Abstract
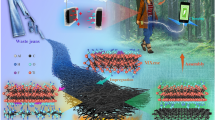
A nanosized architectural (a spider’s web) structure of cellulose (Iα) was extracted from green seaweed Chaetomorpha antennina through bleaching treatment. Furthermore, reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and zinc oxide (ZnO) nanowires were deposited over seaweed cellulose while using a simple hydrothermal method. A simple press method was used to prepare rGO-ZnO seaweed cellulose nanocomposite for the paper supercapacitor. This rGO-ZnO seaweed cellulose paper anode material was characterized by using various analytical techniques such as FT-IR, SEM, TGA, XRD, and tensile tests. XRD peaks reveal that graphene oxide powder when mixed with seaweed cellulose got reduced and gave XRD peak of reduced graphene oxide (rGO). In this paper, supercapacitors were tested in CV, GCD, and EIS. From GCD, the specific energy density of the ZnO-cellulose paper device is found to be 0.00066 Wh/kg whereas, for the rGO-ZnO cellulose, paper device gives a greater energy density of 5.21 Wh/kg. From EIS, the series resistance of ZnO-cellulose is found as 326 Ω and for ZnO-rGO-cellulose as 2.16 Ω. This marine resources based rGO-ZnO seaweed cellulose paper supercapacitor has application in various energy storage domains including electric vehicles and electronic industries as it is bio-degradable, cost-effective, thinnest, bearing high performance, and safe for getting used.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the articels.
References
Sultana, M.A. Wahab, M. Nahiduzzaman, M. Mohiuddin, M.Z. Iqbal, A. Shakil, A. Al Manun , M.S.R. Khan, L. Wong, M. Asaduzzaman (2022). Seaweed farming for food and nutritional security, climate change mitigation and adaptation, and women empowerment: a review. Aquaculture and Fisheries (2022)
A. K. Siddhanta, M.U. Chhatbar, G.K. Mehta, N.D. Sanandiya, S. Kumar, M.D. Oza, P. Kamlesh, R. Meena The cellulose contents of Indian seaweeds. Journal of applied phycology, 23(5) (2011) 919–923
Bhutiya, P. L., Misra, N., Rasheed, M. A., & Hasan, S. Z. (2018). Nested seaweed cellulose fiber deposited with cuprous oxide nanorods for antimicrobial activity. International journal of biological macromolecules., 117, 435–444.
Missoum, K., & Belgacem, M. N. (2013). J. Bras. Nanofibrillated cellulose surface modification: A review. Materials, 6(5), 1745–1766.
Moon, R. J., Martini, A., Nairn, J., Simonsen, J., & Youngblood, J. (2011). Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chemical Society Reviews, 40(7), 3941–3994.
Mihranyan, A. (2011). Cellulose from cladophorales green algae: From environmental problem to high-tech composite materials. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 119(4), 2449–2460.
Gustafsson, S., Lordat, P., Hanrieder, T., Asper, M., Schaefer, O., & Mihranyan, A. (2016). Mille-feuille paper: a novel type of filter architecture for advanced virus separation applications. Materials Horizons, 3(4), 320–327.
Bhutiya, P. L., Misra, N., Rasheed, M. A., & Hasan, S. Z. (2020). Silver nanoparticles deposited algal nanofibrous cellulose sheet for antibacterial activity. BioNanoScience, 10(1), 23–33.
Durairaj, A., Maruthapandi, M., Saravanan, A., Luong, J. H., & Gedanken, A. (2020). Cellulose nanocrystals (CNC)-based functional materials for supercapacitor applications. Nanomaterials, 12(11), 1828.
Jiang, L., Han, S. O., Pirie, M., Kim, H. N., Seong, Y. H., Kim, H., & Foord, J. S. (2021). Seaweed biomass waste-derived carbon as an electrode material for supercapacitor. Energy & Environment, 32(6), 1117–1129.
Jose, J., Thomas, V., Vinod, V., Abraham, R., & Abraham, S. (2019). Nanocellulose based functional materials for supercapacitor applications. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices, 4(3), 333–340.
Tafete, G. A., Abera, M. K., & Thothadri, G. (2022). Review on nanocellulose-based materials for supercapacitors applications. Journal of Energy Storage, 48(2022), 103938.
Wang, Z., Tammela, P., Strømme, M., & Nyholm, L. (2017). Cellulose-based supercapacitors: Material and performance considerations. Advanced Energy Materials, 7(18), 1700130.
Rabani, I., Yoo, J., Bathula, C., Hussain, S., & Seo, Y. S. (2021). The role of uniformly distributed ZnO nanoparticles on cellulose nanofibers in flexible solid state symmetric supercapacitors. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 9(19), 11580–11594.
Hussain, S. Z., Ihrar, M., Hussain, S. B., Oh, W. C., & Ullah, K. (2020). A review on graphene based transition metal oxide composites and its application towards supercapacitor electrodes. SN Applied Sciences, 2(4), 1–23.
Abdah, M. A. A. M., Azman, N. H. M., Kulandaivalu, S., & Sulaiman, Y. Y. (2020). Review of the use of transition-metal-oxide and conducting polymer-based fibres for high-performance supercapacitors. Materials & Design, 186, 108199.
Zhou, S., Kong, X., Zheng, B., Huo, F., Strømme, M., & Xu, C. (2019). Cellulose nanofiber@ conductive metal–organic frameworks for high-performance flexible supercapacitors. ACS Nano, 13(8), 9578–9586.
Etana, B. B., Ramakrishnan, S., Dhakshnamoorthy, M., Saravanan, S., Ramamurthy, P. C., & Demissie, T. A. (2020). Functionalization of textile cotton fabric with reduced graphene oxide/MnO2/polyaniline based electrode for supercapacitor. Materials Research Express, 6(12), 125708.
Wang, K., Gao, S., Du, Z., Yuan, A., Lu, W., & Chen, L. (2016). MnO2-Carbon nanotube composite for high-areal-density supercapacitors with high rate performance. Journal of Power Sources, 305, 30–36.
Saranya, M., Ramachandran, R., & Wang, F. (2016). Graphene-zinc oxide (G-ZnO) nanocomposite for electrochemical supercapacitor applications. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices, 1(4), 454–460.
Xiang, Z., Gao, W., Chen, L., Lan, W., Zhu, J. Y., & Runge, T. (2016). A comparison of cellulose nanofibrils produced from Cladophora glomerata algae and bleached eucalyptus pulp. Cellulose, 23(1), 493–503.
Bhutiya, P. L., Mahajan, M. S., Rasheed, M. A., Pandey, M., Hasan, S. Z., & Misra, N. (2018). Zinc oxide nanorod clusters deposited seaweed cellulose sheet for antimicrobial activity. International journal of biological macromolecules, 112, 1264–1271.
Chauhan, I., Aggrawal, S., & Mohanty, P. (2015). ZnO nanowire-immobilized paper matrices for visible light-induced antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli. Environmental Science: Nano, 2(3), 273–279.
Kuzmenko, V., Wang, N., Haque, M., Naboka, O., Flygare, M., Svensson, K., Gatenholm, P., Liu, J., & Enoksson, P. (2017). Cellulose-derived carbon nanofibers/graphene composite electrodes for powerful compact supercapacitors. RSC advances, 7(73), 45968–45977.
Zhou, S., Kong, X., Zheng, B., Huo, F., Strømme, M., & Xu, C. (2019). Cellulose nanofiber@ conductive metal–organic frameworks for high-performance flexible supercapacitors. Acs Nano, 13(8), 9578–9586.
Liu, G., Wang, L., Wang, B., Gao, T., & Wang, D. (2015). A reduced graphene oxide modified metallic cobalt composite with superior electrochemical performance for supercapacitors. RSC Advances, 5(78), 63553–63560.
Liewhiran, C., Seraphin, S. A., & S. (2006). Phanichphant Synthesis of nano-sized ZnO powders by thermal decomposition of zinc acetate using Broussonetia papyrifera(L.) Vent pulp as a dispersant. Current Applied Physics, 6(3), 499–502.
Johra, F. T., & Jung, W. G. (2015). Hydrothermally reduced graphene oxide as a supercapacitor. Applied Surface Science, 357, 1911–1914.
Reddy, K. O., Maheswari, C. U., & Shukla, M. (2013). Physico-chemical characterization of cellulose extracted from ficus leaves. Journal of Biobased Materials and Bioenergy, 7(4), 496–499.
Gong, Y., Li, D., Fu, Q., & Pan, C. (2015). Influence of graphene microstructures on electrochemical performance for supercapacitors. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 25(5), 379–385.
Kumar, R., Singh, R., Gurjar, A., Kashyap, R., Kumar, M., & Kumar, D. (2019). Study the thermal stability of functionalized graphene oxide. In AIP Conference Proceedings, AIP Publishing LLC, 2142(1), 040015.
Cui, P., Lee, J., Hwang, E., & Lee, H. (2011). One-pot reduction of graphene oxide at subzero temperatures. Chemical Communications, 47(45), 12370–12372.
Magar, H. S., Hassan, R. Y., & Mulchandani, A. (2021). Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS): Principles, construction, and biosensing applications. Sensors, 21(19), 6578.
Wan, C., Jiao, Y., & Li, J. (2017). Flexible, highly conductive, and free-standing reduced graphene oxide/polypyrrole/cellulose hybrid papers for supercapacitor electrodes. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 5(8), 3819–3831.
Ikram, M., Haider, A., Bibi, S. T., Ul-Hamid, A., Haider, J., Shahzadi, I., Nabgan, W., Moeen, S., Ali, S., Goumri-Said, S., & Kanoun, M. B. (2022). Synthesis of Al/starch co-doped in CaO nanoparticles for enhanced catalytic and antimicrobial activities: Experimental and DFT approaches. RSC advances, 12(50), 32142–32155.
I.Shahzadi, M. Islam, H. Saeed, A. Shahzadi, J. Haider, A. Haider, M. Imran, H.A. Rathore, A. Ul-Hamid, W. Nabgan, M. Ikram. Facile synthesis of copolymerized cellulose grafted hydrogel doped calcium oxide nanocomposites with improved antioxidant activity for anti-arthritic and controlled release of doxorubicin for anti-cancer evaluation. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (2023) 123874.
Shahzadi, I., Islam, M., Saeed, H., Haider, A., Shahzadi, A., Haider, J., Ahmed, N., Ul-Hamid, A., Nabgan, W. M., & Ikram, H. A. (2022). Rathore. Formation of biocompatible MgO/cellulose grafted hydrogel for efficient bactericidal and controlled release of doxorubicin. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 220, 1277–1286.
Ikram, M., Haider, A., Imran, M., Haider, J., Naz, S., Ul-Hamid, A., Shahzadi, A., Moeen, S., Nazir, G., Nabgan, W., & Bashir, A. (2023). Cellulose grafted poly acrylic acid doped manganese oxide nanorods as novel platform for catalytic, antibacterial activity and molecular docking analysis. Surfaces and Interfaces, 37, 102710.
I.Shahzadi, M.Islam, H. Saeed, A. Shahzadi, J. Haider, A. Haider, M. Imran, H.A. Rathore, A. Ul-Hamid, W. Nabgan, Ikram, M. Facile synthesis of copolymerized cellulose grafted hydrogel doped calcium oxide nanocomposites with improved antioxidant activity for anti-arthritic and controlled release of doxorubicin for anti-cancer evaluation. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (2023) 123874.
M. Ikram, A., Haider, M. Imran, J.Haider, S.Naz, A. Ul-Hamid, A. Shahzadi, K. Ghazanfar, W. Nabgan, S. Moeen, S. Ali. Assessment of catalytic, antimicrobial and molecular docking analysis of starch-grafted polyacrylic acid doped BaO nanoparticles. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (2023) 123190.
Acknowledgements
Dr. Priyank L. Bhutiya thanks GERMI Director General Dr. Biswajit Roy for providing all facilities and continuous support as well as also acknowledging SRDC-PDEU for instrumental analyses. Mr. Bharat Odedara is also acknowledged for his support in the collection of seaweed. Dr. Mitesh Solanki has high acknowledgement for data interpretation.
Funding
This work was carried out independently without any funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.B., B.T., and Z.H. designed the experiment as well as wrote the manuscript. R.K. and Y.S. were done supercapacitor device analysis. A.R. and P.R. monitored the experiment.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Involving Humans and Animals and Informed Consent
This research does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhutiya, P.L., Kapadiya, R., Tripathi, B. et al. rGO-ZnO Nanowire Deposited Filamentous Seaweed Nanofibrous Cellulose for Paper Supercapacitor. BioNanoSci. 13, 588–599 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-023-01101-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-023-01101-5