Abstract
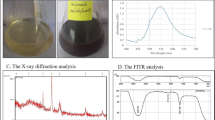
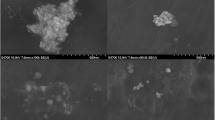
Nanoparticles play a significant role in the development of pharmaceuticals. In the present study, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were synthesized using the microwave irradiation method and evaluated their cytocompatibility and antioxidant properties. Saussurea obvallata plant extract was used as a reducing agent to prepare AuNPs. The UV–visible spectra confirmed the formation of AuNPs with the surface plasmon resonance peak at 530 nm. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy demonstrates that AuNPs were blended with different functional groups, including hydroxyl, amine, and alkyl halide. The scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy results indicate that AuNPs are spherical in size. The XRD analysis provides evidence for the existence of the AuNPs, which are coherent with standard AuNPs. The synthesized AuNPs showed excellent biocompatibility with IMR-32 cells up to 500 μg/mL concentration. Furthermore, the biosynthesized AuNPs exhibited enhanced antioxidative activity at 1000 μg/mL concentration. Hence, the developed AuNPs would have a potential biological application in the medical field.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arif, R., & Uddin, R. (2021). A review on recent developments in the biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and its biomedical applications. Medical Devices & Sensors, 4(1), e10158.
Prasad R (2019) Nanotechnology in the life science. Springer Nature Switzerland
Schröfel, A., Kratošová, G., Šafařík, I., Šafaříková, M., Raška, I., & Shor, L. M. (2014). Applications of biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles–A review. Acta Biomaterialia, 10(10), 4023–4042.
Ojo, O. A., Olayide, I. I., Akalabu, M. C., Ajiboye, B., Ojo, A., Oyinloye, B., & Ramalingam, M. (2021). Nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biointerface Res Appl Chem, 11, 8431–8445.
Lateef, A., Ojo, S. A., Elegbede, J. A., Azeez, M. A., Yekeen, T. A., & Akinboro, A. (2017). Evaluation of some biosynthesized silver nanoparticles for biomedical applications: Hydrogen peroxide scavenging, anticoagulant and thrombolytic activities. Journal of Cluster Science, 28(3), 1379–1392.
Yew, Y. P., Shameli, K., Miyake, M., Khairudin, N. B. B. A., Mohamad, S. E. B., Naiki, T., & Lee, K. X. (2020). Green biosynthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles and biomedical applications in targeted anticancer drug delivery system: A review. Arabian J Chem, 13(1), 2287–2308.
Bansal, S. A., Kumar, V., Karimi, J., Singh, A. P., & Kumar, S. (2020). Role of gold nanoparticles in advanced biomedical applications. Nanoscale Advances, 2(9), 3764–3787.
Nejati K, Dadashpour M, Gharibi T, Mellatyar H, Akbarzadeh A (2021) Biomedical applications of functionalized gold nanoparticles: A review. J Cluster Sci:1–16
Shah, M., Badwaik, V., Kherde, Y., Waghwani, H. K., Modi, T., Aguilar, Z. P., Rodgers, H., Hamilton, W., Marutharaj, T., & Webb, C. (2014). Gold nanoparticles: Various methods of synthesis and antibacterial applications. Frontiers in Bioscience, 19(8), 1320–1344.
Ielo, I., Rando, G., Giacobello, F., Sfameni, S., Castellano, A., Galletta, M., Drommi, D., Rosace, G., & Plutino, M. R. (2021). Synthesis, chemical–physical characterization, and biomedical applications of functional gold nanoparticles: A review. Molecules, 26(19), 5823.
Mulikova, T., Abduraimova, A., Molkenova, A., Em, S., Duisenbayeva, B., Han, D.-W., & Atabaev, T. S. (2021). Mesoporous silica decorated with gold nanoparticles as a promising nanoprobe for effective CT X-ray attenuation and potential drug delivery. Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects, 26, 100712.
Zhao, S., Luo, Y., Chang, Z., Liu, C., Li, T., Gan, L., Huang, Y., & Sun, Q. (2021). BSA-coated gold nanorods for NIR-II photothermal therapy. Nanoscale Research Letters, 16(1), 1–11.
Elia, P., Zach, R., Hazan, S., Kolusheva, S., Ze, P., & Zeiri, Y. (2014). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant extracts as reducing agents. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 9, 4007.
Panda, T., & Deepa, K. (2011). Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 11(12), 10279–10294.
Rao, K. J., & Paria, S. (2014). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using aqueous Aegle marmelos leaf extract and their application for thiamine detection. RSC Advances, 4(54), 28645–28652.
Geetha, R., Ashokkumar, T., Tamilselvan, S., Govindaraju, K., Sadiq, M., & Singaravelu, G. (2013). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their anticancer activity. Cancer Nanotechnology, 4(4), 91–98.
Saifuddin, N., Wong, C., & Yasumira, A. (2009). Rapid biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatant of bacteria with microwave irradiation. Journal of Chemistry, 6(1), 61–70.
Annamalai, J., & Nallamuthu, T. (2015). Characterization of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Chlorella vulgaris and their anti-pathogenic properties. Applied Nanoscience, 5(5), 603–607.
Rajathi, F. A. A., Parthiban, C., Kumar, V. G., & Anantharaman, P. (2012). Biosynthesis of antibacterial gold nanoparticles using brown alga, Stoechospermum marginatum (kützing). Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc, 99, 166–173.
Elahi, N., Kamali, M., & Baghersad, M. H. (2018). Recent biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles: A review. Talanta, 184, 537–556.
Liu, X.-Y., Wang, J.-Q., Ashby, C. R., Jr., Zeng, L., Fan, Y.-F., & Chen, Z.-S. (2021). Gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, physiochemical properties and therapeutic applications in cancer. Drug Discovery Today, 26(5), 1284–1292.
Mandhata CP, Sahoo CR, Padhy RN (2022) Biomedical applications of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles from cyanobacteria: An overview. Biol Trace Elem Res:1–21
Kamal, B. (2013). Brahma Kamal-The spiritually revered, scientifically ignored medicinal plant. Current Science, 104(6), 685.
Semwal, P., & Painuli, S. (2019). Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and GC-MS profiling of Saussurea obvallata (Brahma Kamal) from Uttarakhand Himalaya. Clinical Phytoscience, 5(1), 12.
Ahmed, S., & Ikram, S. (2016). Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles: A green approach. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, B: Biology, 161, 141–153.
Noruzi, M. (2015). Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant extracts. Bioprocess Biosystems Engineering, 38(1), 1–14.
Franco-Romano, M., Gil, M., Palacios-Santander, J., Delgado-Jaén, J., Naranjo-Rodríguez, I., De Cisneros, J.H.-H., & Cubillana-Aguilera, L. (2014). Sonosynthesis of gold nanoparticles from a geranium leaf extract. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 21(4), 1570–1577.
Shankar, S. S., Rai, A., Ahmad, A., & Sastry, M. (2005). Controlling the optical properties of lemongrass extract synthesized gold nanotriangles and potential application in infrared-absorbing optical coatings. Chemistry of Materials, 17(3), 566–572.
Huang, J., Li, Q., Sun, D., Lu, Y., Su, Y., Yang, X., Wang, H., Wang, Y., Shao, W., & He, N. (2007). Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology, 18(10), 105104.
Anuradha, J., Abbasi, T., & Abbasi, S. (2010). Green’synthesis of gold nanoparticles with aqueous extracts of neem (Azadirachta indica). Research Journal of Biotechnology, 5(1), 75–79.
Chandran, S. P., Chaudhary, M., Pasricha, R., Ahmad, A., & Sastry, M. (2006). Synthesis of gold nanotriangles and silver nanoparticles using Aloevera plant extract. Biotechnology Progress, 22(2), 577–583.
Ankamwar, B., Chaudhary, M., & Sastry, M. (2005). Gold nanotriangles biologically synthesized using tamarind leaf extract and potential application in vapor sensing. Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic, Metal-Organic and Nano-Metal Chemistry, 35(1), 19–26.
Ankamwar, B. (2010). Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles (green-gold) using leaf extract of Terminalia catappa. E-Journal of Chemistry, 7(4), 1334–1339.
Nagalingam, M., Kalpana, V., & Panneerselvam, A. (2018). Biosynthesis, characterization, and evaluation of bioactivities of leaf extract-mediated biocompatible gold nanoparticles from Alternanthera bettzickiana. Biotechnology Reports, 19, e00268.
Ankamwar, B., Damle, C., Ahmad, A., & Sastry, M. (2005). Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using Emblica officinalis fruit extract, their phase transfer and transmetallation in an organic solution. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 5(10), 1665–1671.
El-Naggar, M. E., Shaheen, T. I., Fouda, M. M., & Hebeish, A. A. (2016). Eco-friendly microwave-assisted green and rapid synthesis of well-stabilized gold and core–shell silver–gold nanoparticles. Carbohydrate Polymers, 136, 1128–1136.
Bhuvanasree, S., Harini, D., Rajaram, A., & Rajaram, R. (2013). Rapid synthesis of gold nanoparticles with Cissus quadrangularis extract using microwave irradiation. Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc, 106, 190–196.
Roy, A., & Mohanta, B. (2019). Microwave-assisted green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and its catalytic activity. International Journal of Nano Dimension, 10(4), 359–367.
Balalakshmi, C., Gopinath, K., Govindarajan, M., Lokesh, R., Arumugam, A., Alharbi, N. S., Kadaikunnan, S., Khaled, J. M., & Benelli, G. (2017). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a cheap Sphaeranthus indicus extract: Impact on plant cells and the aquatic crustacean Artemia nauplii. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, B: Biology, 173, 598–605.
Wali, M., Sajjad, A., & Sumaira, S. (2017). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their characterizations using plant extract of Papaver somniferum. Nano Science and Nano Technology, 11(2), 118.
Semwal, P., Anthwal, P., Kapoor, T., & Thapliyal, A. (2014). Preliminary investigation of phytochemicals of Saussurea obvallata (Brahm Kamal) and Pittosporum eriocarpum (Agni): Two endangered medicinal plant species of Uttarakhand. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 1(4), 266–269.
Annamalai, A., Babu, S. T., Jose, N. A., Sudha, D., & Lyza, C. V. (2011). Biosynthesis and characterization of silver and gold nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extraction of Phyllanthus amarus Schum & Thonn. World Applied Sciences Journal, 13(8), 1833–1840.
Venkatesan, J., Manivasagan, P., Kim, S.-K., Kirthi, A. V., Marimuthu, S., & Rahuman, A. A. (2014). Marine algae-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a novel Ecklonia cava. Bioprocess Biosystems Engineering, 37(8), 1591–1597.
Correa S, Naranjo A, Herrera A Biosynthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using extracts of Tamarindus indica L leaves. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2016. vol 1. IOP Publishing, p 012082
Sathishkumar, G., Jha, P. K., Vignesh, V., Rajkuberan, C., Jeyaraj, M., Selvakumar, M., Jha, R., & Sivaramakrishnan, S. (2016). Cannonball fruit (Couroupita guianensis, Aubl.) extract mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of its antioxidant activity. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 215, 229–236.
Sunkari, S., Gangapuram, B. R., Dadigala, R., Bandi, R., Alle, M., & Guttena, V. (2017). Microwave-irradiated green synthesis of gold nanoparticles for catalytic and antibacterial activity. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 8(1), 13.
Gutiérrez-Wing, C., Esparza, R., Vargas-Hernández, C., García, M. F., & José-Yacamán, M. (2012). Microwave-assisted synthesis of gold nanoparticles self-assembled into self-supported superstructures. Nanoscale, 4(7), 2281–2287.
Quach, Q., Biehler, E., Elzamzami, A., Huff, C., Long, J. M., & Abdel-Fattah, T. M. (2021). Catalytic activity of beta-cyclodextrin-gold nanoparticles network in hydrogen evolution reaction. Catalysts, 11(1), 118.
Devi, L., Gupta, R., Jain, S. K., Singh, S., & Kesharwani, P. (2020). Synthesis, characterization and in vitro assessment of colloidal gold nanoparticles of Gemcitabine with natural polysaccharides for treatment of breast cancer. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 56, 101565.
Kumar, S., Sharma, S., & Das, P. (2016). Supported gold nanoparticles-catalyzed microwave-assisted hydration of nitriles to amides under base-free conditions. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 358(18), 2889–2894.
Muthuvel, A., Adavallan, K., Balamurugan, K., & Krishnakumar, N. (2014). Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extract and screening their free radical scavenging and antibacterial properties. Biomedicine & Preventive Nutrition, 4(2), 325–332.
Izadiyan, Z., Shameli, K., Hara, H., & Taib, S. H. M. (2018). Cytotoxicity assay of biosynthesis gold nanoparticles mediated by walnut (Juglans regia) green husk extract. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1151, 97–105.
Singh, S., Vidyarthi, A. S., Nigam, V. K., & Dev, A. (2014). Extracellular facile biosynthesis, characterization and stability of gold nanoparticles by Bacillus licheniformis. Artificial Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnology, 42(1), 6–12.
Namvar, F., Azizi, S., Ahmad, M. B., Shameli, K., Mohamad, R., Mahdavi, M., & Tahir, P. M. (2015). Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using the marine macroalgae Sargassum muticum. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 41(8), 5723–5730.
Lunardi, C. N., Barros, M. P., Rodrigues, M. L., & Gomes, A. J. (2018). Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Euphorbia tirucalli latex and the microwave method. Gold Bulletin, 51(4), 131–137.
Eskandari-Nojehdehi, M., Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H., & Jafarizad, A. (2018). Microwave accelerated green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using gum Arabic and their physico-chemical properties assessments. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 232(3), 325–343.
Khusro A, Aarti C, Agastian P (2020) Microwave irradiation-based synthesis of anisotropic gold nanoplates using Staphylococcus hominis as reductant and its optimization for therapeutic applications. J Environ Chem Eng:104526
Chen, M. N., Chan, C. F., Huang, S. L., & Lin, Y. S. (2019). Green biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Chenopodium formosanum shell extract and analysis of the particles’ antibacterial properties. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 99(7), 3693–3702.
Francis, S., Koshy, E., & Mathew, B. (2018). Microwave aided synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their antioxidant, antimicrobial and catalytic potentials. Journal of Nanostructures, 8(1), 55–66.
Valsalam, S., Agastian, P., Esmail, G. A., Ghilan, A.-K.M., Al-Dhabi, N. A., & Arasu, M. V. (2019). Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Musa acuminata colla flower and its pharmaceutical activity against bacteria and anticancer efficacy. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, B: Biology, 201, 111670.
Hassanisaadi, M., Bonjar, G. H. S., Rahdar, A., Pandey, S., Hosseinipour, A., & Abdolshahi, R. (2021). Environmentally safe biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant water extracts. Nanomaterials, 11(8), 2033.
Abdelrazek, E. M., Abdelghany, A. M., Badr, S. I., & Morsi, M. A. (2018). Structural, optical, morphological and thermal properties of PEO/PVP blend containing different concentrations of biosynthesized Au nanoparticles. Journal of materials research and technology, 7(4), 419–431.
Semwal, P., & Painuli, S. (2019). Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and GC-MS profiling of Saussurea obvallata (Brahma Kamal) from Uttarakhand Himalaya. Clinical Phytoscience, 5(1), 1–11.
El-Borady OM, Fawzy M, Hosny M (2021) Antioxidant, anticancer and enhanced photocatalytic potentials of gold nanoparticles biosynthesized by common reed leaf extract. Appl Nanosci:1–12
Vijayan, R., Joseph, S., & Mathew, B. (2018). Eco-friendly synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles with enhanced antimicrobial, antioxidant, and catalytic activities. IET nanobiotechnology, 12(6), 850–856.
Babu, P. J., Sharma, P., Kalita, M. C., & Bora, U. (2011). Green synthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles using Fagopyrum esculentum leaf extract. Frontiers of Materials Science, 5(4), 379–387.
Pourhassan-Moghaddam, M., Zarghami, N., Mohsenifar, A., Rahmati-Yamchi, M., Gholizadeh, D., Akbarzadeh, A., De La Guardia, M., & Nejati-Koshki, K. (2014). Watercress-based gold nanoparticles: Biosynthesis, mechanism of formation and study of their biocompatibility in vitro. Micro & Nano Letters, 9(5), 345–350.
Funding
The Basic Science Research Program supported this research through the National Research Foundation of Korea (2018R1A6A1A03024231 and 2021R1A2C1003566). In addition, this work is also supported by the seed grant from Yenepoya (Deemed to be University) (YU/seed grant/073-2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Research Involving Humans and Animals Statement
None.
Informed Consent
None.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) was performed using microwave irradiation and Saussurea obvallata.
• Rapid formation for gold nanoparticles was formed in less than a minute.
• Saussurea obvallata was used as a reducing agent in the preparation of AuNPs.
• Different analytical techniques including FT-IR, SEM–EDX, TEM, XRD and UV, were utilized to confirm AuNP formation.
• Biocompatibility and antioxidant property of biosynthesized AuNPs were checked with IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells and DPPH assay.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalavi, P.A., V., A.J., Thomas, S. et al. Microwave-Assisted Biosynthesized Gold Nanoparticles Using Saussurea obvallata: Biocompatibility and Antioxidant Activity Assessment. BioNanoSci. 12, 741–751 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-022-00994-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-022-00994-y