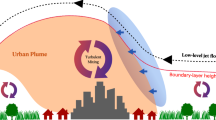
Abstract
To date, the characteristics of the low-level jets (LLJs) that appear below 300 m, referred to in this study as tower-level LLJs (T-LLJs), have remained unidentified. The results in this study show that approximately 22% of LLJs in Tianjin appear below 300 m, indicating that greater attention should be given to T-LLJs. Thus, the characteristics of T-LLJs in Tianjin are investigated using data obtained from a wind-profile radar and a 255-m high meteorological tower. The results show that T-LLJs frequently occur during the transition from the warm season to the cold season and prefer to appear at night. Compared to the LLJs that appear between 300 and 1000 m, T-LLJs exhibit distinct monthly and diurnal variations, likely attributable to specific underlying causes. The case study suggests that the generation of T-LLJs can be partly attributed to inertial oscillation. Moreover, sensitivity tests indicate that the land‒sea thermal contrast is one of the main causes of T-LLJs, and that urban heat islands (UHIs) exert nonnegligible influence on T-LLJs in Tianjin. In addition, since UHIs are mainly nocturnal phenomena, the impacts of nocturnal LLJs on UHIs are investigated. The results show that nocturnal LLJs contribute to enhance turbulent mixing and heat transport, which can weaken atmospheric stability near the surface. Consequently, a nocturnal UHI is always weaker when it occurs concurrently with a LLJ, as opposed to occurring without a LLJ.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data used in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request (tjwbgtjwbg@126.com).
References
Arnfield, A.J.: Two decades of urban climate research: A review of turbulence, exchanges of energy and water, and the urban heat island. Int. J. Climatol. 23, 1–26 (2003)
Banta, R.M., Pichugina, Y.L., Newsom, R.K.: Relationship between low-level jet properties and turbulence kinetic energy in the nocturnal stable boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 60(20), 2549–2555 (2003)
Banta, R.M., Pichugina, Y.L., Brewer, W.A.: Turbulent velocity-variance profiles in the stable boundary layer generated by a nocturnal low-level jet. J. Atmos. Sci. 63, 2700–2719 (2006)
Basara, J.B., Hall, P.K., Jr., Schroeder, A.J., Illston, B.G., Nemunaitis, K.L.: Diurnal cycle of the Oklahoma City urban heat island. J. Geophys. Res. 113, D20109 (2008)
Blackadar, A.K.: Boundary layer wind maxima and their significance for the growth of nocturnal inversions. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 38(5), 283–290 (1957)
Bonner, W.D.: Climatology of the low-level jet. Mon. Weather Rev. 96(12), 833–850 (1968)
Bornstein, R.D.: Observations of the urban heat island effect in New York City. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 7, 575–582 (1968)
Brandsma, T., Wolters, D.: Measurement and statistical modeling of the urban heat island of the city of Utrecht (the Netherlands). J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 51, 1046–1060 (2012)
Businger, J. A.: Turbulent transfer in the atmospheric surface layer. In workshop on micrometeorology. Amer. Met. Soc. 84–87 (1973)
Cao, B., Zhang, Y., Zhao, Y., Wen, X., Jin, L.: Influence of the low-level jet on the intensity of the nocturnal oasis cold island effect over northwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 139(3), 689–699 (2020)
Chen, Y.L., Chen, X.A., Zhang, Y.X.: A diagnostic study of the low-level jet during TAMEX IOP 5. Mon. Wea. Rev. 122, 2257–2284 (1994)
Chen, G.T.J., Wang, C.C., Lin, D.T.W.: Characteristics of low-level jets over northern Taiwan in Mei-Yu season and their relationship to heavy rain events. Mon. Weather Rev. 133(1), 20–43 (2005)
Chen, F., Yang, X., Zhu, W.: WRF simulations of urban heat island under hot-weather synoptic conditions: The case study of Hangzhou City, China. Atmos. Res. 138, 364–377 (2014)
Choi, M.H., Lee, Y.H.: Characteristics of nocturnal low-level jets over Ulsan airport. Asia-Pacific J. Atmos. Sci. 48, 181–189 (2012)
Chou, L.C., Chang, C.P., Williams, R.T.: A numerical simulation of the Mei-yu front and the associated low level jet. Mon. Weather Rev. 118(7), 1408–1428 (1990)
Darby, L.S., Allwine, K.J., Banta, R.M.: Nocturnal low-level jet in a mountain basin complex. Part II: Transport and diffusion of tracer under stable conditions. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 45(5), 740–753 (2006)
Du, Y., Zhang, Q.H., Ying, Y., Yang, Y.M.: Characteristics of low-level jets in Shanghai during the 2008–2009 warm seasons as inferred from wind profiler radar data. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan Ser II. 90(6), 891–903 (2012)
Du, Y., Zhang, Q.H., Chen, Y.L., Zhao, Y.Y., Wang, X.: Numerical simulations of spatial distributions and diurnal variations of low-level jets in China during early summer. J. Clim. 27(15), 5747–5767 (2014)
Du, Y., Rotunno, R.: A simple analytical model of the nocturnal low-level jet over the Great Plains of the United States. J. Atmos. Sci. 71, 3674–3683 (2014)
Du, Y., Chen, G.: Heavy rainfall associated with double low-level jets over southern China. Part I: Ensemble-based analysis. Mon. Wea. Rev. 146, 3827–3844 (2018)
Du, Y., Chen, G.X.: Heavy rainfalls associated with double low-level jets over southern China. Part II: Convection initiation. Mon. Wea. Rev. 147, 543–565 (2019a)
Du, Y., Chen, G.: Climatology of low-level jets and their impact on rainfall over southern China during early-summer rainy season. J. Climate 32, 8813–8833 (2019b)
Fast, J.D., Torcolini, J.C., Redman, R.: Pseudovertical temperature profiles and the urban heat island measured by a temperature datalogger network in Phoenix, Arizona. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 44, 3–13 (2005)
Fernando, H.J.S., Verhoef, B., Di Sabatino, S., Leo, L.S., Park, S.: The Phoenix evening transition flow experiment (TRANSFLEX). Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 147, 443–468 (2013)
Fiedler, S., Schepanski, K., Heinold, B., Knippertz, P., Tegen, I.: Climatology of nocturnal low-level jets over North Africa and implications for modeling mineral dust emission. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118(12), 6100–6121 (2013)
Finnigan, J.J., Clement, R., Malhi, Y., Leuning, R., Cleugh, H.A.: A re-evaluation of long-term flux measurement techniques. Part I: Averaging and coordinate rotation. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 107, 1–48 (2003)
Giannaros, T.M., Melas, D.: Study of the urban heat island in a coastal Mediterranean city: The case study of Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Res. 118, 103–120 (2012)
Guo, J.P., Miao, Y.C., Zhang, Y., Liu, H., Li, Z.Q., Zhang, W.C., He, J., Lou, M.Y., Yan, Y., Bian, L.G., Zhai, P.M.: The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in china derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 16(20), 13309–13319 (2016)
Hawkins, T.W., Brazel, A.J., Stefanov, W.L., Bigler, W., Saffell, E.M.: The role of rural variability in Urban Heat Island Determination for Pheonix, Arizona. J. Appl. Meteorol. 43, 476–486 (2004)
Helmis, C.G., Sgouros, G., Wang, Q.: On the vertical structure and spectral characteristics of the marine low-level jet. Atmos. Res. 152, 74–81 (2015)
Holt, T.R.: Mesoscale forcing of a boundary layer jet along the California coast. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 101(D2), 4235–4254 (1996)
Holton, J.R.: The diurnal boundary layer wind oscillation above sloping terrain. Tellus 19A, 199–205 (1967)
Hu, X.M., Klein, P.M., Xue, M., Zhang, F., Doughty, D.C., Forkel, R., Joseph, E., Fuentes, J.D.: Impact of the vertical mixing induced by low-level jets on boundary layer ozone concentration. Atmos. Environ. 70, 123–130 (2013a)
Hu, X.M., Klein, P.M., Xue, M., Lundquist, J.K., Zhang, F., Qi, Y.: Impact of low-level jets on the nocturnal urban heat island intensity in Oklahoma City. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 52(8), 1779–1802 (2013b)
Hu, X.M., Xue, M.: Influence of synoptic sea-breeze fronts on the urban heat island intensity in Dallas-Fort Worth, Texas. Mon. Wea. Rev. 144, 1487–1507 (2016)
Huang, L.P., Miao, J.F., Liu, Y.K.: Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of urban heat island in Tianjin. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 35(5), 620–632 (2012). ((in Chinese))
Jakobson, L., Vihma, T., Jakobson, E., Palo, T., Männik, A., Jaagus, J.: Low-level jet characteristics over the Arctic Ocean in spring and summer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 13(21), 11089–11099 (2013)
Ju, T.T., Wu, B.G., Wang, Z.Y., Liu, J.L., Chen, D.H., Zhang, H.S.: Relationships between low-level jet and low visibility associated with precipitation, air pollution, and fog in Tianjin. Atmosphere 11(11), 1197 (2020)
Ju, T.T., Wu, B.G., Zhang, H.S., Wang, Z.Y., Liu, J.L.: Impacts of boundary-layer structure and turbulence on the variations of PM2.5 during fog–haze episodes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 183, 469–493 (2022)
Karipot, A., Leclerc, M.Y., Zhang, G.: Characteristics of nocturnal low-level jets observed in the north Florida area. Mon. Weather Rev. 137(8), 2605–2621 (2009)
Kim, Y.-H., Baik, J.-J.: Spatial and temporal structure of the urban heat island in Seoul. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 44, 591–605 (2005)
Li, P.Y., Fu, G., Lu, C.G., Fu, D., Wang, S.: The formation mechanism of a spring sea fog event over the Yellow Sea associated with a low-level jet. Weather Forecast. 27(6), 1538–1553 (2012)
Li, D., Von Storch, H., Yin, B., Xu, Z., Qi, J., Wei, W., Guo, D.: Low-level jets over the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea: Climatology, variability, and the relationship with regional atmospheric circulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 123, 5240–5260 (2018a)
Li, H.D., Meier, F., Lee, X.H., Chakraborty, T., Liu, J.F., Schaap, M., Sodoudi, S.: Interaction between urban heat island and urban pollution island during summer in berlin. Sci. Total Environ. 636, 818–828 (2018b)
Li, X.L., Hu, X.M., Ma, Y.J., Wang, Y.F., Li, L.G., Zhao, Z.Q.: Impact of planetary boundary layer structure on the formation and evolution of air pollution episodes in Shenyang, Northeast China. Atmos. Environ. 214, 116850 (2019)
Lundquist, J.K., Mirocha, J.D.: Interaction of nocturnal low-level jets with urban geometries as seen in joint urban 2003 data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 47(1), 44–58 (2008)
Mahrt, L.: Nocturnal boundary-layer regimes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 88, 255–278 (1998)
Mahrt, L.: Stratified atmospheric boundary layers. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 90(3), 375–396 (1999)
Mahrt, L., Vickers, D.: Contrasting vertical structures of nocturnal boundary layers. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 105(2), 351–363 (2002)
Mahrt, L.: Variability and maintenance of turbulence in the very stable boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 135(1), 1–18 (2010)
Miao, S.G., Chen, F., Lemone, M.A., Tewari, M., Li, Q.C., Wang, Y.C.: An observational and modeling study of characteristics of urban heat island and boundary layer structures in Beijing. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 48, 484–501 (2009)
Miao, Y.C., Guo, J.P., Liu, S., Zhao, C., Li, X., Zhang, G., Wei, W., Ma, Y.: Impacts of synoptic condition and planetary boundary layer structure on the trans-boundary aerosol transport from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region to northeast China. Atmos. Environ. 181, 1–11 (2018)
Mohan, M., Kikegawa, Y., Gurjar, B.R., Bhati, S., Kolli, N.R.: Assessment of urban heat island effect for different land use–land cover from micrometeorological measurements and remote sensing data for megacity Delhi. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 112(3–4), 647–658 (2013)
Morris, C., Simmonds, I., Plummer, N.: Quantification of the influences of wind and cloud on the nocturnal urban heat island of a large city. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 40(2), 169–182 (1992)
Nichol, J.E., Fung, W.Y., Lam, K.S., Wong, M.S.: Urban heat island diagnosis using ASTER satellite images and ‘“in situ”’ air temperature. Atmos. Res. 94, 276–284 (2009)
Perdigón-Morales, J., Romero-Centeno, R., Ordoñez, P., Nieto, R., Gimeno, L., Barrett, B.S.: Influence of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on moisture transport by the Caribbean low level jet during the Midsummer Drought in Mexico. Atmos. Res. 248, 105243 (2021)
Ren, Y., Zhang, H.S., Wei, W., Wu, B.G., Liu, J.L., Cai, X.H., Song, Y.: Comparison of the turbulence structure during light and heavy haze pollution episodes. Atmos. Res. 230, 104645 (2019)
Roy, S., Sentchev, A., Schmitt, F.G., Augustin, P., Fourmentin, M.: Impact of the nocturnal low-level jet and orographic waves on turbulent motions and energy fluxes in the lower atmospheric boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 180, 527–542 (2021)
Ryu, Y.-H., Baik, J.-J.: Quantitative analysis of factors contributing to urban heat island intensity. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 51, 842–854 (2012)
Sai, H., Miao, J.F.: Spatial and temporal characteristics of low-level jet over the Bohai rim from the NCEP FNL global analysis data. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 38(5), 599–610 (2015). ((in Chinese))
Salmond, J.A.: Wavelet analysis of intermittent turbulence in a very stable nocturnal boundary layer: Implications for the vertical mixing of ozone. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 114, 463–488 (2005)
Shahgedanova, M., Burt, T.P., Davies, T.D.: Some aspects of the three-dimensional heat island in Moscow. Int. J. Climatol. 17, 1451–1465 (1997)
Steeneveld, G.J., Koopmans, S., Heusinkveld, B.G., van Hove, L.W.A., Holtslag, A.A.M.: Quantifying urban heat island effects and human comfort for cities of variable size and urban morphology in the Netherlands. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 116, D20129 (2011)
Stensrud, D.J.: Importance of low-level jets to climate: A review. J. Clim. 9(8), 1698–1711 (1996)
Stewart, I.D.: A systematic review and scientific critique of methodology in modern urban heat island literature. Int. J. Climatol. 31(2), 200–217 (2011)
Sullivan, J.T., Rabenhorst, S.D., Dreessen, J., Mcgee, T.J., Delgado, R., Twigg, L., Sumnicht, G.: Lidar observations revealing transport of O3 in the presence of a nocturnal low-level jet: Regional implications for “next-day” pollution. Atmos. Environ. 158, 160–171 (2017)
Tian, M., Wu, B.G., Huang, H., Zhang, H.S., Zhang, W.Y., Wang, Z.Y.: Impact of water vapor transfer on a Circum-Bohai-Sea heavy fog: Observation and numerical simulation. Atmos. Res. 229, 1–22 (2019)
Todd, M.C., Washington, R., Raghavan, S., Lizcano, G., Knippertz, P.: Regional model simulations of the Bodélé low-level jet of northern Chad during the Bodélé Dust Experiment (BoDEx 2005). J. Clim. 21(5), 995–1012 (2008)
Unger, J.: Heat island intensity with different meteorological conditions in a medium-sized town: Szeged, Hungary. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 54, 147–151 (1996)
Van de Wiel, B.J.H., Moene, A.F., Hartogensis, O.K., De Bruin, H.A.R., Holtslag, A.A.M.: Intermittent turbulence in the stable boundary layer over land. Part III: A classification for observations during CASES-99. J. Atmos. Sci. 60, 2509–2522 (2003)
Vickers, D., Mahrt, L.: Quality control and flux sampling problems for tower and aircraft data. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 14, 512–526 (1997)
Vindel, J.M., Yagüe, C.: Intermittency of turbulence in the atmospheric boundary layer: Scaling exponents and stratification influence. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 140, 73–85 (2011)
Wang, Y., Klipp, C.L., Garvey, D.M., Ligon, D.A., Calhoun, R.: Nocturnal low-level-jet-dominated atmospheric boundary layer observed by a doppler lidar over Oklahoma City during ju2003. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 46(12), 2098–2109 (2007)
Wang, D., Zhang, Y., Huang, A.: Climatic features of the south-westerly low-level jet over southeast china and its association with precipitation over east China. Asia-Pacific J. Atmos. Sci. 49, 259–270 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-013-0025-y
Wei, W., Wu, B.G., Ye, X.X., Wang, H.X., Zhang, H.S.: Characteristics and mechanisms of low-level jets in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 149(3), 403–424 (2013)
Wei, W., Zhang, H.S., Ye, X.X.: Comparison of low-level jets along the north coast of China in summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 119(16), 9692–9706 (2014)
Wei, W., Zhang, H.S., Wu, B.G., Huang, Y.X., Cai, X.H., Song, Y., Liu, J.L.: Intermittent turbulence contributes to vertical diffusion of PM2.5 in the North China Plain: Cases from Tianjin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 18, 12953–12967 (2018)
Werth, D., Kurzeja, R., Dias, N.L., Zhang, G., Duarte, H., Fischer, M., Parker, M., Leclerc, M.: The simulation of the southern Great Plains nocturnal boundary layer and the low-level jet with a high-resolution mesoscale atmospheric model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 50(7), 1497–1513 (2011)
Whiteman, C.D., Bian, X.D., Zhong, S.Y.: Low-level jet climatology from enhanced rawinsonde observations at a site in the southern Great Plains. J. Appl. Meteorol. 36(10), 1363–1376 (1997)
Wilczak, J.M., Oncley, S.P., Stage, S.A.: Sonic anemometer tilt correction algorithms. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 99, 127–150 (2001)
Wu, B. G., Li, Z. F., Ju, T. T., Zhang, H. S.: Characteristics of low-level jets during 2015–2016 and the effect on fog in Tianjin. Atmos. Res. 245(105102), 1–14 (2020)
Ye, X.X., Wu, B.G., Zhang, H.S.: The turbulent structure and transport in fog layers observed over the Tianjin area. Atmos. Res. 153, 217–234 (2015)
Zhang, L., Zhu, B., Gao, J.H., Kang, H.Q.: Impact of Taihu Lake on city ozone in the Yangtze River Delta. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 34, 226–234 (2017)
Zhang, F., Zhang, Q.H., Du, Y., Kong, H.: Characteristics of coastal low-level jets in the Bohai sea, China, during the early warm season. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 123, 13763–13774 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [42105084, 41675018], and the Bohai Rim Regional Science and Technology Collaborative Innovation Fund [QYXM202202].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, T., Wu, B., Li, Z. et al. Characteristics of Tower-Level Low-Level Jets and Their Impacts on the Urban Heat Island in Tianjin. Asia-Pac J Atmos Sci 59, 509–527 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-023-00331-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-023-00331-7