Abstract
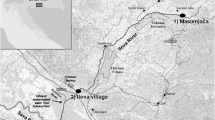
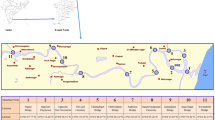
Sediment and water samples were taken at eight points along the Drenica River, Kosovo to determine the distribution of metals (Cr, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Cr) in sediments and the water column near potential sources of contamination. The sampling indicated that the largest impact on sediment quality has come from anthropogenic activities, mostly from urban flows, and pollutants from waste water discharges from a nickel refining site. Based on the values of the content of heavy metals in the water and sediment resulting in locations taken in the study, it can be said that a nickel refining site is the biggest polluter of Drenica River. Parameters in waters, such as electrical conductivity, and total dissolved solids in some sampling points reach relatively high values but do not exceed the maximum concentrations allowed under international standards, even on some places are rather close to them. The concentration of dissolved oxygen in vicinity of the factory is very low and approaches values causing fish kills. According to concentrations of some heavy metals, particularly of Ni, sediments on some stations show values characteristic for highly and extremely contaminated sediments. Further regular monitoring of water and sediment in Drenica River is highly encouraged and advised.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, AWWA, WEF (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. Washington DC
Baba A, Kaya A, Birsoy KY (2003) The effect of Yatagan thermal power plant (Mugla, Turkey) on the quality of surface and ground waters. Water Soil Pollut 149:93–111
Bratli LJ (2000) Classification of the environmental quality of freshwater in Norway. In: Heinonen et al (ed) Hydrological and limnological aspects of lake monitoring. John Willey and Sons Ltd., pp 331–343
Çullaj A, Hasko A, Miho A, Schanz F, Brandl H, Bachofen R (2005) The quality of Albanian natural waters and the human impact. Environ Int 31:133–146
Dalmacija B (2000) Water quality control in towards of quality management, text book
Demaku S, Dobra B, Shehu I, Korca B, Shala F, Kastrati G (2012) Heavy metals in the River Drenica (Kosova) from the deposited ash of the complex “New Ferronickel”. J Int Environ Appl Sci 7(1):178–183
Faiku F, Hazir I, Gashi F, Troni N, Haziri I (2015) Assessment of river water quality Lumbardh of Deçan (Kosovo). Eur Chem Bull 4(3):169–176
Frančišković-Bilinski S (2007) An assessment of multielemental composition in stream sediments of Kupa River drainage basin, Croatia for evaluating sediment quality guidelines. Fresenius Environ Bull 16(5):561–575
Frančišković-Bilinski S, Cuculić V, Bilinski H, Häusler H, Stadler Ph (2013) Geochemical and stable isotopic variability within two rivers rising under the same mountain, but belonging to two distant watersheds. Chem Erde 73:293–308
Gashi F, Frančišković-Bilinski S, Bilinski H (2009) Analysis of sediments of the four main rivers (Drini i Bardhë, Morava e Binces, Lepenc and Sitnica) in Kosovo. Fresenius Environ Bull 18:1462–1471
Gashi F, Frančišković-Bilinski S, Bilinski H, Troni N, Bacaj M (2011) Establishing of monitoring network on Kosovo Rivers: preliminary measurements on the four main rivers (Drini i Bardhë, Morava e Binqës, Lepenc and Sitnica). Environ Monit Assess 175:279–289
Gashi F, Troni N, Faiku F, Laha F, Haziri A, Kastrati I, Beshtica E, Behrami M (2013) Chemical and statistical analyses of elements in river water of Morava e Binçës. Am J Environ Sci 9(2):142–155
Gashi F, Troni N, Hoti R, Faiku F, Ibrahimi R, Laha F, Kurteshi K, Osmani S, Hoti F (2014) Chemical determination of some elements in water of Sitnica (Kosovo) by ICP-MS technique. Fresenius Environ Bull 23(1):91–97
Halamić J, Bukovec D, Miko S, Galović L (2001) A factor model of the relationship between stream sediment geochemistry and adjacent drainage basin lithology, Medvednica Mt., Croatia. Geol Croat 54(1):37–51
ISO 13196:2013 (2015) Soil quality—Screening soils for selected elements by energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry using a handheld or portable instrument
Krasniqi I, Fejza I, Avdullahi S, Vasjari M, Vaso K, Krasniqi K, Behrami A (2010) Level of heavy metals and the impact of anthropogenic pollution on some alternative springs in Drenica and Mitrovica Zone, Kosovo. J Int Environ Appl Sci 5(3):186
Ministry of Environment and Spatial Planning (2011) State of environment in Kosovo 2008–2010, Report. Kosovo Environmental Protection Agency, Prishtina, p 147. Available at: http://www.ammk-rks.net/repository/docs/The_state_of_environment_in_Kosovo_2008-2010_%281%29.pdf
Montgomery JM (1996) Water treatment, principles and design. Wiley, New York
Persaud DR, Jagumagi R, Hayto A (1993) Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediments in Ontario. Standards Development Branch. Ontario Ministry of Environment and Energy, Canada
Skoog DA, West DM, Holler FJ (1992) Fundamentals of analytical chemistry. New York, London
StatSoft Inc. (2001) STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 6. http://www.statsoft.com
Troni N, Faiku F, Gashi F, Hoti R, Teneqja V, Laha F, Berisha R (2013) Chemical characterization of some toxic elements of Lumbardhi River. Int J Green Herbal Chem 2(2):203–207
Tukey JW (1977) Exploratory data analysis. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Veliu A, Syla A, Gashi S (2008) The influence of ferronikeli smelter in surface and ground waters of the River Drenica. Nat Montenegrina 7(2):535–540
WHO (2006) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, vol 1, 3rd edn. Geneva
Acknowledgments
This study is a part of M.sc. Thesis of Leutrim Kika (supervisor Dr. Fatbardh Gashi, from the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Natural Sciences, University of Prishtina, Kosovo). Colleges from the Department of Chemistry and Geography, University of Prishtina are thanked for their assistances.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gashi, F., Frančišković-Bilinski, S., Bilinski, H. et al. Assessment of the effects of urban and industrial development on water and sediment quality of the Drenica River in Kosovo. Environ Earth Sci 75, 801 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5612-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5612-7