin Y, Zhang N, Zhou J, Liu YR (2016) Sedimentary characteristics and processes of the Paleogene Dainan Formation in the Gaoyou Depression, North Jiangsu Basin, eastern China. Pet Sci 13(3):385–401
Zhang Y, Tian J, Zhang X, Li J, Liang Q, Zheng X (2022a) Diagenesis evolution and pore types In tight sandstone of Shanxi formation reservoir in Hangjinqi Area, Ordos Basin. Northern China Energies 15(2):470
Zou C, Zhu R, Liu K, Su L, Bai B, Zhang X, Wang J (2012) Tight gas sandstone reservoirs in China: characteristics and recognition criteria. J Petrol Sci Eng 88:82–91
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledged the School of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum, for providing experimental facilities. I am also thankful to CSC (Chin scholarship council) who provide me financial support to complete my research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to writing, interpreting, removing grammatical mistakes, software work, etc.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Work is original and not submitted to any other journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Isgandarov, O., Shaochun, Y., Kashif, M. et al. Sedimentology and diagenesis impact on Sanduo formation (E2S) in Zhen 11 block of Gaoyou Sag, East China. Carbonates Evaporites 38, 47 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-023-00873-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-023-00873-x