Abstract
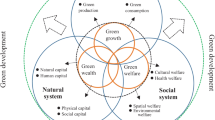
To develop the economy on the premise of protecting the environment and apply modern emerging technologies such as big data to rural work, China put forward the rural revitalization strategy. The focus of rural revitalization is to promote green technologies, such as big data and artificial intelligence, turn rich green resources into green capital, and let these technologies drive people to develop green lifestyles, build beautiful China and realize the sustainable development of the Chinese nation. To measure the level of rural green development in Hunan Province, this paper selects 14 indicators from four aspects: green economy, green investment, green utilization and green security. The entropy method is used to give weight to each index of the evaluation system of rural green development level in Hunan Province, and comprehensive evaluation and classification measurement are carried out. The research in this paper enriches the empirical data of rural green development, and also provides ideas for China and other countries to use emerging technologies to develop green economy, which has important reference significance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Chenghao Q (2017) Research on evaluation of China’s agricultural green development level in the economic transition period—based on entropy method [J]. Prices China 11:16–19
Gheisari M, Esmaeili-Najafabadi H, Alzubi JA et al (2021) OBPP: an ontology-based framework for privacy-preserving in IoT-based smart city [J]. Future Gener Comput Syst 123:13
Gil J, Torres JM, González-Crespo R (2020) The application of artificial intelligence in project management research: a review [J]. Int J Interact Multimed Artif Intell 6(6):54
Huan Z, Chang L, Jinhua C, Hongtao W (2016) Measurement of green development level and its spatial relationship in Hubei Province [J]. Econ Geogr 36(09):158–165
Huang DP, Wang YF, Sun JJ (2019) Comprehensive evaluation of agricultural green development level in Anhui Province [J]. J Inner Mongolia Agric Univ (social Science Edition) 21(04):7–13
Khan S, Kannapiran T (2019) Indexing issues in spatial big data management [J]. SSRN Electr J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3387792
Li C, Chuanhao W (2019) Study on the level of rural green development in the Yangtze river economic belt and its multi-dimensional interpretation [J]. J Nantong Univ (Social Science Edition) 35(04):29–37
Li X, Jin-jin W (2016) Spatial differences of rural green development performance in China [J]. China Popul Resour Environ 26(06):20–26
Saravanan V, Pralhaddas KD, Kothari DP et al (2015) An optimizing pipeline stall reduction algorithm for power and performance on multi-core CPUs [J]. Hum Cent Comput Inform Sci. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13673-014-0016-8
Weilin S, Ruibo W, Qian J, Shengnan H (2019) Study on the connotation and evaluation of agricultural green development [J]. J Agric Resour Reg Plan China 40(04):14–21
Xiang X, Li Q, Khan S, Khalaf OI (2021) Urban water resource management for sustainable environment planning using artificial intelligence techniques [J]. Environ Impact Assess Rev 86:106515
Xiaonan L, Erxun Z, Ruoang F (2018) Green Development level measurement and spatial difference analysis in Shandong Province [J]. Land Nat Resour Res 01:38–44
Yang C, Zhu YL (2015) Dynamic research on green development at home and abroad. J Cent South Univ For Technol (Social Science Edition) 9(06):43–50
Ye LN, Gao GY (2018) Study on measurement of agricultural green development level and influencing factors in Ningxia [J]. Res Agric Sci 39(01):1–5
Yu KH, Li YZD, Montenegro-Marin CE et al (2021) Environmental planning based on reduce, reuse, recycle and recover using artificial intelligence [J]. Environ Impact Assess Rev 86:106492
Yue WB (2016) Construction and evaluation of agricultural green development index system in China [J]. J Jiamusi Voc Coll 07:470–471
Zhang N, Zhang L, Zhao H, Han Y, Duan Y (2018) Construction and application of evaluation index system for agricultural green development [J]. Ecol Econ 34(11):21-24+46
Zhichuan Z, Xinxin W (2019) Measurement analysis of China’s agricultural green development based on DEA model [J]. J Mudanjiang Norm Univ (Natural Science Edition) 03:1–9
Zhou HC (2018) Agricultural and rural green development under the background of rural revitalization. Environ Prot 46(07):16–20
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Social Science Fund “Design and Measurement of Evaluation Index System of China’s High-quality Economic Development” (20BTJ011).
Funding
This work was supported by National Social Science Fund “Design and Measurement of Evaluation Index System of China's High-quality Economic Development” (20BTJ011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZT and GX, conceptualized the model, collected relevant index details, analyzed and visualized the model through valuable evaluation and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
No conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of a Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on Deep learning for earth resource and environmental remote sensing, guest edited by Carlos Enrique Montenegro Marin, Xuyun Zhang and Nallappan Gunasekaran.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, Z., Xiang, G. Empirical measurement and evaluation of rural green development: take Hunan Province, China as an example. Environ Earth Sci 81, 268 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10398-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10398-6