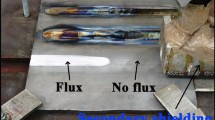
Abstract
Flux-bounded tungsten inert gas welding is a variant of activated tungsten inert gas welding wherein activating flux is applied on the weld surface with a narrow flux gap along the line of weld. In this study, bead-on-plate welds were performed with flux gaps of 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 mm using the fluxes silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide and calcium fluoride. The weld bead profiles were obtained using a stereomicroscope from which the depth-to-width ratios (DWRs) were calculated and compared with the DWR of a tungsten-inert-gas-welded plate. The reasons for differences in DWR were explained using the mechanisms involved and the captured images of the welding arc profile. The microstructure of the weld beads revealed no entrapment of flux particles. The increase in the DWR in the presence of activating flux was also substantiated using a numerical simulation model.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Messler R W Jr, Principles of Welding: Processes, Physics, Chemistry and Metallurgy, Wiley, Hoboken (2004) p 51.
Paskell C, Weld J 76 (1997) 57.
Lucas W, Howse D, Savitsky M M, and Kovalenko I V, in IIW/IIS Budapest Proceedings (1996) p 257.
Jayakrishnan S, and Chakravarthy P, J Manuf Process 28 (2017) 116.
Sire S and Marya S, Int J Form Process 5 (2002) 39.
Kuang-Hung T, Powder Technol 233 (2013) 72.
Goldak J A, and Akhlaghi M, Computational Welding Mechanics, Springer, Berlin (2005) p 28.
Howse D S, and Lucas W, Sci Technol Weld Join 5 (2000) 189.
Sugden S, J Chem Soc Trans 125 (1924) 32.
Leitner T, Thermophysical Properties of Liquid Aluminium Determined by Means of Electromagnetic Levitation, Master’s Thesis, Graz University of Technology, Graz (2016).
Thomas B. Reed, Free Energy of Formation of Binary Compounds, MIT Press, Cambridge (1971).
Leconte S, Paillard P, Chapelle P, Henrion G, and Saindrenan J, Sci Technol Weld Join 12 (2007) 120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neethu, N., Togita, R.G., Neelima, P. et al. Effect of Nature of Flux and Flux Gap on the Depth-to-Width Ratio in Flux-Bounded TIG Welding of AA6061: Experiments and Numerical Simulations. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 1585–1588 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01654-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01654-8