Abstract
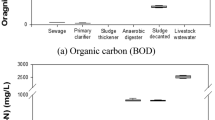
This study focused on nitritation reactions for the removal of highly concentrated nitrogen from water recycled by a MWTP (Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant) for the preparation of effluent standards which will be strengthened. To examine the changes that occur during a nitritation reaction with a variety of SRT operations when inducing a stable nitritation reaction, a reactor was operated on a laboratory scale in this study. Digestion tank supernatant flowed into a laboratory-scale reactor and organic matter in the effluent under various operation conditions was classified into four types according to ASM standards using the test known as the OUR (Oxygen Uptake Rate)-test. Most organic matter in the digestion tank supernatant appeared to consist of mainly the SI component out of non-biodegradable organic matter. During the operation period of the effluent in the laboratory-scale reactor, if a nitritation reaction occurs in a stable manner, most biodegradable organic matter is removed, consisting of mainly the SI component, like the influent. Particularly, nitrogen was removed after the SS was removed from the organic matters. Moreover, through a multiple correlation analysis between the operation results from a laboratory-scale reaction bath and the organic composition of the effluent, a method to predict the organic composition of effluents that relies on the operation result of the effluent is proposed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthonisen AC, Loehr RC, Prakasam TBS, Srinath EG (1976) Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J Wat Pollut 45(5):835–852
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Choi JH, Lee YW, Yoon ZH (2001) Removal of concentrated nitrogen from the recycle water by biological nitritation-denitritation. J Korean Soc Environ Engin 23(3):371–381
Choi YG, Kim KD, Kim HJ, Kim YJ, Jung TH (2003) Respirometry for COD Fractionation of Wastewater. J Korean Soc Water Wastewater 17(4):503–509
Dircks K, Pind PF, Mosb KH, Henze M (1999) Yield determination by respirometry: the possible influence of storage under aerobic conditions in activated sludge. Water SA 25(1):69–74
Gali A, Dosta J, Lopez-palau S, Mata-Alvarez J (2008) SBR technology for high ammonium loading rates. Water Sci Tech 58(2):467–472
Gil KI (2006) Nitritation of anaerobic digester supernatant from sludge processing in MWTP. J Korean Soc Water Qual 22(3):540–545
Gil KI, Rho HY, Kim DI, Michael KS (2012) Comparison of Bio-P module and the modified Bio-P module in the Step-feed biological nutrient removal process. Environ Earth Sci 65:929–936
Han DJ, Kang SW, Rim JM (1998) Factors influencing nitrite build-up in nitrification of high strength ammonia wastewater. Korean J Sanit 13(2):128–138
Hellinga C, Schellen AAJC, Mulder JW, van Loosdrecht MCM, Heijnen JJ (1998) The sharon process: an innovative method for nitrogen removal from ammonium-rich waste water. Water Sci Tech 37(9):135–142
Hong JY, Shin EB, Kim YK, Kim BJ (2003) Evaluation of the changes of microbial biomass fraction using OUR measurement. J Korean Soc Water Qual 19(4):445–454
Im JY, Gil KY (2011a) Evaluation of nitritation of high strength ammonia with variation of SRT and temperature using piggery wastewater. J Korean Soc Water Qual 27(5):563–571
Im JY, Gil KY (2011b) Effect of anaerobic digestion on the high rate of nitritation treating piggery wastewater. J Environ Sci 23(11):1787–1793
Mertoglu B (2008) Long-term assessment of nitrification in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. Environ Technol 43(5):538–546
Pochana K, Keller J, Lant P (2000) Model development for simultaneous nitrification and denitrification. Water Sci Tech 39(1):235–243
Ruiz G, Jeison D, Chamy R (2003) Nitrification with high nitrite accumulation for the treatment of wastewater with high ammonia concentration. Water Sci Tech 37(1):1371–1377
Samson KA, Ekama GA (2000) An assessment of sewage sludge stability with a specific oxygen utilization rate (SOUR) test method. Water Sci Tech 42(9):37–40
Wang J, Yang N (2004) Partial nitrification under limited dissolved oxygen conditions. Process Biochem 39(10):1223–1229
Wei YX, Li YF, Ye ZF (2010) Enhancement of removal efficiency of ammonia nitrogen in sequencing batch reactor using natural zeolite. Environ Earth Sci 60:1407–1413
Zeng W, Peng YZ, Wang SY (2004) A Two-stage SBR process for removal of organic substrate and nitrogen via nitrite: type nitrification-denitrification. Environ Technol 39(8):2229–2239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Im, J., Gil, K. Changes in the characteristics of organic compounds depending on the nitritation efficiency. Environ Earth Sci 70, 1297–1305 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2216-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2216-3