Abstract
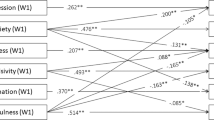
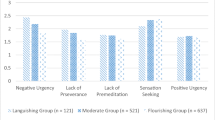
Two studies examined the correlational relationships between self-reported mindfulness and impulsivity in samples of 347 and 227 university students. Using multidimensional measures of both mindfulness and impulsivity, results from both studies indicate that several aspects of mindfulness are negatively correlated with elements of impulsivity, even after controlling for trait-level negative affect in Study 1 and current general distress in Study 2. However, the relationships between different facets of mindfulness and types of impulsivity varied in strength and significance level. These results suggest that mindfulness skills may be related to the ability to refrain from maladaptive impulsive behavior in the presence of negative affect or distress and that specific mindfulness skills may be most helpful in addressing different types of impulsive behaviors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Hopkins, J., Krietemeyer, J., & Toney, L. (2006). Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment, 13, 27–45.
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Lykins, E., Button, D., Krietemeyer, J., Sauer, S., et al. (2008). Construct validity of the five-facet mindfulness questionnaire in meditating and nonmeditating samples. Assessment, 15, 329–342.
Bagge, C., Nickell, A., Stepp, S., Durrett, C., Jackson, K., & Trull, T. J. (2004). Borderline personality disorder features predict negative outcomes 2 years later. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 113, 279–288.
Barratt, E. S. (1993). Impulsivity: Integrating cognitive, behavioral, biological and environmental data. In: McCowan, W., Johnson, J. & Shure, M. The impulsive client: theory, research, and treatment. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Bornovalova, M. A., Lejuez, C. W., Daughters, S. B., Zachary Rosenthal, M., & Lynch, T. R. (2005). Impulsivity as a common process across borderline personality and substance use disorders. Clinical Psychology Review, 25, 790–812.
Brown, K. W., & Ryan, R. M. (2003). The benefits of being present: Mindfulness and its role in psychological well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84, 822–848.
Chapman, A. L., Gratz, K. L., & Brown, M. Z. (2006). Solving the puzzle of deliberate self-harm: The experiential avoidance model. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 44, 371–394.
Cyders, M. A., & Smith, G. T. (2010). Longitudinal validation of the urgency traits over the first year of college. Journal of Personality Assessment, 92, 63–69.
Dickman, S. J. (1990). Functional and dysfunctional impulsivity: Personality and cognitive correlates. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 58, 95–102.
Dimeff, L. A., & Koerner, K. (Eds.). (2007). Dialectical behavior therapy in clinical practice: Applications across disorders and settings. New York: Guilford.
Dom, G., De Wilde, B., Hulstijn, W., & Sabbe, B. (2007). Dimensions of impulsive behaviour in abstinent alcoholics. Personality and Individual Differences, 42, 465–476.
Eysneck, S. B., & Eysneck, H. J. (1977). The place of impulsiveness in a dimensional system of personality description. The British Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 16, 57–68.
Hayes, S. C., Wilson, K. G., Gifford, E. V., Follette, V. M., & Strosahl, K. (1996). Experimental avoidance and behavioral disorders: A functional dimensional approach to diagnosis and treatment. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 64, 1152–1168.
Linehan, M. M. (1993). Cognitive-behavioral treatment of borderline personality disorder. New York: The Guilford Press.
Lovibond, S. H., & Lovibond, P. F. (1993). Manual for the depression anxiety stress scales (DASS), Psychology Foundation Monograph. New South Wales: University of New South Wales.
Lovibond, P. F., & Lovibond, S. H. (1995). The structure of negative emotional states: Comparison of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales with the Beck Depression and Anxiety Inventories. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 33, 335–343.
Lynam, D., Smith, G. T., Cyders, M. A., Fisher, S. & Whiteside, S. A. (2007). The UPPS-P: A multidimensional measure of risk for impulsive behavior. Unpublished technical report.
Lynch, T. R., Trost, W. T., Salsman, N., & Linehan, M. M. (2007). Dialectical behavior therapy for borderline personality disorder. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 3, 181–205.
McCrae, R. R., & Costa, P. T., Jr. (1990). Personality in adulthood. New York: Guilford.
Patton, J. H., Stanford, M. S., & Barratt, E. S. (1995). Factor structure of the Barratt Impulsivity Scale. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 51, 768–774.
Reynolds, B., Ortengren, A., Richards, J. B., & de Wit, H. (2006). Dimensions of impulsive behavior: Personality and behavioral measures. Personality and Individual Differences, 40, 305–315.
Robins, C. J., & Chapman, A. L. (2004). Dialectical behavior therapy: Current status, recent developments, and future directions. Journal of Personality Disorders, 18, 73–89.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2000). Using multivariate statistics. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 1063–1070.
Whiteside, S. P., & Lynam, D. R. (2001). The Five Factor Model and impulsivity: Using a structural model of personality to understand impulsivity. Personality and Individual Differences, 30, 669–689.
Whiteside, S. P., Lynam, D. R., Miller, J. D., & Reynolds, S. K. (2005). Validation of the UPPS impulsive behaviour scale: A four-factor model of impulsivity. European Journal of Personality, 19, 559–574.
Wingrove, J., & Bond, A. J. (1997). Impulsivity: A state as well as trait variable. Does mood awareness explain low correlations between trait and behavioural measures of impulsivity? Personality and Individual Differences, 22, 333–339.
Wupperman, P., Neumann, C. S., & Axelrod, S. R. (2008). Do deficits in mindfulness underlie borderline personality features and core difficulties? Journal of Personality Disorders, 25, 466–482.
Young, S. (2005). Coping strategies used by adults with ADHD. Personality and Individual Differences, 38, 809–816.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, J.R., Erisman, S.M., Upton, B.T. et al. A Preliminary Investigation of the Relationships Between Dispositional Mindfulness and Impulsivity. Mindfulness 2, 228–235 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-011-0065-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-011-0065-2