Abstract
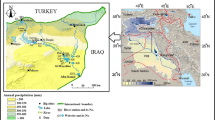
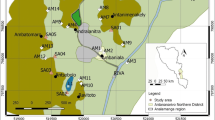
This study is focused on the groundwater system of the Rashche Spring which serves as the main source of drinking water for the City of Skopje, located at the foot of the widely karstified Zeden massif. Investigations were made to define the mechanisms of groundwater recharge and its residence time. This was done using isotope tracers including 1H, 2H, 3H, and 18O in water samples from the local hydrological cycle, as well as noble gases for the application of 3H/3He dating method. A linear regression model of stable isotope data of precipitation samples resulted in the best-fit equation of δ2H = 7.46 · δ18O + 9.56, and shows a δ2H dependence from the altitude of precipitation formation with a gradient of − 3.06‰/100 m. Local precipitation, surface waters and Rashche Spring water showed a relatively narrow range of tritium values of 5 ± 1 TU, whereas the deep artesian water from Polog Valley yielded very low tritium contents (< 0.5 TU). In addition to this, we applied a one-cell mixing model with three inlet components (precipitation, Vardar River and deep artesian water). Numerical simulation based on tritium data of local precipitation and based on a defined ratio of the inlet components allowed calculation of the MRT (mean residence time) of 30 years for the water of the aquifer located below the Zeden Massif which is recharging the Rashche Spring. Using the 3H/3He dating method, the ages of observed ground water including the water from the Rashche Spring were determined showing a good agreement with the calculated MRT. This result also provides substantial information about the vulnerability of this water resource and the necessity for better conservation of the investigated local surface and groundwater.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeschbach-Hertig W, Peeters F, Beyerle U, Kipfer R (1999) Interpretation of dissolved atmospheric noble gases in natural waters, hydrogeochemistry and water chemistry. Water Resour Res 35(9):2779–2792
Anovska-Jovcheva E (2010) Appl. of the boundary element method, multi-domain approach and simulation of tritium concentration to determining the properties of the Galichica Mountain Aquifer. M. Phil. Thesis, Univ. of Wales, UK, p 121 (in English)
Anovska-Jovcheva E, Jovchev Z, Anovski T, Popov V (2011) Determining MRT of groundwater by application of the distribution of environmental (hydrogen and oxygen) isotopes. In: Proceedings of international symposium on isotopes in hydrology, marine ecosystems, and climate change studies, IAEA-CN-186. Monaco (27 March–1 April, 2011)
Anovska-Jovcheva E, Lisichkov K, Anovski K, Matsumoto T, Aggarwal P, Leis A, Micevski E, Anovski T (2013) Modeling the mechanisms of water recharge of the Rasche Spring by using of tritium simulations supported by T(3He) method. Geophysical Research Abstract, vol. 15.EGU, 3373-4
Anovski T (1977) Application of tritium in establishing the origin of water in Springs. Master Thesis, University of Zagreb, Croatia
Arsovski M (1966) General characteristics of the Geological structures at the territory of the SRM. Fund of the Geological Survey, Skopje
Arsovski M (1997) Tectonics of the Republic of Macedonia (Tectonic Map), fund of the faculty for mining and geology. Stip, Republic of Macedonia
Bear J (1969) Hydrodynamic dispersion. In: De Wiest RJM (ed) Flow through porous media. Academic Press, New York
Brand WA, Geilmann H, Crosson ER, Rella CW (2009) Cavity ring-down spectroscopy versus high-temperature conversion isotope ratio mass spectrometry; a case study on δ2H and δ18O of pure water samples and alcohol/water mixtures. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23(12):1879–1884
Craig H (1961a) Standards for reporting concentrations of deuterium and oxygen-18 in natural waters. Science 133:1833–1834
Craig H (1961b) Isotopic variation in meteoric waters. Science 133:1702–1703
IHP-V (2000) Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle. Mook WG (ed) Technical document in hydrology (no. 39, vol. I). UNESCO, Paris
Jovanovic PS (1925) Spring.., Bull. of the Geographic Soc., Series 11. Belgrade
Kekic A (1973) Hydrogeological characteristics of the Polog Plane, Ph.D. Thesis at the University of Belgrade (in Serbo-Croatian with an abstract in English)
Kirkov P, Kacurkov D, Tolev M, Anovski T (1974) Determination of the origin of water in springs from the simultaneous application of natural and artificial isotopes. Some aspects of the origin of water in the Rashche Spring. In: Proc. of the Inter. Symp. on Isotope Tech.in Groundwater Hydrology. IAEA-SM-182/23
Kotevski Gj (1987) Hydrogeologijata na mineralnite, termalnite i termomineralnite vodi vo teritorijata na SRM. Samoupravna praktika, Skopje
Manakovic D (1962) Origin…., Bull. of the Univ. of Skopje, Geogr. and geol., v. 13, ser. 1
Matsumoto T, Solomon K, Han L-H, Hillegonds JD, Araguas-Araguas L, Aggarwal P, The CRP Participating Teams (2016) Tritium-Helium-3 dating and noble gas techniques in water resources management: Noble gas analysis at the IAEA & Data synthesis from the coordinated research project, Geochemical Journal (Submitted, 2016)
Mitrov T, Angelovski A (1974) Summary on Hydrogeological and Hydro- meteorological investigations related to the origin of water of the Rashche Spring. Department of Faculty for Architecture and Civil Engineering, Skopje
Moser H et al (1978) Jahresbericht 1978. Inst. Fur Radiohydrometrie der Gesellschaft f. Strahen und Umweltforschung mbH, Munich, pp 99–103
Schlosser P (1992) Tritium/3He dating of waters in naturals systems. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): IAEA
Simpson ES (1972) Application of the multi-cell mixing models to the interpretation of the environmental isotope data, IAEA Internal Report
SYNTHESIS REPORT (1967) On performed investigation related to the determination of the Origin of the water in Rashche Spring. Archive of the City of Skopje
REPORT on Lab. tritium analyses (1976) Fund of the Center for Application of radioisotopes in Science and Industry (CARSI)
REPORT on Lab. tritium analyses, 2000. Fund of the Center for Application of radioisotopes in Science and Industry (CARSI)
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Dr. Takuya Matsumoto from the Isotope Hydrology Section, IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency), Vienna, Austria, for his useful comments and suggestions toward improving the overall scope of the presented paper. Thanks are also directed to the Municipality of Skopje City, Republic of North Macedonia and to the IAEA, for their valuable support during the realization of the performed investigations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anovski, T., Anovska-Jovcheva, E., Lisichkov, K. et al. Application of environmental isotope techniques for determining the origin and mechanisms of recharge of the Rashche Spring. Environ Earth Sci 78, 656 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8674-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8674-5