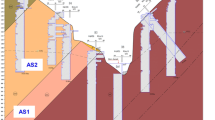
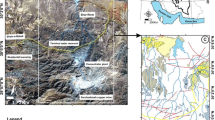
Abstract
Hydrochemical studies were carried out in parts of Oban Massif and Mamfe Embayment, Southeastern Nigeria to examine the contributions of barite mining activities on water quality. Pond and stream water samples were collected from six abandoned barite mines and adjoining streams areas during dry and wet seasons. These samples were analysed for physicochemical parameters using standard techniques. The results showed that the quality of water samples in the vicinity of barite mine sites was characterized by low pH, low mineralization, high suspended solids and deep colour. Sodium (Na+) and calcium (Ca2+) are the dominant cations and bicarbonate (HCO3 −) and sulphate (SO4 2−) the dominant anions. The low concentration of dissolved silica, relatively high concentrations of Na+, HCO3 − and SO4 2− suggest a combined influence of silicate, carbonate and weathering of mine spoils. The total dissolved solids, total suspended solids, electrical conductivity and major ions (except Na+ and K+) are higher for water draining barite mines from Cretaceous sediments, while Na+, K+, Ba2+ are higher in basement rock areas. Correlation and factor analyses suggest that the main components of the water samples are related to anthropogenic, geogenic, mineralization and environmental controls, while Gibbs diagram plots indicate weathering as the main process controlling the chemistry of water. Computed values of hardness and some irrigational parameters showed that the pond and stream water samples are generally soft and can be used for irrigation. Generally, the water quality satisfied the WHO (2008) and NIS (2007) standards for domestic, agriculture and industrial. However, there is the need to assess the impact of the pollution on the ecosystem and human health while remediation measures are being considered.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamu CI (2000) Environmental geochemical studies of Arufu Pb–Zn–Ag mining districts, Northeastern Nigeria. M.Sc. Thesis. University of Calabar, Nigeria
Adamu CI (2011) Geoenvironmental studies of barite mines in parts of Oban Massif and Mamfe embayment, Southeastern Nigeria. PhD Dissertation. University of Calabar, Nigeria
Adamu CI, Nyiatagher T (2005) Physico-chemical and bacteriological quality of surfacewater of River Benue, Nigeria. Glob J Geol Sci 3(1):45–48
Adamu CI, Nganje TN, Edet A (2009) Hydrochemistry of waters near some barite mining areas, Cross River State, Nigeria. DAAD Alumni expert seminar on “Mining and Water” October 5th–9th, Namibia
Adiuku-Brown ME, Ogezi AE (1991) Heavy metal pollution from mining practices: a case study of Zurak. J Mining Geol 27(2):205–211
Akpeke GB (2008) Investigation of the origin, nature and occurrence of barite mineralization in CRS, Southeastern Nigeria. PhD Dissertation University of Calabar, Nigeria
Alam M, Sumbul R, Aslam M (2012) Hydrochemical investigation and quality assessment of groundwater in rural areas of Delhi, India. Environ Earth Sci 66:97–110
Alloway BJ (1990) Heavy metals in Soil. J Agric Scis 241:1511–1514
ALPHA (1995) Study methods for the examination of water and waste, 2nd edn. DC Willey, Washington
Bahar MM, Reza MS (2010) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in a coastal area of southwest Bangladesh. Environ Earth Sci 61:1065–1073
Baldi F, Pepi M, Burini D, Kniewald G, Scali D, Lanciotti E (1996) Dissolution of barium from barite in sewage sludges and cultures of Desulforibrin desulfuricans. Appl Environ mineral 67(7):2398–2404
Bell RG, Rusell C (2002) Environmental policy for developing countries. Issues in science and technology. Springer University Press, New York
Chukwuma C (1995) Evaluating baseline data for Cu, Mn, Ni and Zn in rice, yams, cassava and guinea grass from cultivated soils in Nigeria. Agric Ecosyst Environ 53:47–61
Cox PA (1995) The elements on earth: Inorganic geochemistry in the environment. Oxford University Press, New York
Cross River Basin Development Authority, CRBDA (1992) Inventory of Natural Site Conditions-Soil, Slope, Hydrology, Landuse and Vegetation throughtout the areas of operation of the Authority. Surveys and Mapping Geodata Ltd (Nigeria) with Institute of Applied Geosciences (Germany), pp 145
Dogan PA (1999) Characterization of mine waste for prediction of acid mine drainage. In: Azcue JM (ed) Environmental impact of mining activities. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 19–38
Doneen LD (1964) Notes on water quality in agriculture. Published in Water Science and Engineering University of California, Davis
Eaton FM (1950) Significance of carbonates in irrigation waters. Soil Sci 39:123–133
Edet AE (1993) Hydrogeology of parts of Cross River State, Nigeria: Evidence from Aero-Geological and Surface Resistivity Studies. PhD Dissertation, University of Calabar, Calabar, Nigeria
Edet AE, Markel BI, Offiong OE (2003) Trace element hydrochemical assessment of the Calabar coastal plain aquifer, Southeastern Nigeria: using statistical methods. Environ Geol 44:137–149
Edet AE, Worden RH, Mohammed EA, Preston MR (2012) Hydrogeochemical processes in a populated shallow Coastal Plain Sand Aquifer southeastern Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 65:1933–1953
Egeh EU, Ekwueme BN, Akpeke B (2004) The appraisal of a proposed barite quarry in Akpet area, Cross River State, from resistivity investigation. Global J Geol Sci 2(2):171–175
Ekwueme BN (1995a) Geochemistry of the crystalline basement rocks in SW Ugep, Nigeria. Dee-Ford J Pure Appl Sci 1:15–28
Ekwueme BN (1995b) Geological excursion guide book. Bachude Print Press, Calabar
Ellis KU (1993) Surface water pollution and its control. Macmillan Press, London
European Union, EU (1975) Council Directive 75/440/EEC of 16 June 1975 concerning the quality required of surface water intended for the abstraction of drinking water in the Member States as amended by Council Directive 79/869/EEC (further amended by Council Directive 81/855/EEC and Council Regulation 807/2003/EC) and both amended by Council Directive 91/692/EEC (further amended by Regulation 1882/2003/EC)
Franciskovic-Bilinski S (2006) Barium anomaly in Kupa River Drainage Basin. J Geochem Explor 88:106–109
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling water chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters. US Geol. Survey Water Supply Paper 1473, 3rd edn. Harvard University Press, Massachusetts
Iloeje NP (1997) A new geography of Nigeria. Longman Ltd, Benin
Jeong CH (2001) Effect of landuse and urbanization on hydrochemistry and contamination of groundwater from Taejon area, Korea. J Hydrol 253:194–210
Jung MC (2001) Heavy metal contamination of soils and waters in and around the Inacheon Au-Ag mine, Korea. Appl Geochem 16:1369–1375
Kelly WP (1940) Permissible composition and concentration of irrigated waters. Proc AFCS 66:607
Lee JS, Chon HT, Jung MC (2005) Toxic risk assessment and environmental contamination of heavy metals around abandoned metal mine sites in Korea, Key Eng. Materials 277:542–547
Matalas CN, Reiher JB (1967) Some comments on the use of factor analysis. Water Resour 3:213–223
Moncur MC, Ptacek CJ, Blowers DW, Jambor JL (2006) Release, transport and attenuation of metals from an old tailings impoundment. Appl Geochem 20:639–659
Nagarajan R, Rajmohan N, Mahendran U, Senthamilkumar S (2010) Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Thanjavur city, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 171(1–4):289–308. doi:10.1007/s1066-009-1279-9
Nagaraju A, Suresh S, Killam K, Hudson-Edwards K (2006) Hydrogeochemistry of waters of Mangompeta barite mining area, Cuddapah Basin, Andhra Pradesh, India. Turkish J Environ Sci 30:203–219
NEST (1995) The challenge of sustainable development in Nigeria. In: Aina TA, Salan AT (eds) Nigerian Environmental study Action Team Report. Nigeria pp 16–44
Nganje TN, Adamu CI, Ugbaja AN, Ebieme E, Sikakwe GU (2010) Environemntal contamination of trace elements in the vicinity of Okpara coal mine, Enugu Southeastern Nigeria. Arabian J Geosci. doi:10.1007/-S12517-010-0673-7
Nganje TN, Adamu CI, Ugbaja AN, Ebieme E, Sikakwe GU (2011) Environmental contamination of trace elements in the vicinity of Okpara coal mine, Enugu Southeastern Nigeria. Arabian J Geosci 4(1 & 2):195–200
Nigerian Industrial Standard, NIS (2007) Nigerian Standards for drinking water quality. SON Wuse, Abuja
Nwabufo-Ene KE (1993) Non – oil mineral exploration in Nigeria. J Sci Technol 1(1):15–30
Oden MI (2001) Mineral potentials of Cross River State; Strategies for optimal utilization. Paper presented at the 1st NNDC stakeholders forum and workshop, Calabar, 2001
Okereke CS, Esu EO, Edet AE (1998) Determination of potential groundwater sites using geological and geophysical techniques in the Cross River State, Southeasthern Nigeria. J Afr Earth Sci 27(1):149–163
Olade MA (1976) On the genesis of Pb–Zn deposits in Nigeria’s Benue rift (aulacogen): a reinterpretation. J Mining Geol 13:20–27
Paliwal KV (1967) Effect of Gypsum application on the quality of irrigated waters. Madras Agric J 59:646–647
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) Users guide to PHREEQC (version 2)—a computer program for speciation, batch – reactions one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. US Geol. Survey Water Resour. Invest. Rept
Petters SW (1989) A regional hydrogeological study of rural water supply options for planning and implementations of phase II rural water programme of Cross River State. DFRRI, Cross River State, Unpublished report
Petters SW, Okereke CS, Nwajide CS (1987) Geology of the Mamfe Rift Southeastern Nigeria. In: Matheis G, Schadelimeirer HS (eds) Current research in African Earth Sciences. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 299–302
Piper AM (1944) A graphical procedure in geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Prasanna MV, Chidambaram S, Gireesh TV, Jabir Ali TV (2011) A study on hydrochemical characteristics of surface and subsurface water in and around Perumal Lake, Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu, South India. Environ Earth Sci 63:31–47
Ragunath HM (1987) Groundwater. Wiley Eastern Ltd, New Delhi
Rahman AAMS, Ukpong EE, Azumatullah M (1981) Geology of parts of the Oban Massif, Southeastern Nigeria. J Mining Geol 18(1):60–65
Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline alkali soils. US Department of Agriculture, Handbook 60, pp 160
Rose AW, Cravotta CA (1998) Geochemistry of coal mine drainage. In: Brady KBC, Smith MW, Schueck J (eds) Coal mine drainage prediction and pollution prevention in Pennsylvania. Dept. of Enviro. Protection, Harrisburg, pp 53–82
Sawyer CN, McCarthy PL (1967) Chemistry for sanitary engineers, 2nd edn. McGraw Hill, New York
Siegel FR (2002) Environmental geochemistry of potential toxic metals. Springer, Heidelberg
Sinclair AJ (1974) Selection of thresholds in geochemical data using probability graphs. J Geochem Explor 3:129–149
Subba Rao N (2006) Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in a part of Guhur district, Andhra Pradesh India. Environ Geol 49:413–429
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Udom GJ, Esu EO, Ekwere SJ (1998) Status of groundwater in Calabar Municipality, Southeastern Nigeria. Global J Pure Appl Sci 4(2):163–169
WHO (2008) Guideline for drinking-water quality (3rd edn incorporating 1st and 2nd Agenda) vol 1, Recommandations Genva
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation water. USDA circular, Washington
World Health Organization, WHO (1993) Guideline for drinking water quality, Geneva
World Health Organization, WHO (1996) Guideline for drinking water quality, vol 1. Geneva, pp 53–73
World Health Organization, WHO (2004) Guideline for drinking water quality, Geneva
Younger P, Banwart S, Hedin R (2002) Mine water hydrology, pollution and remediation. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Acknowledgments
This study is part of the PhD dissertation of the first author. The authors are grateful to the Benue State Government for financial support. We appreciate the support and assistance we received from the traditional rulers and youth leaders of Nde, Alese, Okumurutet, Iyametet, Akpet 1 and Ibogo communities during the field work. The support and encouragement from Prof. C. S. Okereke of the Department of Geology University of Calabar is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adamu, C.I., Nganje, T. & Edet, A. Hydrochemical assessment of pond and stream water near abandoned barite mine sites in parts of Oban massif and Mamfe Embayment, Southeastern Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 71, 3793–3811 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2757-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2757-5