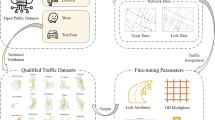
Abstract
Monitoring traffic conditions on urban signalized road networks is an essential component of urban traffic control systems. Due to the sparseness of trajectory data and the influence of signal timing, it is challenging to estimate the traffic condition of large-scale urban signalized networks based on trajectory data. In this study, a novel and integrated data-driven learning approach (NEI-SE) is proposed, incorporating road network segmentation, speed matching, and sparse data imputation for the estimation of travel speed. First, the urban traffic network is divided according to signalized intersection and road segment length, considering the influence of signal timing on urban traffic speed. Then, based on taxi trajectory data and the divided road network, a traffic condition matrix is constructed describing the road conditions. Finally, a lightweight multi-view learning method that integrates temporal patterns and spatial topological relations is proposed to fill the missing values of the traffic condition matrix. The approach was validated on real-world traffic trajectory data collected in Wuhan, China. The results showed that NEI-SE outperformed nine existing baselines in terms of imputation accuracy. In addition, the AutoNavi congestion data was used to evaluate the data quality of the estimated traffic speed data due to lack ground truth of traffic speed. The results showed that the congestion index data had a significant negative correlation with imputed traffic speed series, with an average correlation coefficient of − 0.67, proving that the traffic speed data estimated by the proposed approach have satisfactory quality.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data and codes availability statement
The data and codes that support the findings of this study are available in ‘figshare.com’ with the identifier https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.14946009.
References
Angayarkanni SA, Sivakumar R, Ramana Rao YV (2021) Hybrid Grey Wolf: Bald Eagle search optimized support vector regression for traffic flow forecasting. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 12(1):1293–1304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02182-w
Aryaputera AW, Yang D, Zhao L, Walsh WM (2015) Very short-term irradiance forecasting at unobserved locations using spatio-temporal kriging. Sol Energy 122:1266–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2015.10.023
Cai P, Wang Y, Lu G, Chen P, Ding C, Sun J (2016) A spatiotemporal correlative k-nearest neighbor model for short-term traffic multistep forecasting. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 62:21–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2015.11.002
Campbell JY, Thompson SB (2008) Predicting excess stock returns out of sample: can anything beat the historical average? Rev Financ Stud 21(4):1509–1531. https://doi.org/10.1093/rfs/hhm055
Chen X, Sun L (2021) Bayesian temporal factorization for multidimensional time series prediction. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3066551
Chen X, He Z, Wang J (2018) Spatial-temporal traffic speed patterns discovery and incomplete data recovery via SVD-combined tensor decomposition. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 86:59–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2017.10.023
Chen X, Yang J, Sun L (2020) A nonconvex low-rank tensor completion model for spatiotemporal traffic data imputation. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 117:102673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102673
Cheng S, Lu F (2017) A two-step method for missing spatio-temporal data reconstruction. ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 6(7):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6070187
Cheng S, Lu F, Peng P, Wu S (2019) Multi-task and multi-view learning based on particle swarm optimization for short-term traffic forecasting. Knowl-Based Syst 180:116–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.05.023
Cheng S, Lu F, Peng P (2020a) Short-term traffic forecasting by mining the non-stationarity of spatiotemporal patterns. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.2991781
Cheng S, Peng P, Lu F (2020b) A lightweight ensemble spatiotemporal interpolation model for geospatial data. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 34(9):1849–1872. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2020.1725016
Cheng S, Zhang B, Peng P, Yang Z, Lu F (2020c) Spatiotemporal evolution pattern detection for heavy-duty diesel truck emissions using trajectory mining: a case study of Tianjin, China. J Clean Prod 244:118654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118654
Cheng S, Lu F, Peng P, Zheng J (2021) Emission characteristics and control scenario analysis of VOCs from heavy-duty diesel trucks. J Environ Manag 293:112915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112915
Chung J, Gulcehre C, Cho K, Bengio Y (2014) Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3555 [Cs]
Gardner ES (2006) Exponential smoothing: the state of the art—Part II. Int J Forecast 22(4):637–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijforecast.2006.03.005
González CL, Zapotecatl JL, Gershenson C, Alberola JM, Julian V (2020) A robustness approach to the distributed management of traffic intersections. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 11(11):4501–4512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01424-w
Guo Q, Li L, Ban X (2019a) Urban traffic signal control with connected and automated vehicles: a survey. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 101:313–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2019.01.026
Guo S, Lin Y, Li S, Chen Z, Wan H (2019b) Deep spatial-temporal 3D convolutional neural networks for traffic data forecasting. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 20(10):14
Hara Y, Suzuki J, Kuwahara M (2018) Network-wide traffic state estimation using a mixture Gaussian graphical model and graphical lasso. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 86:622–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2017.12.007
Hou Q, Leng J, Ma G, Liu W, Cheng Y (2019) An adaptive hybrid model for short-term urban traffic flow prediction. Physica A 527:121065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.121065
Hu M-G, Wang J-F, Zhao Y, Jia L (2013) A B-SHADE based best linear unbiased estimation tool for biased samples. Environ Model Softw 48:93–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2013.06.011
Jiang L, Zhang X, Zuo W, Xu H, Zhao J, Qiu X, Tian Y, Zhu Y (2018) A neural network method for the reconstruction of winter wheat yield series based on spatio-temporal heterogeneity. Comput Electron Agric 154:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.08.047
Li L, Losser T, Yorke C, Piltner R (2014) Fast inverse distance weighting-based spatiotemporal interpolation: a web-based application of interpolating daily fine particulate matter PM2:5 in the contiguous US using parallel programming and k-d tree. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11(9):9101–9141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110909101
Li L, Du B, Wang Y, Qin L, Tan H (2020) Estimation of missing values in heterogeneous traffic data: application of multimodal deep learning model. Knowl-Based Syst 194:105592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105592
Ma D, Luo X, Li W, Jin S, Guo W, Wang D (2017) Traffic demand estimation for lane groups at signal-controlled intersections using travel times from video-imaging detectors. IET Intel Transp Syst 11(4):222–229. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-its.2016.0233
Praveen DS, Raj DP (2021) Smart traffic management system in metropolitan cities. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 12(7):7529–7541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02453-6
Salamanis A, Kehagias DD, Filelis-Papadopoulos CK, Tzovaras D, Gravvanis GA (2016) Managing spatial graph dependencies in large volumes of traffic data for travel-time prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 17(6):1678–1687. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2015.2488593
Shang J, Zheng Y, Tong W, Chang E, Yu Y (2014) Inferring gas consumption and pollution emission of vehicles throughout a city. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1145/2623330.2623653
Tang J, Zhang X, Yin W, Zou Y, Wang Y (2020a) Missing data imputation for traffic flow based on combination of fuzzy neural network and rough set theory. J Intell Transp Syst. https://doi.org/10.1080/15472450.2020.1713772
Tang K, Tan C, Cao Y, Yao J, Sun J (2020b) A tensor decomposition method for cycle-based traffic volume estimation using sampled vehicle trajectories. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 118:102739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102739
Tao S, Manolopoulos V, Rodriguez S, Rusu A (2012) Real-time urban traffic state estimation with A-GPS mobile phones as probes. J Transp Technol 2(1):22–31. https://doi.org/10.4236/jtts.2012.21003
Vigos G, Papageorgiou M (2010) A simplified estimation scheme for the number of vehicles in signalized links. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 11(2):312–321. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2010.2042807
Wang Y, Zheng Y, Xue Y (2014) Travel time estimation of a path using sparse trajectories. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 25–34. https://doi.org/10.1145/2623330.2623656
Wang P, Hu T, Gao F, Wu R, Guo W, Zhu X (2022a) A hybrid data-driven framework for spatiotemporal traffic flow data imputation. IEEE Internet Things J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2022.3151238
Wang P, Zhang T, Zheng Y, Hu T (2022b) A multi-view bidirectional spatiotemporal graph network for urban traffic flow imputation. Int J Geogr Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2022.2032081
Wilby MR, Díaz JJV, Gonźlez ABR, Sotelo MÁ (2014) Lightweight occupancy estimation on freeways using extended floating car data. J Intell Transp Syst 18(2):149–163. https://doi.org/10.1080/15472450.2013.801711
Xie P, Li T, Liu J, Du S, Yang X, Zhang J (2020) Urban flow prediction from spatiotemporal data using machine learning: a survey. Inf Fusion 59:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2020.01.002
Xu C-D, Wang J-F, Hu M-G, Li Q-X (2013) Interpolation of missing temperature data at meteorological stations using P-BSHADE*. J Clim 26(19):7452–7463. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00633.1
Xu D, Wei C, Peng P, Xuan Q, Guo H (2020) GE-GAN: a novel deep learning framework for road traffic state estimation. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 117:102635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102635
Yang B, Kang Y, Yuan Y, Huang X, Li H (2021) ST-LBAGAN: spatio-temporal learnable bidirectional attention generative adversarial networks for missing traffic data imputation. Knowl-Based Syst 215:106705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106705
Yi X, Zheng Y, Zhang J, Li T (2016) ST-MVL: filling missing values in geo-sensory time series data. In: Proceedings of the twenty-fifth international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2704–2710
Younes MB (2021) Real-time traffic distribution prediction protocol (TDPP) for vehicular networks. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 12(8):8507–8518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02585-9
Yozgatligil C, Aslan S, Iyigun C, Batmaz I (2013) Comparison of missing value imputation methods in time series: the case of Turkish meteorological data. Theor Appl Climatol 112(1):143–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-012-0723-x
Yu B, Song X, Guan F, Yang Z, Yao B (2016a) K-nearest neighbor model for multiple-time-step prediction of short-term traffic condition. J Transp Eng 142(6):04016018. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)TE.1943-5436.0000816
Yu H-F, Rao N, Dhillon IS (2016b) Temporal regularized matrix factorization for high-dimensional time series prediction. In: 30th conference on neural information processing systems (NIPS 2016b), p 15
Yu B, Yin H, Zhu Z (2018) Spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks: a deep learning framework for traffic forecasting. In: Proceedings of the twenty-seventh international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 3634–3640. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2018/505
Yu J, Stettler MEJ, Angeloudis P, Hu S, Chen X (2020) Urban network-wide traffic speed estimation with massive ride-sourcing GPS traces. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 112:136–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.01.023
Zhan X, Li R, Ukkusuri SV (2015) Lane-based real-time queue length estimation using license plate recognition data. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 57:85–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2015.06.001
Zhan X, Zheng Y, Yi X, Ukkusuri SV (2017) Citywide traffic volume estimation using trajectory data. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 29(2):272–285. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2016.2621104
Zhang Z, Li M, Lin X, Wang Y (2020) Network-wide traffic flow estimation with insufficient volume detection and crowdsourcing data. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 121:102870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102870
Zhao Y, Zheng J, Wong W, Wang X, Meng Y, Liu HX (2019) Various methods for queue length and traffic volume estimation using probe vehicle trajectories. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 107:70–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2019.07.008
Funding
This project was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (International Scientific & Technological Cooperation Program) under Grant 2019YFE0106500, National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 41871308.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Zhang, T. & Hu, T. Traffic condition estimation and data quality assessment for signalized road networks using massive vehicle trajectories. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 15, 305–322 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-03892-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-03892-z