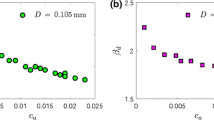
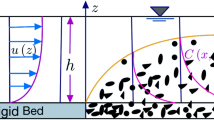
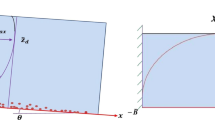
Abstract
In this paper the effect of variation of bed roughness along lateral direction on suspension concentration distribution in open channel turbulent flows was investigated. Starting from the mass and momentum conservation equations, this study demonstrates that both the Reynolds shear stress \((-\overline{u'v'})\) and sediment diffusivity depends on bed roughness. From the theoretical analysis, it is found that both the Reynolds shear stress and the sediment diffusivity increase over smooth bed surfaces and decrease over rough bed surfaces. At the junction of smooth and rough bed surface, the effect of bed roughness on the Reynolds shear stress and sediment diffusion is almost negligible. Including this effect, suspension concentration distribution is also studied and from the Hunt’s diffusion equation, an analytical model for predicting suspension concentration is proposed. Apart from this effect, the effects of moveable bed roughness and stratification are also considered in the model. It is observed that the Rouse equation is obtained from the proposed model as a special case when the flow is considered as single phase and there is no effect of secondary current, stratification and bed roughness variation. On the basis of experimental data available in literature, the proposed model is validated and also compared with the Rouse equation. To get a quantitative idea about the goodness of fit, weighted relative error is calculated. The comparison results and calculated errors indicate that the present model is capable of describing the suspension concentration distribution more accurately than Rouse model throughout the flow depth in open channel flow.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(A+1\) :
-
\((=\rho _{\rm s}/\rho _{\rm f})\) Specific gravity of particles
- Ar:
-
\((=b/h)\) Channel aspect ratio
- \({\rm Ar}_{\rm crit}\) :
-
Critical aspect ratio
- \(B_{\rm s}\) :
-
Log law constant
- b :
-
Channel width
- C :
-
Volumetric sediment concentration
- \(C_{\rm a}\) :
-
Reference concentration
- \(C_{\rm d}\) :
-
Drag coefficient
- \(C_{\rm m}\) :
-
Maximum volumetric concentration
- d :
-
Particle diameter
- \(d_*\) :
-
Dimensionless particle diameter
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration
- h :
-
Flow depth
- \(k_{\rm s}\) :
-
Bed roughness height
- \(l_{\rm r}\) :
-
\((=k_{\rm s}/h)\) Relative bed roughness height
- \(M_*\) :
-
Density coefficient of bed material
- n :
-
Number of data points
- \(P_*\) :
-
Grain size percentage
- \({\rm Re}_*\) :
-
Roughness Reynolds number
- \({\rm R}_i\) :
-
Richardson number
- S :
-
Channel slope
- \(S_*\) :
-
Fluid-sediment parameter
- \(S_1\) :
-
Sum of residuals
- \(S_{\rm c}\) :
-
(\(1/\gamma \)) Schmidt number
- \(S_{\rm co}\) :
-
Computed concentration
- \(S_{\rm o}\) :
-
Observed concentration
- u :
-
Streamwise velocity
- \(u'\) :
-
Fluctuating part of u
- \(u_*\) :
-
Shear velocity
- \(u_{\rm surf}\) :
-
Fluid surface velocity
- v :
-
Vertical component of velocity
- \(v'\) :
-
Fluctuating part of v
- \(V_{\rm wind}\) :
-
Wind velocity
- w :
-
Lateral component of velocity
- \(w'\) :
-
Fluctuating part of w
- \(\overline{u'v'}\), \(\overline{u'w'}\) :
-
Reynolds shear stresses
- x :
-
Longitudinal co-ordinate
- y :
-
Vertical co-ordinate
- \(y_0\) :
-
Moveable bed roughness height
- z :
-
Lateral co-ordinate
- \(\alpha \) :
-
A parameter
- \(\beta \) :
-
Parameter
- \(\beta _1\) :
-
Stratification parameter
- \(\varepsilon _{\rm s}\) :
-
Sediment diffusion coefficient
- \(\varepsilon _{\rm sn}\) :
-
Sediment diffusivity in neutral flow
- \(\varepsilon _{\rm m}\) :
-
Momentum diffusion coefficient
- \(\varepsilon _{\rm mn}\) :
-
Momentum diffusivity in neutral flow
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Proportionality constant
- \(\kappa \) :
-
von Karman coefficient
- \(\mu \) :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- \(\mu _*\) :
-
Relative viscosity
- \(\nu \) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \(\psi \) :
-
Shields parameter
- \(\psi _*\) :
-
Critical shields parameter
- \(\phi \), \(\varPhi \), \(\varPsi \) :
-
functions
- \(\rho _{\rm f}\) :
-
Density of fluid
- \(\rho _{\rm air}\) :
-
Density of air
- \(\theta \) :
-
Angle for channel slope
- \(\tau \) :
-
Total shear stress
- \(\tau _{\rm b}\) :
-
Bed shear stress
- \(\tau _{xy}\), \(\tau _{xz}\) :
-
Components of total shear stresses
- \(\eta \) :
-
\((=z/h)\) Dimensionless lateral coordinate
- \(\xi \) :
-
\((=y/h\)) Dimensionless depth
- \(\omega _0\) :
-
Particle settling velocity
- \(\omega _*\) :
-
Relative settling velocity
References
Armenio V, Sarkar S (2002) An investigation of stably stratified turbulent channel flow using large-eddy simulation. J Fluid Mech 459:1–42. doi:10.1017/S0022112002007851
Bogardi J (1974) Sediment transport in alluvial streams. Akademial Kiodo, Budapest
Bonakdari H, Larrarte F, Lassabatere L, Joannis C (2008) Turbulent velocity profile in fully-developed open channel flows. Environ Fluid Mech 8:1–17
Bose SK, Dey S (2009) Suspended load in flows on erodible bed. Int J Sediment Res 24:315–324
Businger JA, Wyngaard JC, Izumi Y, Bradley EF (1971) Flux-profile relationships in the atmospheric surface layer. J Atmos Sci 28:181–189
Cao Z, Wei L, Xie J (1995) Sediment-laden flow in open channels from two-phase flow viewpoint. J Hydraul Eng 121(10):725–735
Cheng NS (2003) A diffusive model for evaluating thickness of bedload layer. Adv Water Resour 26:875–882
Chiu CL, McSparran JE (1966) Effect of secondary flow on sediment transport. Proc ASCE 92(HY5):57–70
Coleman JM (1969) Brahmaputra river; channel process and sedimentation. Sediment Geol 3:129–239
Coleman NL (1986) Effects of suspended sediment on the open-channel velocity distribution. Water Resour Res 22(10):1377–1384
Colombini M (1993) Turbulence driven secondary flows and the formation of sand ridges. J Fluid Mech 254:701–719. doi:10.1017/S0022112093002319
Dallali M, Armenio V (2015) Large eddy simulation of two-way coupling sediment transport. Adv Water Resour 81:33–44. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2014.12.004
Einstein HA, Chien NS (1955) Effects of heavy sediment concentration near the bed on velocity and sediment distribution. US Army Corps of Engineers, Missouri River Division, Report No. 8
Falcomer L, Armenio V (2002) Large-eddy simulation of secondary flow over longitudinally-ridged walls. J Turbul 3:1–17. doi:10.1088/1468-5248/3/1/008
Graf WH (1971) Hydraulics of sediment transport. McGraw-Hill, New York
Guo J, Julien PY (2001) Turbulent velocity profiles in sediment-laden flows. J Hydraul Res 39(1):11–23
Herrmann MJ, Madsen OS (2007) Effect of stratification due to suspended sand on velocity and concentration distribution in unidirectional flows. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2006JC003569
Huang S, Sun Z, Xu D, Xia S (2008) Vertical distribution of sediment concentration. J Zhejiang Univ Sci A 9(11):1560–1566
Immamoto H, Ishigaki T (1988) Measurement of secondary flow in an open channel. In: Proceedings of the 6th IAHR-APD Congress, Kyoto, Japan, pp 513–520
Jan CD, Wang JS, Chen TH (2006) Discussion of simulation of flow and mass dispersion in meandering channel. J Hydraul Eng 132(3):339–342
Karcz I (1981) Reflections on the origin of small scale longitudinal streambed scours. In: Morisawa M (ed) Fluvial geomorphology: a Proceedings of the forth annual geomorphology symposia series. Allen and Unwin, London, pp 149–177
Kinoshita R (1967) An analysis of the movement of flood waters by aerial photography; concerning characteristics of turbulence and surface. Photogr Surv 6:1–17 (in Japanese)
Kundu S, Ghoshal K (2012) An analytical model for velocity distribution and dip-phenomenon in uniform open channel flows. Int J Fluid Mech Res 39(5):381–395
Kundu S, Ghoshal K (2014) Effects of secondary current and stratification on suspension concentration in an open channel flow. Environ Fluid Mech 14(6):1357–1380
Liao K, Qu J, Tang J, Ding F, Liu H, Zhu S (2010) Activity of wind-blown sand and the formation of feathered sand ridges in the Kumtagh Desert, China. Bound Layer Meteorol 135:333–350. doi:10.1007/s10546-010-9469-0
Mazumder BS, Ghoshal K (2006) Velocity and concentration profiles in uniform sediment-laden flow. Appl Math Model 30:164–176
Monin AS, Yaglom AM (1971) Statistical fluid mechanisms. MIT Press, Cambridge
Nezu I, Nakagawa H (1993) Turbulence in open-channel flows. IAHR monograph. Balkema, Rotterdam
Nezu I, Rodi W (1985) Experimental study on secondary currents in open channel flow. In: 21th IAHR congress. IAHR, Melbourne, pp 115–119
Nezu I, Nakagawa H, Kawashima N (1988) Cellular secondary currents and sand ribbons in fluvial channel flows. In: Proceedings of the 6th congress APD-IAHR, Madrid, vol 2, pp 51–58
Nikuradse J (1933) Stromungsgesetz in rauhren rohren, vDI Forschungshefte 361 (English translation: Laws of flow in rough pipes). Tech Rep NACA Technical Memorandum 1292. National Advisory Commission for Aeronautics, Washington, DC, USA (1950)
Prandtl, L.: Bericht nber untersuchungen zur ausgebildeten turbulenz. Zeitschrift f\(\ddot{u}\)r Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik 5, 136–139 (1925)
Rouse H (1937) Modern concepts of the mechanics of turbulence. Trans ASCE 102:463–543
Sambrook Smith GH, Ferguson RI (1996) The gravel-sand transition: flume study of channel response to reduce slope. Geomorphology 16:147–159. doi:10.1016/0169-555X(95)00140-Z
Smith JD, McLean S (1977) Patially averaged flow over a wavy surface. J Geophys Res 82(12):1735–1746
Soulsby R (1997) Dynamics of marine sands. Thomas Telford, London
Sun ZL, Sun ZF, Donahue J (2003) Equilibrium bed-concentration of nonuniform sediment. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 4(2):186–194
Taylor J, Sarkar S, Armenio V (2005) Large eddy simulation of stably stratified open channel flow. Phys Fluids. doi:10.1063/1.2130747
Tracy H (1965) Turbulent flow in a three-dimentional channel. J Hydraul Eng 91(6):9–35
Umeyama M (1992) Vertical distribution of suspended sediment in uniform open channel flow. J Hydraul Eng 118(6):936–941
Vanoni VA (1940) Experiments on the transportation of suspended sediment by water. Ph.D. thesis, California Institute of Technology, Pasadina, California
Vanoni VA (1946) Transportation of suspended sediment by running water. Trans ASCE 111:67–133
Wang X, Qian N (1989) Turbulence characteristics of sediment-laden flows. J Hydraul Eng 115(6):781–799
Wang ZQ, Cheng NS (2005) Secondary flows over artificial bed strips. Adv Water Resour 28(5):441–450
Wang ZQ, Cheng NS (2006) Time-mean structure of secondary flows in open channel with longitudinal bedforms. Adv Water Resour 29(11):1634–1649
White FM (1991) Viscous fluid flow. McGraw Hill Book Company, New York
Wright S, Parker G (2004a) Density stratification effects in sand-bed rivers. J Hydraul Eng 130(8):783–795
Wright S, Parker G (2004b) Flow resistance and suspended load in sand-bed rivers: Simplified stratification model. J Hydraul Eng 130(8):796–805
Yang SQ (2007) Turbulent transfer mechanism in sediment-laden flow. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2005JF000452
Yang SQ, Tan SK, Lim SY (2004) Velocity distribution and dip-phenomenon in smooth uniform open channel flows. J Hydraul Eng 130(12):1179–1186
Zhiyao S, Tingting W, Fumin X, Ruijie L (2008) A simple formula for predicting settling velocity of sediment particles. Water Sci Eng 1(1):37–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundu, S. Effect of lateral bed roughness variation on particle suspension in open channels. Environ Earth Sci 75, 631 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5418-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5418-7