Abstract
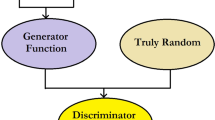
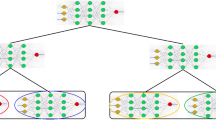
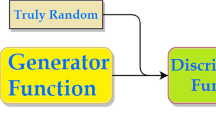
In this paper, effective synchronization of a group of neural networks using a generative adversarial network is proposed for secured neural key exchange over public channels. Two artificial neural networks (ANNs) are synchronized by reciprocal training to exchange the key across a public network. The most important aspect of neural coordination is determining how well two parties’ ANNs synchronize in the absence of weights from the other. Existing approaches have a delay in measuring coordination, which compromises the secrecy of neuronal coordination. Moreover, there is a scarcity of study into the reciprocal learning of a cluster of ANNs and the generation of a common input vector through robust PRNG. This study offers a mutual learning approach for rapidly and effectively assessing the complete synchronization of a group of ANNs. The frequency with which the two networks have had the same outcome in previous rounds is used to determine cooperation. When a particular threshold is reached, the hash is used to check if all networks are correctly coordinated. To accomplish full coordination between two communicating entities, the proposed approach employs the hash value of the weight vectors. This method has several advantages, including (1) the use of a GAN-based PRNG to generate the input vector. (2) Over the public channel, complete binary tree-based group mutual neural synchronization of ANNs generates the session key. (3) In contrast to previous approaches, the proposed method enables two communication entities to detect full coordination more quickly. (4) This suggested system considers brute force, geometry, and majority assaults. Tests are carried out to test the proposed methodology’s performance, and the findings demonstrate that it outperforms similar techniques currently in use.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalrdha ZK, AL-Qinani IH, Abbas FN (2019) Subject review: key generation in different cryptography algorithm. Int J Sci Res Sci Eng Technol 6(5):230–240. https://doi.org/10.32628/ijsrset196550
Chourasia S, Bharadwaj HC, Das Q, Agarwal K, Lavanya K (2019) Vectorized neural key exchange using tree parity machine. Secur Commun Netw 2021:3140–3145. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6680782
Dolecki M, Kozera R (2015) The impact of the TPM weights distribution on network synchronization time. In: Computer information systems and industrial management, Springer International Publishing, vol 9339, pp 451–460
Dong T, Huang T (2020) Neural cryptography based on complex-valued neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(11):4999–5004. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2955165
Dorokhin Édgar Salguero, Fuertes W, Lascano E (2019) On the development of an optimal structure of tree parity machine for the establishment of a cryptographic key. Secur Commun Netw 2019:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8214681
Gao J, Yang X, Jiang Y, Song H, Choo KKR, Sun J (2021) Semantic learning based cross-platform binary vulnerability search for IoT devices. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 17(2):971–979. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2019.2947432
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2672–2680
Hadke PP, Kale SG (2016) Use of neural networks in cryptography: a review. In: Proceedings of the 2016 world conference on futuristic trends in research and innovation for social welfare (Startup Conclave), pp 1–4
Jeong YS, Oh K, Cho CK, Choi HJ (2018) Pseudo random number generation using LSTMs and irrational numbers. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on big data and smart computing (BigComp), pp 541–544
Jeong S, Park C, Hong D, Seo C, Jho N (2021) Neural cryptography based on generalized tree parity machine for real-life systems. Secur Commun Netw. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6680782
Jo M, Jangirala S, Das AK, Li X, Khan MK (2020) Designing anonymous signature-based authenticated key exchange scheme for IoT-enabled smart grid systems. IEEE Trans Ind Inform. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.3011849
Kanter I, Kinzel W, Kanter E (2002) Secure exchange of information by synchronization of neural networks. Europhys Lett EPL 57(1):141–147. https://doi.org/10.1209/epl/i2002-00552-9
Karakaya B, Gülten A, Frasca M (2019) A true random bit generator based on a memristive chaotic circuit: analysis, design and FPGA implementation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 119:143–149
Liu L, Miao S, Hu H, Deng Y (2016) Pseudo-random bit generator based on non-stationary logistic maps. IET Inf Secur 10:87–94
Liu P, Zeng Z, Wang J (2019) Global synchronization of coupled fractional-order recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(8):2358–2368
Lu Y, Huang X, Dai Y, Maharjan S, Zhang Y (2020) Blockchain and federated learning for privacy-preserved data sharing in industrial IoT. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 16(6):4177–4186. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2019.2942190
Makkar A, Garg S, Kumar N, Hossain MS, Ghoneim A, Alrashoud M (2021) An efficient spam detection technique for IoT devices using machine learning. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 17(2):903–912. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.2968927
Mehic M, Niemiec H, Siljak M, Voznak (2020) Error reconciliation in quantum key distribution protocols. In: Proceedings of the international conference on reversible computation, pp 222–236
Niemiec (2019) Error correction in quantum cryptography based on artificial neural networks. Quantum Inf Process 18:174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2296-4
Niemiec M, Mehic M, Voznak (2018) Security verification of artificial neural networks used to error correction in quantum cryptography. In: Proceedings of the 26th tele-communications forum (TELFOR), pp 1–4
NIST (2020) NIST statistical test. http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/ST/toolkit/rng/stats_tests.html. Accesssed 10 July 2021
Pal SK, Mishra S, Mishra S (2019) An TPM based approach for generation of secret key. Int J Comput Netw Inf Secur 11(10):45–50. https://doi.org/10.5815/ijcnis.2019.10.06
Patidar V, Sud KK, Pareek NK (2009) A pseudo random bit generator based on chaotic logistic map and its statistical testing. Informatica 33:441–452
Protic D (2016) Neural cryptography. Vojnoteh Glas 64(2):483–495. https://doi.org/10.5937/vojtehg64-8877
Rosen-Zvi M, Kanter I, Kinzel W (2002) Cryptography based on neural networks analytical results. J Phys A Math Gen 35(47):L707–L713. https://doi.org/10.1088/0305-4470/35/47/104
Ruttor A, Kinzel W, Naeh R, Kanter I (2006) Genetic attack on neural cryptography. Phys Rev E. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.73.036121
Ruttor A, Kinzel W, Kanter I (2007) Dynamics of neural cryptography. Phys Rev E. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.75.056104
Sarkar A (2019) Multilayer neural network synchronized secured session key based encryption in wireless communication. Int J Artif Intell 8(1):44–53. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v14.i1.pp169-177
Sarkar A (2021) Deep learning guided double hidden layer neural synchronization through mutual learning. Neural Process Lett 53:1355–1384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10443-8
Sarkar A, Mandal J (2012) Swarm intelligence based faster public-key cryptography in wireless communication (SIFPKC). Int J Comput Sci Eng Technol IJCSET 3(7):267–273
Shacham LN, Klein E, Mislovaty R, Kanter I, Kinzel W (2004) Cooperating attackers in neural cryptography. Phys Rev E. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.69.066137
Shishniashvili E, Mamisashvili L, Mirtskhulava L (2020) Enhancing IoT security using multi-layer feedforward neural network with tree parity machine elements. Int J Simul Syst Sci Technol 21(2):371–383. https://doi.org/10.5013/ijssst.a.21.02.37
Teodoro A, Gomes O, Saadi M et al (2021) An FPGA-based performance evaluation of artificial neural network architecture algorithm for IoT. Wirel Pers Commun. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08566-1
Tirdad K, Sadeghian A (2010) Hopfield neural networks as pseudo random number generators. In: Fuzzy Information Processing Society (NAFIPS), 2010 annual meeting of the North American, pp 1–6
Acknowledgements
The authors expressed deep gratitude for the moral and congenial atmosphere support provided by Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira, Belur Math, India.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, A. Generative adversarial network-based efficient synchronization of group of neural networks to exchange the neural key. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 6463–6488 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03521-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03521-1