Abstract
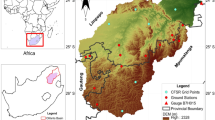
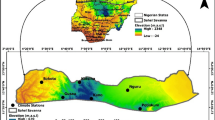
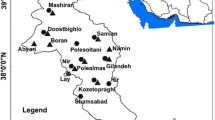
This study aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of meteorological and hydrological droughts in the lower Tigris-Euphrates basin, Türkiye over 12-month time scale using the standardized precipitation index (SPI) and the Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) and the standardized streamflow index (SDI). To evaluate monthly trends of the SPI, SPEI, and SDI series, Mann–Kendall (MK), Spearman Rho (SR), and innovative trend analysis (ITA) tests are employed. The intrinsic relationships between the hydrological and meteorological drought in the study area as well as the specifics of how the oscillation period changes over time can also be obtained via wavelet transform coherence (WTC), which can reveal essential information. The results of all trend tests performed a decreasing trend consistently at stations 17275, 17810, 17948, 17950, and 17968 for all months in terms of SPI. SPEI is more sensitive to trend detection than SPI when taking into account all trend testing. In addition, the three trend tests are found to be more consistent with each other when SPEI is compared to SPI. According to SDI, the ITA method is clearly superior to the other two methods for identifying hidden trends. The ITA method, for example, captures a considerably increasing/decreasing trend at stations E26A038 (January and February), E26A012 (January, February, and from May to December), and E26A033 (from June to December) despite MK and SR tests finding no significant trends at any of the stations. When considering the WTC, positive month signals are strongly correlated with 12-month periods, according to the majority of stations.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request. Due to a non-disclosure agreement, the data used in the present study are not publicly accessible.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abeysingha NS, Wickramasuriya MG, Meegastenna TJ (2020) Assessment of meteorological and hydrological drought: a case study in Kirindi Oya river basin in Sri Lanka. Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 10:429–447. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2020.109947
Abro MI, Elahi E, Chand R et al (2022) Estimation of a trend of meteorological and hydrological drought over Qinhuai River Basin. Theor Appl Climatol 147:1065–1078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03870-z
Achite M, Ceribasi G, Ceyhunlu AI et al (2021) The innovative polygon trend analysis (IPTA) as a simple qualitative method to detect changes in environment—example detecting trends of the total monthly precipitation in semiarid area. Sustainability 13:12674. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212674
Akbari H, Rakhshandehroo GR, Sharifloo AH, Ostadzadeh E (2015) Drought analysis based on standardized precipitation index (SPI) and streamflow drought index (SDI) in Chenar Rahdar river Basin Southern Iran. Watershed Manag Doi. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784479322.002
Akçay F, Kankal M, Şan M (2022) Innovative approaches to the trend assessment of streamflows in the Eastern Black Sea basin, Turkey. Hydrol Sci J 67:222–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2021.1998509
Alam J, Saha P, Mitra R, Das J (2023) Investigation of spatio-temporal variability of meteorological drought in the Luni River Basin, Rajasthan India. Arab J Geosci 16:201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11290-8
Alivi A, Yildiz O, Aktürk G (2021) Investigating the climate change effects on annual average streamflows in the EuphratesTigris basin using the climate elasticity method. J Fac Eng Archit Gazi Univ 36:1449–1465
Bayer Altin T, Altin BN (2021) Response of hydrological drought to meteorological drought in the eastern Mediterranean Basin of Turkey. J Arid Land 13:470–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-021-0064-7
Bhunia P, Das P, Maiti R (2020) Meteorological drought study through spi in three drought prone districts of West Bengal, India. Earth Syst Environ 4:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-019-00137-6
Cao S, Zhang L, He Y et al (2022) Effects and contributions of meteorological drought on agricultural drought under different climatic zones and vegetation types in Northwest China. Sci Total Environ 821:153270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153270
Chang L-L, Niu G-Y (2023) The impacts of interannual climate variability on the declining trend in terrestrial water storage over the Tigris-Euphrates river basin. J Hydrometeorol 24:549–560. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-22-0026.1
Cheraghalizadeh M, Ghameshlou AN, Bazrafshan J, Bazrafshan O (2018) A copula-based joint meteorological–hydrological drought index in a humid region (Kasilian basin, North Iran). Arab J Geosci 11:300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3671-7
Christian JI, Basara JB, Hunt ED et al (2021) Global distribution, trends, and drivers of flash drought occurrence. Nat Commun 12:6330. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26692-z
Danandeh Mehr A, Sorman AU, Kahya E, Hesami Afshar M (2020) Climate change impacts on meteorological drought using SPI and SPEI: case study of Ankara, Turkey. Hydrol Sci J 65:254–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1691218
Ding Y, Gong X, Xing Z et al (2021) Attribution of meteorological, hydrological and agricultural drought propagation in different climatic regions of China. Agric Water Manag 255:106996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106996
Dlamini T, Songsom V, Koedsin W, Ritchie RJ (2022) Intensity, duration and spatial coverage of aridity during meteorological drought years over northeast Thailand. Climate 10:137. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10100137
Edossa DC, Babel MS, Das Gupta A (2010) Drought analysis in the Awash river basin, Ethiopia. Water Resour Manag 24:1441–1460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9508-0
Elouissi A, Benzater B, Dabanli I et al (2021) Drought investigation and trend assessment in Macta watershed (Algeria) by SPI and ITA methodology. Arab J Geosci 14:1329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07670-7
Farris S, Deidda R, Viola F, Mascaro G (2021) On the role of serial correlation and field significance in detecting changes in extreme precipitation frequency. Water Resour Res 57:e2021WR030172. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021WR030172
Farrokhi A, Farzin S, Mousavi S-F (2021) Meteorological drought analysis in response to climate change conditions, based on combined four-dimensional vine copulas and data mining (VC-DM). J Hydrol 603:127135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127135
Gidey E, Dikinya O, Sebego R et al (2018) Modeling the spatio-temporal meteorological drought characteristics using the standardized precipitation index (SPI) in Raya and its environs, Northern Ethiopia. Earth Syst Environ 2:281–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-018-0057-7
Grinsted A, Moore JC, Jevrejeva S (2004) Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process Geophys 11:561–566. https://doi.org/10.5194/npg-11-561-2004
Gumus V, Simsek O, Avsaroglu Y, Agun B (2021) Spatio-temporal trend analysis of drought in the GAP Region, Turkey. Nat Hazards 109:1759–1776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04897-1
Gumus V, Avsaroglu Y, Simsek O (2022) Streamflow trends in the Tigris river basin using Mann−Kendall and innovative trend analysis methods. J Earth Syst Sci 131:34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-021-01770-4
Han X, Wu J, Zhou H et al (2020) Intensification of historical drought over China based on a multi-model drought index. Int J Climatol 40:5407–5419. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6527
Hisdal H, Tallaksen LM (2003) Estimation of regional meteorological and hydrological drought characteristics: a case study for Denmark. J Hydrol 281:230–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(03)00233-6
Jahangir MH, Yarahmadi Y (2020) Hydrological drought analyzing and monitoring by using Streamflow Drought Index (SDI) (case study: Lorestan, Iran). Arab J Geosci 13:110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5059-8
Katipoğlu OM (2022) Analysis of spatial variation of temperature trends in the semiarid Euphrates basin using statistical approaches. Acta Geophys 70:1899–1921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00819-2
Katipoğlu OM, Acar R (2022) Space-time variations of hydrological drought severities and trends in the semi-arid Euphrates Basin, Turkey. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 36:4017–4040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02246-7
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation methods. Griffin, London
Khalili D, Farnoud T, Jamshidi H et al (2011) Comparability analyses of the SPI and RDI meteorological drought indices in different climatic zones. Water Resour Manag 25:1737–1757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9772-z
King-Okumu C, Tsegai D, Pandey RP, Rees G (2020) Less to lose? Drought impact and vulnerability assessment in disadvantaged regions. Water 12:1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041136
Lin Q, Wu Z, Zhang Y et al (2023) Propagation from meteorological to hydrological drought and its application to drought prediction in the Xijiang River basin, South China. J Hydrol 617:128889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128889
Lorenzo-Lacruz J, Vicente-Serrano SM, González-Hidalgo JC et al (2013) Hydrological drought response to meteorological drought in the Iberian Peninsula. Climate Res 58:117–131. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr01177
Ma L, Huang Q, Huang S et al (2021) Propagation dynamics and causes of hydrological drought in response to meteorological drought at seasonal timescales. Hydrol Res 53:193–205. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2021.006
Malik A, Kumar A, Singh RP (2019) Application of heuristic approaches for prediction of hydrological drought using multi-scalar streamflow drought index. Water Resour Manag 33:3985–4006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02350-4
Malik A, Kumar A, Salih SQ, Yaseen ZM (2021) Hydrological drought investigation using streamflow drought index. In: Deo RC, Samui P, Kisi O, Yaseen ZM (eds) Intelligent data analytics for decision-support systems in hazard mitigation: theory and practice of hazard mitigation. Springer, Singapore, pp 63–88
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. Am Meteorol Soc 17:179–183
Meresa H, Zhang Y, Tian J, Abrar Faiz M (2023) Understanding the role of catchment and climate characteristics in the propagation of meteorological to hydrological drought. J Hydrol 617:128967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128967
Mishra V, Cherkauer KA, Shukla S (2010) Assessment of drought due to historic climate variability and projected future climate change in the midwestern United States. J Hydrometeorol 11:46–68. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JHM1156.1
Mohammed S, Alsafadi K, Enaruvbe GO et al (2022) Assessing the impacts of agricultural drought (SPI/SPEI) on maize and wheat yields across Hungary. Sci Rep 12:8838. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-12799-w
Nalbantis I (2008) Evaluation of a hydrological drought ındex. Eur Water 23(24):67–77
Nalbantis I, Tsakiris G (2009) Assessment of hydrological drought revisited. Water Resour Manag 23:881–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9305-1
Pang Z, Wang Z (2021) Temperature trend analysis and extreme high temperature prediction based on weighted Markov Model in Lanzhou. Nat Hazards 108:891–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04711-y
Paulo AA, Pereira LS (2006) Drought concepts and characterization. Water Int 31:37–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060608691913
Pei J, Deng L, Song S et al (2019) Towards artificial general intelligence with hybrid Tianjic chip architecture. Nature 572:106–111. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1424-8
Salimi H, Asadi E, Darbandi S (2021) Meteorological and hydrological drought monitoring using several drought indices. Appl Water Sci 11:11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01345-6
Şen Z (2012) Innovative trend analysis methodology. J Hydrol Eng 17:1042–1046. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000556
Şen Z (2017) Innovative trend significance test and applications. Theor Appl Climatol 127:939–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1681-x
Şen Z, Şişman E, Dabanli I (2019) Innovative polygon trend analysis (IPTA) and applications. J Hydrol 575:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.05.028
Sharafati A, Nabaei S, Shahid S (2020) Spatial assessment of meteorological drought features over different climate regions in Iran. Int J Climatol 40:1864–1884. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6307
Sheffield J, Goteti G, Wen F, Wood EF (2004) A simulated soil moisture based drought analysis for the United States. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JD005182
Tabari H, Grismer ME, Trajkovic S (2013) Comparative analysis of 31 reference evapotranspiration methods under humid conditions. Irrig Sci 31:107–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-011-0295-z
Tabrizi AA, Khalili D, Kamgar-Haghighi AA, Zand-Parsa S (2010) Utilization of time-based meteorological droughts to investigate occurrence of streamflow droughts. Water Resour Manage 24:4287–4306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9659-z
Tang H, Wen T, Shi P et al (2021) Analysis of characteristics of hydrological and meteorological drought evolution in southwest China. Water 13:1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131846
Tareke KA, Awoke AG (2022) Hydrological drought analysis using streamflow drought index (SDI) in Ethiopia. Adv Meteorol 2022:e7067951. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7067951
Tigkas D, Vangelis H, Tsakiris G (2012) Drought and climatic change impact on streamflow in small watersheds. Sci Total Environ 440:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.08.035
Torrence C, Webster PJ (1999) Interdecadal changes in the ENSO–monsoon system. J Clim 12:2679–2690. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012%3c2679:ICITEM%3e2.0.CO;2
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, López-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23:1696–1718. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI2909.1
Wang H, Pan Y, Chen Y (2017) Comparison of three drought indices and their evolutionary characteristics in the arid region of northwestern China. Atmos Sci Lett 18:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1002/asl.735
Wang F, Wang Z, Yang H et al (2020) Comprehensive evaluation of hydrological drought and its relationships with meteorological drought in the Yellow River basin, China. J Hydrol 584:1751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124751
WEF (2020) 5 droughts that changed human history. In: World Economic Forum. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2019/05/5-droughts-that-changed-human-history/. Accessed 23 Feb 2020
Wilhite D (2000) Chapte drought as a natural hazard: concepts and definitions. Drought Mitigation Center Faculty Publications
Wilhite DA, Glantz MH (1985) Understanding: the drought phenomenon: the role of definitions. Water International 10:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508068508686328
Wu J, Chen X, Yao H et al (2017) Non-linear relationship of hydrological drought responding to meteorological drought and impact of a large reservoir. J Hydrol 551:495–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.029
Xu Z, Wu Z, He H et al (2019) Evaluating the accuracy of MSWEP V2.1 and its performance for drought monitoring over mainland China. Atmos Res 226:17–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.04.008
Yeh H-F (2019) Using integrated meteorological and hydrological indices to assess drought characteristics in southern Taiwan. Hydrol Res 50:901–914. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2019.120
Yılmaz M, Alp H, Tosunoğlu F et al (2022) Impact of climate change on meteorological and hydrological droughts for Upper Coruh Basin, Turkey. Nat Hazards 112:1039–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05217-x
Yuan X, Zhang M, Wang L, Zhou T (2017) Understanding and seasonal forecasting of hydrological drought in the anthropocene. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 21:5477–5492. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-21-5477-2017
Yuce MI, Esit M (2021) Drought monitoring in Ceyhan Basin, Turkey. J Appl Water Eng Res 9:293–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/23249676.2021.1932616
Yuce MI, Deger IH, Esit M (2023) Hydrological drought analysis of Yeşilırmak Basin of Turkey by streamflow drought index (SDI) and innovative trend analysis (ITA). Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04545-7
Yue S, Pilon P, Cavadias G (2002a) Power of the Mann-Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J Hydrol 259:254–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00594-7
Yue S, Pilon P, Phinney B, Cavadias G (2002b) The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol Process 16:1807–1829. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1095
Zhang T, Su X, Zhang G et al (2022) Evaluation of the impacts of human activities on propagation from meteorological drought to hydrological drought in the Weihe River Basin China. Sci Tot Environ 819:153030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153030
Zhou Z, Shi H, Fu Q et al (2020) Assessing spatiotemporal characteristics of drought and its effects on climate-induced yield of maize in Northeast China. J Hydrol 588:125097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125097
Zhou Z, Shi H, Fu Q et al (2021) Characteristics of propagation from meteorological drought to hydrological drought in the pearl river basin. J Geophys Res 126:e2020JD033959. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JD033959
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgements are due to state water Works (DSI), general directorate of meteorology (MGM) for providing meteorological data
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.E. wrote the manuscript, prepared analysis; R.Ç. read and revised manuscript; E.A. prepared good quailty figures
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Informed consent
This study did not include any human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Esit, M., Çelik, R. & Akbas, E. Long-term meteorological and hydrological drought characteristics on the lower Tigris-Euphrates basin, Türkiye: relation, impact and trend. Environ Earth Sci 82, 491 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11182-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11182-w