Abstract
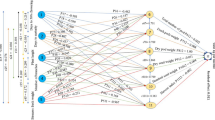
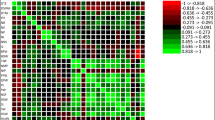
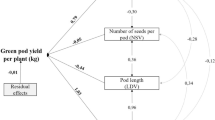
Cowpea as a low-input crop has a potential to significantly ameliorate poor nutrition and food insecurity in sub-Sahara Africa if problem of poor seed yield is addressed. Adequate information on the relationship between yield components and seed yield is, however, crucial for the development of better quality varieties to improve farmers’ field yield. To this end, twelve cowpea accessions of different seed sizes and mixed pedigrees were evaluated for two years in field trials of three replications laid out in a randomized complete block design. Data collected on plant vigour indices, yield components and seed yield were analyzed for variance components, Pearson correlation coefficient and structural equation modeling for path analysis. The accessions exhibited significant variation for all yield components including seed yield. In addition, the variance estimates indicated that substantial variations recorded were mostly genetic with high heritability values. Earliness in flowering and pod maturity recorded highly significant correlations and direct effect with yield components and seed yield. Positive correlation between precocity and high yield could be exploited in the development of improved varieties with early maturity for the savannah ecology with a characteristic short wet season. Importantly, all seed yield components are significantly correlated with each other and to total seed yield. Pods per plant, however, recorded highest coefficient values (r = 0.85; P < 0.001; 1.38**) for both Pearson correlation and path analysis, respectively, suggesting its importance as a yield component with highest direct effect on seed yield and should be a core selection index in cowpea breeding. The effect of size-number trade-off accounts for the counter-balance of direct effects of seeds per pod/plant (number) and seed weight (size) in cowpea and should be determined on genotype and/or seed size basis during selection. Plant vigour characters had no direct contribution to seed yield.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addae PC, Ishiyaku MF, Tignegre JB, Ba MN, Bationo JB, Atokple IDK, Abudulai M, Dabiré-Binso CL, Traore F, Saba M, Umar ML, Adazebra GA, Onyekachi FN, Nemeth MA, Huesing JE, Beach LR, Higgins TJV, Hellmich RL, Pittendrigh BR (2020) Efficacy of a cry1Ab gene for control of Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in cowpea (Fabales: Fabaceae). J Econ Entomol 113(2):974–979
Aliyu OM (2006) Phenotypic correlation and path coefficient analysis of nut yield and yield components in cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.). Silvae Genetica 55(1):19–25
Aliyu OM, Makinde BO (2016) Phenotypic analysis of seed yield and yield components in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). Plant Breed Biotechnol 4(2):252–261
Aliyu OM, Lawal OO, Wahab AA, Ibrahim UY (2019) Evaluation of advanced breeding lines of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) for high seed yield under farmers’ field conditions. Plant Breed Biotechnol 7(1):12–23
Allard RW (1960) Principles of plant breeding. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York, p 485
Animasaun DA, Oyedeji S, Azeez YK, Mustapha OT, Azeez MA (2015) Genetic variability study among ten cultivars of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp) using morpho-agronomic traits and nutritional composition. J Agric Sci 10(2):119–130
Bizeti HS, Portela de Carvalho CG, Pinto de Souza JR, Destro D (2004) Path analysis under multicollinearity in soybean. Braz Arch Biol Technol 47(5):669–676
Bolarinwa K, Ogunkanmi A, Ogundipe O, Oludare A, Amusa OD (2021) An investigation of cowpea production constraints and preferences among small holder farmers in Nigeria. GeoJournal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-021-10405-6
Burton GW (1952) Quantitative inheritance in grasses. Proc 6th Int Congr 1:277–283
Carey G (1998) Multiple regression and path analysis. http://ibgwww.colorado.edu/~carey/p7291dir/handouts/pathanal2.pdf. Accessed 13 June 2020
Chaudhary RR, Joshi BK (2005) Correlation and path coefficient analyses in sugarcane. Nepal Agric Res J 6:24–27
Cramer CS, Wehner TC (2000) Path analysis of the correlation between fruit number and plant traits of cucumber populations. HortScience 35:708–711
Dakora FD, Belane AK (2019) Evaluation of protein in edible cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) leaves and seeds. Front Sustain Food Syst. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2019.00070
Dempster ER, Lerner IM (1950) Heritability of threshold characters. Genetics 35:212–236
Dewey OR, Lu KH (1959) A correlation and path coefficient analysis of components of crested wheatgrass seed production. Agronomy J 57:515–518
Diouf D (2011) Recent advances in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) “omics” research for genetic improvement. Afr J Biotechnol 10(14):2803–2819
Drabo I, Redden R, Smithson JB, Aggarwal VD (1984) Inheritance of seed size in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.). Euphytica 33:929–934
Drabo I, Ladeinde TAO, Redden R, Smithson JB (1985) Inheritance of seed size and number per pod in cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.). Field Crops Res 11:335–344
Falconer DS (1989) Introduction to quantitative genetics. Longman Group UK, Harlow, Essex, p 438
Goncalves FV, Medici LO, Dan Fonseca MPS, Pimentel C, Gaziola SA, Azevedo RA (2020) Protein, phytate and minerals in grains of commercial cowpea genotypes. Ann Braz Acad Sci 92(1):e20180484
Hall AE, Cisse N, Thiaw S, Elawad HOA, Ehlers JD (2003) Development of cowpea cultivars and germplasm by Bean/Cowpea CRSP. Field Crop Res 82:103–134
Henshaw FO (2008) Varietal differences in physical characteristics and proximate composition of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). World J Agric Sci 4(3):302–306
Johnson AW, Robinson HF, Comstock RE (1955) Estimates of genetic and environmental variability in soyabean. Agron J 47:314–318
Kebede E, Bekeko Z (2020) Expanding the production and importance of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) in Ethiopia. Congent Food Agric 6(1):1769805. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311932.2020.1769805
Manggoel W, Uguru MI, Ndam ON, Dasbak MA (2012) Genetic variability, correlation and path coefficient analysis of some yield components of ten cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp) accessions. J Plant Breed Crop Sci 4(5):80–86
Mekonnen G, Sharma JJ, Negatu LW, Tana T (2016) Growth and yield response of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) to integrated use of planting pattern and herbicide mixtures in Wollo, Northern Ethiopia. Adv Crop Sci Tech 4(6):245. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-8863.1000245
Mortimore MJ, Singh BB, Harris F, Blade SF (1997) Cowpea in traditional cropping systems. In: Singh BB, Mohan Raj DR, Dashiel KE, Jackai LEN (eds) Advance in Cowpea Research. International Institute of Tropical Agricultural (IITA) and Japan International Research Centre for Agricultural Sciences (JIRCAS), IITA, Ibadan, Nigeria, p 113
Nielson S, Ohler T, Mitchell C (1997) Cowpea leaves for human consumption: production, utilization and nutrient composition. In: Singh SR, Rachie KO (eds) Cowpea research, production and utilization. Wiley, New York, pp 145–162
Nwosu DJ, Olatunbosun BD, Adetiloye IS (2013) Genetic variability, heritability and genetic advance in cowpea genotypes in two agro-ecological environments. Greener J Biol Sci 3(5):202–207
Ogunbodede BA (1989) Comparison between three methods of determining the relationships between yield and eight of its components in cowpea, Vigna unguiculata L. Walp. Sci Hortic 38:201–205
Omoigu LO, Ishiyaku MF, Kamara AY, Alabi SO, Mohammed SG (2006) Genetic variability and heritability studies of some reproductive traits in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.). Afr J Biotechnol 5(13):1191–1195
Peksen A (2004) Fresh pod yield and some pod characteristics of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) genotypes from Turkey. Asian J Plant Sci 3(3):269–273
Rachie KO, Roberts LM (1974) Grain legumes of the lowland tropics. Adv Agron 26:1–132
Santos A, Ceccon G, Davide LMC, Correa AM, Alves VB (2014) Correlation and path analysis of yield components in cowpea. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 14:82–87
Sapara GK, Javia RM (2014) Correlation and path analysis in vegetable cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.). Int J Plant Sci 9(1):138–141
Sharma M, Sharma PP, Upadhyay B, Bairwa HL (2016) Study of correlation coefficient and path analysis in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) germplasm line. Int J Dev Res 6(8):9011–9016
Singh RK, Chaudhary BD (1977) Path Analysis. In: Singh RK, Chaudhary BD (eds) Biometrical methods in quantitative genetic analysis. Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi, India, pp 70–79
Singh R, Joshi BS, Singh S (1982) Correlation studies in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.). Trop Grain Legume Bull 26(6):3–5
Srinivas J, Kale VS, Nagre PK (2017) Correlation and path analysis study in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) genotypes. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 6(6):3305–3313
Stata Corp. 4905 Lakeway Dr, College Station, TX 77845, Texas. www.stata.com
Uarrota VG (2010) Response of cowpea (V. unguiculata L. Walp) to water stress and phosphorus fertilization. J Agron 9(3):87–91
Udensi O, Ikpeme EV, Edu EA, Ekpe DE (2012) Relationship studies in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) landraces grow under humid lowland condition. Int J Agric Res 7(1):33–45
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Mr. Omotayo Jimoh, Mr. Usman Mohammed and Mr. Ismail Idris for their support in the field management and data collection during this study. Technical support of Mr. Wasiu Ibrahim of Department of Statistics and Mathematical Sciences, Kwara State University, Malete, for the path analysis is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aliyu, O.M., Tiamiyu, A.O., Usman, M. et al. Variance components, correlation and path analyses in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L., Walp). J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 25, 173–182 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-021-00121-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-021-00121-5