Abstract
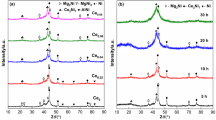
In this work, synthesis of Ni doped Mg–Ti nanostructured alloys were made using mechanical alloying method. The structural and optical properties of Mg–Ti alloys were studied by X-Ray diffraction (XRD), UV–Vis spectroscopy and Density Functional theoritical (DFT) studies. The electrochemical performance of Mg–Ti alloys was studied by cyclic voltammetry and impedance studies. The XRD pattern of 20 h milled powders revealed the formation of Mg(Ti) solid solution, Mg2Ni and TiNi compounds. DFT studies confirmed the strong modification of the valence band structure of the Ni doped Mg–Ti alloys which could significantly hasten the hydrogenation and dehydrogenation properties. UV–Vis spectrum revealed increase in band gap energy due to blue shift and hyperchromic shift in both absorption and transmission peaks. Obviously, electrochemical studies revealed high exchange current density and Warburg impedance, as well as decrease in diffusion coefficient and charge transfer resistance. Ultimately, it showed the result of high catalytic activity and faster kinetic reaction rates for the good reversibility of hydrogen ions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zou J, Long S, Chen X, Zeng X, and Ding W, Int J Hydrogen Energy 40 (2015) 1820.
Makridis S S, Gkanas E I, Panagakos G, Kikkinides E S, Stubos A K, Wagener P, and Barcikowski S, Int J Hydrogen Energy 38 (2013) 11530.
Jain I P, Lal C, and Jain A, Int J Hydrogen Energy 35 (2010) 5133.
Jia Y, Sun C, Shen S, Zou J, Mao S S, and Yao X, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev 44 (2015) 289.
Wu Z, Zhang Z X, Yang F S, Feng P H, and Wang Y Q, Int J Hydrogen Energy 41 (2016) 2771.
Zou J, Zeng X, Ying Y, Chen X, Guo H, Zhou S, and Ding W, Int J Hydrogen Energy 38 (2013) 2337.
Shaoa H, Xin G, Zheng J, Lib X, and Akibaa E, Nano Energy 1 (2012) 590.
Liu T, Wang C, and Wu Y, Int J Hydrogen Energy 39 (2014) 14262.
Chen B H, Kuo C H, Ku J R, Yan P S, Huang C J, Jeng M S, and Tsau F H, J Alloys Comp 568 (2013) 78.
Yao X, Wu C, Du A, Lu G Q, Cheng H, Smith S C, Zou J, and He Y, J Phys Chem B 110 (2006) 11697.
Long S, Zou J, Chen X, Zeng X, and Ding W, J Alloys Comp 615 (2014) S684.
Suryanarayana C, Prog Mater Sci 46 (2001) 101.
Yuan J, Zhu Y, Li Y, Zhang L, and Li L, Int J Hydrogen Energy 39 (2014) 10184.
Khrussanova M, Grigorova E, Bobet J L, Khristov M, and Peshev P, J Alloys Comp 365 (2004) 308.
Sun N, Xu B, Zhao S, Sun Z, Li X, and Meng L, Int J Hydrogen Energy 40 (2015) 10516.
Zhong H C, Wang H, Ouyang L Z, and Zhu M, J Alloys Comp 509 (2011) 4268.
Yelsukov E P, Dorofeev G A, Ulyanov A L, and Maratkanova A N, Chem Sustainable Development 13 (2005) 191.
Sundaresan R, and Froes F H, Metal Powder Rep 44 (1989) 195.
Oleszak D, Acta Physica Polonica A 96 (1999) 1.
Jurczyk M, Nowak M, Szajek A, and Jezierski A, Int J Hydrogen Energy 37 (2012) 3652.
Gao J, Hou Z, Ge Q, Zhao D, Guo1 S, and Zhang Y, Mater Sci Appl 1 (2010) 168.
Anik M, J Alloys Comp 491 (2010) 565.
Yadav T P, Yadav R M, and Singh D P, Nanosci Nanotechnol 2(3) (2012) 22.
Liang G, J Alloys Comp 370 (2004) 123.
Liang G, and Schulz R, J Metastable Nanocryst Mater 12 (2002) 93.
Liang G, and Schulz R, J Mater Sci 38 (2003) 1179.
Asano K, Enoki H, and Akiba E, Mater Trans 48(2) (2007) 121.
Fukai Y, The Metal Hydrogen System, 2nd ed., Springer, Berlin (2005), p 497.
Niessen R A H, and Notten P H L, Electrochem Solid State Lett 8 (2005) 534.
Kalisvaart W P, and Notten P H L, J Mater Res 23 (2008) 2179.
Asano K, Enoki H, and Akiba E, Mater Trans JIM 48 (2007) 121.
Huot J, Ravnsbæk D B, Zhang J, Cuevas F, Latroche M, and Jensen T R, Prog Mater Sci 58 (2013) 30.
Li Y, Tao Y, Ke D, Yang S, and Han S, J Alloys Comp 615 (2014) 91.
Liu T, Cao Y, Li H, Chou W, and Li X, J Power Sources 267 (2014) 598.
Al-Gaashani R, Radiman S, Daud A R, Tabet N, and Al-Douri Y, Ceramics International 39 (2013) 2283.
Wang L, Zhao J, He X, Gao J, Li J, Wan C, and Jiang C, Int J Electrochem Sci 7 (2012) 345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muthu, P., Sinnaeruvadi, K. Structural and Optical Properties Correlation of Nickel Doped Magnesium–Titanium Alloys with Sorption Kinetics Reaction for Hydrogen Storage Application. Trans Indian Inst Met 70, 581–587 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017-1057-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017-1057-2