Abstract
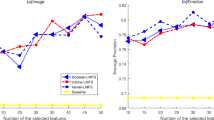
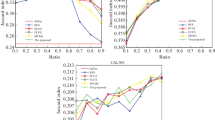
Multi-label learning deals with data associated with different labels simultaneously. Like traditional single-label learning, multi-label learning suffers from the curse of dimensionality as well. Feature selection is an efficient technique to improve learning efficiency with high-dimensional data. With the least square regression model, we incorporate feature manifold learning and sparse regularization into a joint framework for multi-label feature selection problems. The graph regularization is used to explore the feature geometric structure for gaining a better regression coefficient matrix which reflects the importance of varying features. Besides, the \(\ell _{2,1}\)-norm is imposed on the sparsity term to guarantee the sparsity of the regression coefficients. Furthermore, we design an iterative updating algorithm with proved convergence to tackle the aforementioned formulated problem. The proposed method is validated in six publicly available data sets from real-world applications. Finally, extensively experimental results demonstrate its superiority over the compared state-of-the-art multi-label feature selection methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belkin M, Niyogi P (2001) Laplacian eigenmaps and spectral techniques for embedding and clustering. NIPS 14:585–591
Bolón-Canedo V, Sánchez-Maroño N, Alonso-Betanzos A (2016) Feature selection for high-dimensional data. Prog Artif Intell 5(2):65–75
Boutell MR, Luo J, Shen X, Brown CM (2004) Learning multi-label scene classification. Pattern Recognit 37(9):1757–1771
Cai D, Zhang C, He X (2010) Unsupervised feature selection for multi-cluster data. In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, ACM, pp 333–342
Cai X, Nie F, Huang H (2013) Exact top-k feature selection via l2, 0-norm constraint. In: IJCAI
Chang X, Nie F, Yang Y, Huang H (2014) A convex formulation for semi-supervised multi-label feature selection. In: AAAI, pp 1171–1177
Chen W, Yan J, Zhang B, Chen Z, Yang Q (2007) Document transformation for multi-label feature selection in text categorization. In: Seventh IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM 2007), IEEE, pp 451–456
Chinnaswamy A, Srinivasan R (2016) Hybrid feature selection using correlation coefficient and particle swarm optimization on microarray gene expression data. In: Innovations in bio-inspired computing and applications, Springer, pp 229–239
Clare A, King RD (2001) Knowledge discovery in multi-label phenotype data. In: European Conference on Principles of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, Springer, pp 42–53
Demšar J (2006) Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J Mach Learn Res 7:1–30
Doquire G, Verleysen M (2011) Feature selection for multi-label classification problems. In: International work-conference on artificial neural networks, Springer, pp 9–16.
Dougherty J, Kohavi R, Sahami M et al (1995) Supervised and unsupervised discretization of continuous features. In: Machine learning: proceedings of the 12th international conference, vol. 12, pp 194–202
Dumais S, Platt J, Heckerman D, Sahami M (1998) Inductive learning algorithms and representations for text categorization. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on information and knowledge management, ACM, pp 148–155
Efron B, Hastie T, Johnstone I, Tibshirani R et al (2004) Least angle regression. Ann Stat 32(2):407–499
Elisseeff A, Weston J (2001) A kernel method for multi-labelled classification. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 14:681–687
Ghamrawi N, McCallum A (2005) Collective multi-label classification. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management, ACM, pp 195–200
Gharroudi O, Elghazel H, Aussem A (2014) A comparison of multi-label feature selection methods using the random forest paradigm. In: Canadian conference on artificial intelligence, pp 95–106
Godbole S, Sarawagi S (2004) Discriminative methods for multi-labeled classification. In: Pacific-Asia conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 22–30
Gu Q, Li Z, Han J (2011) Correlated multi-label feature selection. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management, ACM, pp 1087–1096
Gu Q, Zhou J (2009) Co-clustering on manifolds. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, ACM, pp 359–368
Guo S, Guo D, Chen L, Jiang Q (2016) A centroid-based gene selection method for microarray data classification. J Theor Biol 400:32–41
He X, Cai D, Niyogi P (2005) Laplacian score for feature selection. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 186:507–514
He X, Cai D, Yan S, Zhang HJ (2005) Neighborhood preserving embedding. In: 10th IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV’05), vol. 1, vol. 2, IEEE, pp 1208–1213
Ji S, Tang L, Yu S, Ye J (2010) A shared-subspace learning framework for multi-label classification. ACM Trans Knowl Discov Data (TKDD) 4(2):1–29
Jolliffe I (2002) Principal component analysis. Wiley Online Library
Jungjit S, Michaelis M, Freitas AA, Cinatl J (2013) Two extensions to multi-label correlation-based feature selection: a case study in bioinformatics. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics, IEEE, pp 1519–1524
Kohavi R, John GH (1997) Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artif Intell 97(1):273–324
Kong D, Ding C, Huang H, Zhao H (2012) Multi-label relieff and f-statistic feature selections for image annotation. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2012 IEEE conference on, IEEE, pp 2352–2359
Kong X, Philip SY (2012) gmlc: a multi-label feature selection framework for graph classification. Knowl Inf Syst 31(2):281–305
Lee J, Kim DW (2013) Feature selection for multi-label classification using multivariate mutual information. Pattern Recognit Lett 34(3):349–357
Lee J, Kim DW (2015) Fast multi-label feature selection based on information-theoretic feature ranking. Pattern Recognit 48(9):2761–2771
Lee J, Lim H, Kim D (2012) Approximating mutual information for multi-label feature selection. Electron Lett 48(15):929–930
Lin Y, Hu Q, Liu J, Duan J (2015) Multi-label feature selection based on max-dependency and min-redundancy. Neurocomputing 168:92–103
McCallum A (1999) Multi-label text classification with a mixture model trained by em. In: AAAI99 Workshop on Text Learning, pp 1–7
Nie F, Huang H, Cai X, Ding C (2010) Efficient and robust feature selection via joint \(\ell _{2,1}\)-norms minimization. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1813–1821
Nie F, Wang X, Jordan MI, Huang H (2016) The constrained laplacian rank algorithm for graph-based clustering. In: Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Citeseer
Nie F, Xiang S, Jia Y, Zhang C, Yan S (2008) Trace ratio criterion for feature selection. AAAI 2:671–676
Niyogi X (2004) Locality preserving projections. In: Neural information processing systems, vol. 16, MIT, pp 153–160
Read J (2008) A pruned problem transformation method for multi-label classification. In: Proc. 2008 New Zealand Computer Science Research Student Conference (NZCSRS 2008), pp 143–150
Read J, Pfahringer B, Holmes G, Frank E (2011) Classifier chains for multi-label classification. Mach Learn 85(3):333–359
Schapire RE, Singer Y (2000) Boostexter: a boosting-based system for text categorization. Mach Learn 39(2–3):135–168
Sharma A, Dehzangi A, Lyons J, Imoto S, Miyano S, Nakai K, Patil A (2014) Evaluation of sequence features from intrinsically disordered regions for the estimation of protein function. Plos One 9:2, e89, 890
Sharma A, Imoto S, Miyano S, Sharma V (2011) Null space based feature selection method for gene expression data. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 3(4):269–276
Sharma A, Koh CH, Imoto S, Miyano S (2011) Strategy of finding optimal number of features on gene expression data. Electron Lett 47(8):480–482
Sharma A, Paliwal KK, Imoto S, Miyano S (2014) A feature selection method using improved regularized linear discriminant analysis. Mach Vis Appl 25(25):775–786
Slavkov I, Karcheska J, Kocev D, Kalajdziski S, Dzeroski S (2013) Extending relieff for hierarchical multi-label classification. Mach Learn 4:1–13
Song L, Smola A, Gretton A, Bedo J, Borgwardt K (2012) Feature selection via dependence maximization. J Mach Learn Res 13(1):1393–1434
Spolaôr N, Cherman EA, Monard MC, Lee HD (2013) A comparison of multi-label feature selection methods using the problem transformation approach. Electron Notes Theor Comput Sci 292:135–151
Spolaôr N, Cherman EA, Monard MC, Lee HD (2013) Relieff for multi-label feature selection. In: Intelligent Systems (BRACIS), 2013 Brazilian Conference on, IEEE, pp 6–11
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 58(1):267–288
Trohidis K, Tsoumakas G, Kalliris G, Vlahavas IP (2008) Multi-label classification of music into emotions. ISMIR 8:325–330
Tsoumakas G, Katakis I, Vlahavas I (2011) Random k-labelsets for multilabel classification. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 23(7):1079–1089
Wang D, Nie F, Huang H (2015) Feature selection via global redundancy minimization. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(10):2743–2755
Wang FY (2016) Control 5.0: newton to merton in popper’s cyber-social-physical spaces. IEEE/CAA J Autom Sin 3(3):233–234
Wang FY, Wang X, Li L, Li L (2016) Steps toward parallel intelligence. IEEE/CAA J Autom Sin 3(4):345–348
Wang FY, Zhang JJ, Zheng X, Wang X, Yuan Y, Dai X, Zhang J, Yang L (2016) Where does alphago go: from church-turing thesis to alphago thesis and beyond. IEEE/CAA J Autom Sin 3(2):113–120
Wang S, Pedrycz W, Zhu Q, Zhu W (2015) Subspace learning for unsupervised feature selection via matrix factorization. Pattern Recognit 48(1):10–19
Wang S, Wang J, Wang Z, Ji Q (2014) Enhancing multi-label classification by modeling dependencies among labels. Pattern Recognit 47(10):3405–3413
Xiang S, Nie F, Meng G, Pan C, Zhang C (2012) Discriminative least squares regression for multiclass classification and feature selection. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(11):1738–1754
Yu K, Yu S, Tresp V (2005) Multi-label informed latent semantic indexing. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, ACM, pp 258–265
Yu Y, Pedrycz W, Miao D (2014) Multi-label classification by exploiting label correlations. Expert Syst Appl 41(6):2989–3004
Zhang M, Ding CH, Zhang Y Nie F (2014) Feature selection at the discrete limit. In: AAAI, pp 1355–1361
Zhang ML, Peña JM, Robles V (2009) Feature selection for multi-label naive bayes classification. Inf Sci 179(19):3218–3229
Zhang ML, Wu L (2015) Lift: Multi-label learning with label-specific features. Pattern Anal Mach Intell IEEE Trans 37(1):107–120
Zhang ML, Zhou ZH (2006) Multilabel neural networks with applications to functional genomics and text categorization. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 18(10):1338–1351
Zhang ML, Zhou ZH (2007) Ml-knn: a lazy learning approach to multi-label learning. Pattern Recognit 40(7):2038–2048
Zhang ML, Zhou ZH (2014) A review on multi-label learning algorithms. Knowl Data Eng IEEE Trans 26(8):1819–1837
Zhang Y, Zhou ZH (2010) Multilabel dimensionality reduction via dependence maximization. ACM Trans Knowl Discov Data (TKDD) 4(3):1–21
Zhu P, Zuo W, Zhang L, Hu Q, Shiu SCK (2015) Unsupervised feature selection by regularized self-representation. Pattern Recognit 48(2):438–446
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61379049 and 61379089.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Z., Zhu, W. Multi-label feature selection via feature manifold learning and sparsity regularization. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 9, 1321–1334 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0647-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0647-y