Abstract
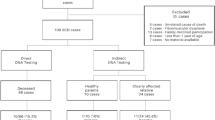
Currently, no standardized system exists for evaluating and testing at-risk family members of decedents with abnormal post-mortem genetic testing in cases of sudden unexpected death (SUD). The goal of this study was to evaluate the outcomes of referrals made by an urban medical examiner’s office to a multi-disciplinary cardiogenetics clinic. Relatives of decedents with pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants or variants of unknown significance (VUS) in genes known to be associated with cardiomyopathies and/or arrhythmias were identified by the New York City Office of Chief Medical Examiner and referred to the Cardiogenetics Clinic at Montefiore Medical Center. Familial referrals of 15 decedents (median 15 years, range 2 days to 57 years) were evaluated. Variants in 13 genes were identified among decedents (9 arrhythmia, 5 cardiomyopathy). P/LP variants were identified in both arrhythmia (RYR2, SCN5A) and cardiomyopathy syndrome (MYBPC3 (2), MYH7) genes. Thirty-two family members were referred, and 14 variants were detected. One pathogenic (MYBPC3) and two likely pathogenic (RYR2, MYH7) mutations were identified. Referral of at-risk family members of decedents who experienced SUD based on informative post-mortem genetic testing for cardiac and genetic evaluation is warranted, as family studies help to reclassify variants and prevent additional sudden death.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Zeitone A, Peterson DR, Polonsky B, McNitt S, Moss AJ (2014) Efficacy of different beta-blockers in the treatment of long QT syndrome. Jacc 64:1352–1358
Ackerman MJ (2009) State of postmortem genetic testing known as the cardiac channel molecular autopsy in the forensic evaluation of unexplained sudden cardiac death in the young. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 32(Suppl 2):S86-89
Ackerman MJ, Priori SG, Willems S, Berul C, Brugada R, Calkins H, Camm aJ, Ellinor PT, Gollob M, Hamilton R, Hershberger RE, Judge DP, Le Marec H, McKenna WJ, Schulze-Bahr E, Semsarian C, Ja Towbin, Watkins H, Wilde A, Wolpert C, Zipes DP (2011) HRS/EHRA expert consensus statement on the state of genetic testing for the channelopathies and cardiomyopathies: this document was developed as a partnership between the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) and the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA). Heart Rhythm 8:1308–1339
Basso C, Aguilera B, Banner J, Cohle S, d’Amati G, de Gouveia RH, di Gioia C, Fabre A, Gallagher PJ, Leone O, Lucena J, Mitrofanova L, Molina P, Parsons S, Rizzo S, Sheppard MN, Mier MPS, Kim Suvarna S, Thiene G, van der Wal A, Vink A, Michaud K (2017) Guidelines for autopsy investigation of sudden cardiac death: 2017 update from the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology. Virchows Archiv International Journal of Pathol 471:691–705
Behr E, Wood DA, Wright M, Syrris P, Sheppard MN, Casey A, Davies MJ, McKenna W (2003) Cardiological assessment of first-degree relatives in sudden arrhythmic death syndrome. Lancet 362:1457–1459
Boczek NJ, Tester DJ, Ackerman MJ (2012) The molecular autopsy: an indispensable step following sudden cardiac death in the young? Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol 23:167–173
Chugh SS, Senashova O, Watts A, Tran PT, Zhou Z, Gong Q, Titus JL, Hayflick SJ (2004) Postmortem molecular screening in unexplained sudden death. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:1625–1629
di Gioia CR, Autore C, Romeo DM, Ciallella C, Aromatario MR, Lopez A, Pagannone E, Giordano C, Gallo P, d’Amati G (2006) Sudden cardiac death in younger adults: autopsy diagnosis as a tool for preventive medicine. Hum Pathol 37:794–801
Erskine KE, Hidayatallah NZ, Walsh CA, McDonald TV, Cohen L, Marion RW, Dolan SM (2014) Motivation to pursue genetic testing in individuals with a personal or family history of cardiac events or sudden cardiac death. J Genet Couns 23:849–859
Farrugia A, Keyser C, Hollard C, Raul JS, Muller J, Ludes B (2015) Targeted next generation sequencing application in cardiac channelopathies: analysis of a cohort of autopsy-negative sudden unexplained deaths. Forensic Sci Int 254:5–11
Fellmann F, van El CG, Charron P, Michaud K, Howard HC, Boers SN, Clarke AJ, Duguet AM, Forzano F, Kauferstein S, Kayserili H, Lucassen A, Mendes Á, Patch C, Radojkovic D, Rial-Sebbag E, Sheppard MN, Tassé AM, Temel SG, Sajantila A, Basso C, Wilde AAM, Cornel MC (2019) European recommendations integrating genetic testing into multidisciplinary management of sudden cardiac death. Eur J Hum Genet 27:1763–1773
Gimeno JR, Lacunza J, García-Alberola A, Cerdán MC, Oliva MJ, García-Molina E, López-Ruiz M, Castro F, González-Carrillo J, de la Morena G, Valdés M (2009) Penetrance and risk profile in inherited cardiac diseases studied in a dedicated screening clinic. Am J Cardiol 104:406–410
Hershberger RE, Givertz MM, Ho CY, Judge DP, Kantor PF, McBride KL, Morales A, Taylor MRG, Vatta M, Ware SM (2018) Genetic evaluation of cardiomyopathy: a clinical practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet Med 20:899–909
Hofman N, Tan HL, Alders M, Kolder I, de Haij S, Mannens MM, Lombardi MP, Dit Deprez RH, van Langen I, Wilde AA (2013) Yield of molecular and clinical testing for arrhythmia syndromes: report of 15 years’ experience. Circulation 128:1513–1521
Kumar S, Peters S, Thompson T, Morgan N, Maccicoca I, Trainer A, Zentner D, Kalman JM, Winship I, Vohra JK (2013) Familial cardiological and targeted genetic evaluation: low yield in sudden unexplained death and high yield in unexplained cardiac arrest syndromes. Heart Rhythm 10:1653–1660
Lahrouchi N, Behr ER, Bezzina CR (2016) Next-generation sequencing in post-mortem genetic testing of young sudden cardiac death cases. Front Cardiovasc Med 3:13
Lin Y, Williams N, Wang D, Coetzee W, Zhou B, Eng LS, Um SY, Bao R, Devinsky O, McDonald TV, Sampson BA, Tang Y (2017) Applying high-resolution variant classification to cardiac arrhythmogenic gene testing in a demographically diverse cohort of sudden unexplained deaths. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 10(6):e001839
McGorrian C, Constant O, Harper N, O’Donnell C, Codd M, Keelan E, Green A, O’Neill J, Galvin J, Mahon NG (2013) Family-based cardiac screening in relatives of victims of sudden arrhythmic death syndrome. Europace 15:1050–1058
Priori SG, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J, Elliott PM, Fitzsimons D, Hatala R, Hindricks G, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen K, Kuck KH, Hernandez-Madrid A, Nikolaou N, Norekval TM, Spaulding C, Van Veldhuisen DJ (2015) 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: the Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Europace 17:1601–1687
Scheiper-Welling S, Tabunscik M, Gross TE, Jenewein T, Beckmann BM, Niess C, Gradhand E, Wunder C, Schneider PM, Rothschild MA, Verhoff MA, Kauferstein S (2022) Variant interpretation in molecular autopsy: a useful dilemma. Int J Legal Med 136:475–482
Semsarian C, Ingles J (2016) Molecular autopsy in victims of inherited arrhythmias. J Arrhythm 32:359–365
Semsarian C, Ingles J, Wilde AA (2015) Sudden cardiac death in the young: the molecular autopsy and a practical approach to surviving relatives. Eur Heart J 36:1290–1296
Skinner JR, Crawford J, Smith W, Aitken A, Heaven D, Evans CA, Hayes I, Neas KR, Stables S, Koelmeyer T, Denmark L, Vuletic J, Maxwell F, White K, Yang T, Roden DM, Leren TP, Shelling A, Love DR (2011) Prospective, population-based long QT molecular autopsy study of postmortem negative sudden death in 1 to 40 year olds. Heart Rhythm 8:412–419
Steinberg C, Padfield GJ, Champagne J, Sanatani S, Angaran P, Andrade JG, Roberts JD, Healey JS, Chauhan VS, Birnie DH, Janzen M, Gerull B, Klein GJ, Leather R, Simpson CS, Seifer C, Talajic M, Gardner M, Krahn AD (2016) Cardiac abnormalities in first-degree relatives of unexplained cardiac arrest victims: a report from the cardiac arrest survivors with preserved ejection fraction registry. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 9(9):e004274
Stiles MK, Wilde AAM, Abrams DJ, Ackerman MJ, Albert CM, Behr ER, Chugh SS, Cornel MC, Gardner K, Ingles J, James CA, Jimmy Juang JM, Kääb S, Kaufman ES, Krahn AD, Lubitz SA, MacLeod H, Morillo CA, Nademanee K, Probst V, Saarel EV, Sacilotto L, Semsarian C, Sheppard MN, Shimizu W, Skinner JR, Tfelt-Hansen J, Wang DW (2021) 2020 APHRS/HRS expert consensus statement on the investigation of decedents with sudden unexplained death and patients with sudden cardiac arrest, and of their families. Heart Rhythm 18:e1–e50
Tan HL, Hofman N, van Langen IM, van der Wal AC, Wilde AA (2005) Sudden unexplained death: heritability and diagnostic yield of cardiological and genetic examination in surviving relatives. Circulation 112:207–213
Tester DJ, Ackerman MJ (2012) The molecular autopsy: should the evaluation continue after the funeral? Pediatr Cardiol 33:461–470
Tester DJ, Medeiros-Domingo A, Will ML, Haglund CM, Ackerman MJ (2012) Cardiac channel molecular autopsy: insights from 173 consecutive cases of autopsy-negative sudden unexplained death referred for postmortem genetic testing. Mayo Clin Proc 87:524–539
van der Werf C, Onderwater AT, van Langen IM, Smets EM (2014) Experiences, considerations and emotions relating to cardiogenetic evaluation in relatives of young sudden cardiac death victims. Eur J Hum Genet : EJHG 22:192–196
Wang D, Shah KR, Um SY, Eng LS, Zhou B, Lin Y, Mitchell AA, Nicaj L, Prinz M, McDonald TV, Sampson BA, Tang Y (2014) Cardiac channelopathy testing in 274 ethnically diverse sudden unexplained deaths. Forensic Sci Int 237:90–99
Wellens HJ, Schwartz PJ, Lindemans FW, Buxton AE, Goldberger JJ, Hohnloser SH, Huikuri HV, Kääb S, La Rovere MT, Malik M, Myerburg RJ, Simoons ML, Swedberg K, Tijssen J, Voors AA, Wilde AA (2014) Risk stratification for sudden cardiac death: current status and challenges for the future. Eur Heart J 35:1642–1651
Wilde AAM, Semsarian C, Márquez MF, Sepehri Shamloo A, Ackerman MJ, Ashley EA, Sternick EB, Barajas-Martinez H, Behr ER, Bezzina CR, Breckpot J, Charron P, Chockalingam P, Crotti L, Gollob MH, Lubitz S, Makita N, Ohno S, Ortiz-Genga M, Sacilotto L, Schulze-Bahr E, Shimizu W, Sotoodehnia N, Tadros R, Ware JS, Winlaw DS, Kaufman ES, Aiba T, Bollmann A, Choi JI, Dalal A, Darrieux F, Giudicessi J, Guerchicoff M, Hong K, Krahn AD, MacIntyre C, Mackall JA, Mont L, Napolitano C, Ochoa JP, Peichl P, Pereira AC, Schwartz PJ, Skinner J, Stellbrink C, Tfelt-Hansen J, Deneke T (2022) European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA)/Heart Rhythm Society (HRS)/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS)/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS) Expert consensus statement on the state of genetic testing for cardiac diseases. Heart Rhythm 19:e1–e60
Williams N, Manderski E, Stewart S, Bao R, Tang Y (2020) Lessons learned from testing cardiac channelopathy and cardiomyopathy genes in individuals who died suddenly: a two-year prospective study in a large medical examiner’s office with an in-house molecular genetics laboratory and genetic counseling services. J Genet Couns 29:293–302
Yeates L, Hunt L, Saleh M, Semsarian C, Ingles J (2013) Poor psychological wellbeing particularly in mothers following sudden cardiac death in the young. Eur J Cardiovasc 12:484–491
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TS: data collection and analysis, first draft of the manuscript.
NW, BS, YT: assistance with patient identification, data analysis.
MS, RB, TM, CW: data collection and analysis, final approval of the manuscript.
BC: data analysis, revision of the manuscript, senior author.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Siskind, T., Williams, N., Sebastin, M. et al. Genetic screening of relatives of decedents experiencing sudden unexpected death: medical examiner’s office referrals to a multi-disciplinary cardiogenetics program. J Community Genet 13, 629–639 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12687-022-00611-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12687-022-00611-1