Abstract
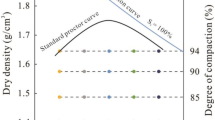
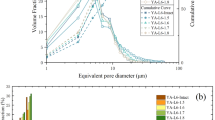
Compacted loess soil is used as a geo-material in many engineering projects, such as building foundations and highway embankments. Water infiltration characteristics and post settlement of the compacted loess in large construction projects of Northwest China have received increasing attention from researchers and investors. These behaviors are closely related to the soil water characteristics. This study aims to investigate the soil water characteristic curves (SWCCs) of compacted loess soil with different dry densities and to reveal the responsible micro-mechanisms for soil water characteristics. Loess soil collected from the new district of Yan’an City, China, is prepared into five dry density groups. The SWCC of each group in the suction range of 0–105 kPa is measured using the filter paper method (FPM). Two-dimensional (2D) images and the pore size distribution (PSD) curves of the specimens are tested by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and the mercury pressure method (MIP), respectively. The results of this study highlight that the compaction behavior mainly influences the pores with a radius (r) in the range of 1–10 μm, and has no influence on the pores of r < 0.5 μm. The particle shapes among the five dry densities groups are similar. The characteristics of the PSD curves of the compacted loess soil correspond well to the SWCCs. The suction of the SWCCs increases with increasing dry density in the lower suction range of 0–100 kPa. In contrast, suction among the five dry density groups is almost identical in the suction range exceeding 100 kPa. The results of the study are helpful to understand the SWCC and microstructure characteristics of compacted loess with different dry densities.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Al-Khafaf S, Hanks RJ (1974) Evaluation of the filter paper method for estimating soil water potential. Soil Sci 117(4):194–199. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-197404000-00003
Altuhafi FN, Coop MR, Georgiannou VN (2016) Effect of particle shape on the mechanical behavior of natural sands. J Geotechn Geoenviron Eng 142(12):4016071. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001569
ASTM (2003) Standard test method for measurement of soil potential (suction) using filter paper. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA. https://doi.org/10.1520/D5298-94
Baker R, Frydman S (2009) Unsaturated soil mechanics: critical review of physical foundations. Eng Geol 106(1–2):26–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.02.010
Bharat TV, Gapak Y (2021) Soil-water characteristic curves of bentonites in isochoric conditions during wetting: measurement and prediction. Canadian Geotech J 58(5):711–721. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2019-0818
Birle E, Heyer D, Vogt N (2008) Influence of the initial water content and dry density on the soil-water retention curve and the shrinkage behavior of a compacted clay. Acta Geotech 3(3):191–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-008-0059-y
Birle E (2012) Effect of initial water content and dry density on the pore structure and the soil-water retention curve of compacted clay. In: Mancuso C, Jommi C, D’Onza F (eds) Unsaturated soils: research and applications. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31116-1_19
Deacon LJ, Grinev DV, Crawford JW, Harris J, Ritz K, Young IM (2008) Simultaneous preservation of soil structural properties and phospholipid proflles: a comparison of three drying techniques. Pedosphere 18(3):284–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(08)60018-1
Delage P, Audiguier M, Cui YJ, Howat MD (1996) Microstructure of a compacted silt. Can Geotech J 33(1):150–158. https://doi.org/10.1139/t96-030
Delage P (2007) Microstructure features in the behaviour of engineered barriers for nuclear waste disposal. In: Schanz T (ed) Experimental unsaturated soil mechanics. Springer Proceedings in Physics, vol 112. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-69873-6_2
Della Vecchia G, Jommi C, Romero E (2011) An insight into the water retention properties of compacted clayey soils. Géotechnique 61(4):313–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-69873-6_2
Diamond S (1970) Pore size distributions in clays. Clays Clay Miner 18(1):7–23. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1970.0180103
Eyo E, Ngambi S, Abbey SJ (2020) An overview of soil-water characteristic curves of stabilised soils and their influential factors. J King Saud Univers Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2020.07.013
Fredlund DG (2006) Unsaturated soil mechanics in engineering practice. J Geotechn Geoenviron Eng 132(3):286–321. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:3(286
Genuchten V, Th M (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44(5):892–898. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
Guorui G, Guoyou G (1980) Microstructures of loess soil in China. Mon J Sci 7:63–67 (in Chinese)
Guorui G (1981) Classification of microstructure of loess in China and their collapsibility. Scientia Sinica Ser A 7:962–974 (in Chinese)
Hou X, Qi S, Li T, Guo S, Wang Y, Li Y, Zhang L (2020) Microstructure and soil-water retention behavior of compacted and intact silt loess. Eng Geol 277:105814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105814
Jiang M, Zhang F, Hu H, Cui Y, Peng J (2014) Structural characterization of natural loess and remolded loess under triaxial tests. Eng Geol 181:249–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.021
Jiang Y, Chen W, Wang G, Sun G, Zhang F (2017) Influence of initial dry density and water content on the soil-water characteristic curve and suction stress of a reconstituted loess soil. Bull Eng Geol Env 76(3):1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0899-x
Jiang M (2019) New paradigm for modern soil mechanics: geomechanics from micro to macro. Chin J Geotech Eng 41.02(2019):195–254 (in Chinese)
Li Y (2013) Effects of particle shape and size distribution on the shear strength behavior of composite soils. Bull Eng Geol Env 72(3–4):371–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0482-7
Li X, Li L (2017) Quantification of the pore structures of Malan loess and the effects on loess permeability and environmental significance, Shaanxi Province, China: an experimental study. Environ Earth Sci 76(15):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6855-7
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2014) Environment: Accelerate research on land creation. Nature 510(7503):29–31. https://doi.org/10.1038/510029a
Li P, Li T, Vanapalli SK (2018) Prediction of soil-water characteristic curve for Malan loess in Loess Plateau of China. J Central South Univers 25(2):432–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3748-1
Li X, Li L, Song Y, Hong B, Wang L, Sun J (2019) Characterization of the mechanisms underlying loess collapsibility for land-creation project in Shaanxi Province, China—a study from a micro perspective. Eng Geol 249:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.12.024
Li H, Li TL, Li P, Zhang YG (2020a) Prediction of loess soil-water characteristic curve by mercury intrusion porosimetry. J Mt Sci 17(9):2203–2213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5929-2
Li H, Li T, Jiang R, Wang Y, Zhang Y (2020b) A new method to simultaneously measure the soil–water characteristic curve and hydraulic conductivity function using filter paper. Geotech Test J 43(6):20190162. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20190162
Lu N (2016) Generalized soil water retention equation for adsorption and capillarity. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 142(10):04016051. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001524
Lu N (2019) Linking soil water adsorption to geotechnical engineering properties. In: Lu N, Mitchell J (eds) Geotechnical fundamentals for addressing new world challenges. Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06249-1_4
Lu N, Khorshidi M (2015) Mechanisms for soil-water retention and hysteresis at high suction range. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 141(8):04015032. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001325
Lu N, Likos WJ (2006) Suction stress characteristic curve for unsaturated soil. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 132(2):131–142. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:2(131)
Mbonimpa M, Aubertin M, Maqsoud A, Bussière B (2006) Predictive model for the water retention curve of deformable clayey soils. J Geotechn Geoenviron Eng 132(9):1121–1132. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:9(1121)
Miguel MG, Bonder BH (2012) Soil-water characteristic curves obtained for a colluvial and lateritic soil profile considering the macro and micro porosity. Geotech Geol Eng 30(6):1405–1420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-012-9545-y
Mijares RG, Khire MV (2010) Soil water characteristic curves of compacted clay subjected to multiple wetting and drying cycles. Geotech Spec Publ 199:400–409. https://doi.org/10.1061/41095(365)37
Nie B, Liu X, Yang L, Meng J, Li X (2015) Pore structure characterization of different rank coals using gas adsorption and scanning electron microscopy. Fuel 158:908–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.06.050
Pagliai M, Vignozzi N, Pellegrini S (2004) Soil structure and the effect of management practices. Soil Tillage Res 79(2):131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2004.07.002
Pincus HJ, Houston SL, Houston WN, Wagner AM (1994) Laboratory filter paper suction measurements. Geotech Test J 17(2):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ10090J
Rahardjo H, Leong EC (2006) Suction measurements. Unsaturated Soils. https://doi.org/10.1061/40802(189)3
Ran H, Chen Y, Liu H, Zhou C (2013) A water retention curve and unsaturated hydraulic conductivity model for deformable soils: consideration of the change in pore-size distribution. Géotechnique 63(16):1389–1405. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.12.P.182
Revil A, Lu N (2013) Unified water isotherms for clayey porous materials. Water Resour Res 49(9):5685–5699. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrcr.20426
Romero E, Gens A, Lloret A (1999) Water permeability, water retention and microstructure of unsaturated compacted Boom clay. Eng Geol 54(1–2):117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(99)00067-8
Salager S, Nuth M, Ferrari A, Laloui L (2013) Investigation into water retention behaviour of deformable soils. Can Geotech J 50(2):200–208. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2011-0409
Sasanian S, Newson TA (2013) Use of mercury intrusion porosimetry for microstructural investigation of reconstituted clays at high water contents. Eng Geol 158:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.03.002
Shepard FP (1954) Nomenclature based on sand-silt-clay ratios. J Sediment Res 24(3):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1306/D4269774-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Vanapalli SK, Fredlund DG, Pufahl DE (2001) Influence of soil structure and stress history on the soil-water characteristics of a compacted till. Géotechnique 51(6):573–576. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.51.6.573.40456
Wang JD, Li P, Ma Y, Vanapalli SK, Wang XG (2019) Change in pore-size distribution of collapsible loess due to loading and inundating. Acta Geotech 15(5):1081–1094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-019-00815-9
Washburn EW (1921) Note on a method of determining the distribution of pore sizes in a porous material. Proc Natl Acad Ences USA 7(4):115–116. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.7.4.115
Xu P, Zhang Q, Qian H, Qu W, Li M (2020) Microstructure and permeability evolution of remolded loess with different dry densities under saturated permeation. Eng Geol 282(7):105875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105875
Zhang P, Fang YG, Yan XQ, He ZW (2011) Study of different dry methods for drying remolded bentonite sample with mercury intrusion test. Rock Soil Mech 32:388–391 (in Chinese)
Zhang X, Mavroulidou M, Gunn MJ (2017) A study of the water retention curve of lime-treated London Clay. Acta Geotech 12(1):23–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-015-0432-6
Zhou AN, Sheng D, Carter JP (2012) Modelling the effect of initial density on soil-water characteristic curves. Geotechnique 62(8):669–680. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.10.P.120
Funding
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41790442, 41772278, 41807242). The above financial supports are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Li, T., Zhao, C. et al. A study on the effect of pore and particle distributions on the soil water characteristic curve of compacted loess soil. Environ Earth Sci 80, 764 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09973-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09973-0