Abstract
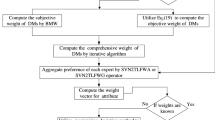
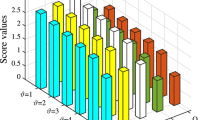
Knowledge plays a vital role in multi-attribute group decision-making (MAGDM), where experts from different-fields present their knowledge to support decision-making by employing multi-granularity linguistic model. The main goals of current work are targeted to present a novel MAGDM approach by integrating the extended Archimedean Copulas (EACs), group-individual best-worst method (GIBWM) and multi-attributive border approximation area comparison (MABAC) approach to fuse multi-source knowledge with multi-granularity intuitionistic 2-tuple linguistic information (I2TLI) with unknown weight information of attributes and experts. To begin with, for the sake of modeling the relationships between attributes (experts), the Copula-based aggregation operators with I2TLI are recommended together with some of its variations discussed; In addition, taking the merits of GIBWM methods, an algorithm of weight information of expert and attributes is designed; Thirdly, considering the decision maker’s behaviour preference and psychology, a modified MABAC method is proposed by modified prospect matrix. Simultaneously, an algorithm for MAGDM based on I2TLI with different granularity is designed by integrating GIBWM and modified MABAC approach. Last of all, an example is furnished to manifest the significance of the proposed method along with related discussions, the advantages of this method are analyzed by comparing with the extant decision-making approaches.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemi-Ardakani M, Milani AS, Yannacopoulos S, Shokouhi G (2016) On the effect of subjective, objective and combinative weighting in multiple criteria decision making: a case study on impact optimization of composites. Expert Syst Appl 46:426–438
Ashraf S, Abdullah S, Mahmood T (2020) Spherical fuzzy dombi aggregation operators and their application in group decision making problems. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 11(7):1–19
Beg I, Rashid T (2014) Aggregation operators of interval-valued 2-tuple linguistic information. Int J Intell Syst 29(7):634–667
Beg I, Rashid T (2016) An intuitionistic 2-tuple linguistic information model and aggregation operators. Int J Intell Syst 31(6):569C592
Chen Z, Ben-Arieh D (2006) On the fusion of multi-granularity linguistic label sets in group decision making. Comput Ind Eng 51(3):526–541
Chen Z, Liu P, Pei Z (2015) An approach to multiple attribute group decision making based on linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Int J Comput Int Syst 8(4):747–760
Chen T, He SS, Wang JQ, Li L, Luo H (2019) Novel operations for linguistic neutrosophic sets on the basis of archimedean copulas and co-copulas and their application in multi-criteria decision-making problems. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 37(3):1–26
Darko AP, Liang DC (2020) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy hamacher aggregation operators and their application to multiple attribute group decision making with modified edas method. Eng Appl Artif Intel 87:103259
Dong Y, Li CC, Herrera F (2016) Connecting the linguistic hierarchy and the numerical scale for the 2-tuple linguistic model and its use to deal with hesitant unbalanced linguistic information. Inf Sci 367–368:259–278
Faizi S, Nawaz S, Ur-Rehman A (2020) Intuitionistic 2-tuple linguistic aggregation information based on einstein operations and their applications in group decision making. Artif Intell Rev 53(6):4625–4650
Feng XQ, Pang XD, Wei CP (2020) Distance-based consistency measure and priority weights of best-worst multi-criteria decision making method. Int J Uncertain Fuzz 28(5):853–878
Genest C (1986) Copulas archimediennes et familles delois bidimensionanelles dont les marges sont donness. Int J Uncertain Fuzz 14(1):145–159
Giráldez-Cru J, Chica M, Cordón O, Herrera F (2019) Modeling agent-based consumers decision-making with 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic perceptions. Int J Intell Syst 35(4):283–299
Guiwu W (2011) Grey relational analysis model for dynamic hybrid multiple attribute decision making. Knowl-Based Syst 24:672–679
Hafezalkotob A, Hafezalkotob A (2017) A novel approach for combination of individual and group decisions based on fuzzy best-worst method. Appl Soft Comput 59:316–325
Hafezalkotob A, Hafezalkotob A, Liao H, Herrera F (2019) Interval multimoora method integrating interval borda rule and interval best-worst-method-based weighting model: case study on hybrid vehicle engine selection. IEEE T Cyb 50(3):1157–1169
Han B, Tao Z, Chen H, Zhou L, Liu J (2020) A new computational model based on archimedean copula for probabilistic unbalanced linguistic term set and its application to multiple attribute group decision making. Comput Ind Eng 140:106264
Herrera F, Martinez L (2000) An approach for combining linguistic and numerical information based on the 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model in decision-making. Int J Uncertain Fuzz 8(5):539–562
Herrera F, Martínez L (2001) The 2-tuple linguistic computational model advantages of its linguistic description, accuracy and consistency. Int J Uncertain Fuzz 9(1):33–48
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Martínez L (2000) A fusion approach for managing multi-granularity linguistic term sets in decision making. Fuzzy Set Syst 114(1):43–58
Ju Y, Wang A, Ma J, Gao H, Gonzalez E (2020) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy 2-tuple linguistic muirhead mean aggregation operators and their applications to multiple-attribute group decision making. Int J Intell Syst 35(1):184–213
Kuo T (2016) A modified topsis with a different ranking index. Eur J Oper Res 260(1):152–160
Labella A, Liu Y, Rodrguez R, Martnez L (2017) Analyzing the performance of classical consensus models in large scale group decision making: a comparative study. Appl Soft Comput 67:677–690
Li C, Zeng S, Pan T, Zheng L (2014) A method based on induced aggregation operators and distance measures to multiple attribute decision making under 2-tuple linguistic environment. J Comput Syst Sci 80(7):1339–1349
Liang FQ, Brunelli M, Rezaei J (2019) Consistency issues in the best worst method: measurements and thresholds. Omega. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2019.102175
Liang Y, Liu J, Qin J, Tu Y (2018) An improved multi-granularity interval 2-tuple todim approach and its application to green supplier selection. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(1):129–144
Liu P, Chen SM (2018) Multiattribute group decision making based on intuitionistic 2-tuple linguistic information. Infor Sci 430–431:599–619
Liu Y, Liu J, Qin Y, Xu Y (2019) A novel method based on extended uncertain 2-tuple linguistic muirhead mean operators to magdm under uncertain 2-tuple linguistic environment. Int J Comput Int Syst 12(2):498–512
Liu Y, Wei G, Abdullah S, Liu J, Liu H (2021a) Banzhaf cchoquet-copula-based aggregation operators for managing q-rung orthopair fuzzy information. Soft Comput 25(10):6891–6914
Liu Y, Wei G, Liu H, Xu L (2021b) Group decision making for internet public opinion emergency based upon linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy information. Int J Mach Learn Cyb. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01262-9
Llamazares B (2018) An analysis of the generalized todim method. Eur J Oper Res 269(2):1041–1049
Luo SZ, Xing LN (2019) A hybrid decision making framework for personnel selection using bwm, mabac and promethee. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(8):2421–2434
Massanet S, Riera JV, Torrens J, Herrera-Viedma E (2014) A new linguistic computational model based on discrete fuzzy numbers for computing with words. Inf Sci 258:277–290
Merigó J, Gil-Lafuente AM (2013) Induced 2-tuple linguistic generalized aggregation operators and their application in decision-making. Inf Sci 236:1–16
Morente-Molinera JA, Perez IJ, Urena MR, Herrera-Viedma E (2015) On multi-granular fuzzy linguistic modeling in group decision making problems: a systematic review and future trends. Knowl Based Syst 74:49–60
Nelsen RB (2000) An introduction to copulas. Technometrics 42(3)
Pamuar D, Stevi E, Zavadskas EK (2018) Integration of interval rough ahp and interval rough mabac methods for evaluating university web pages. Appl Soft Comput 67:141–163
Pamucar D, Cirovic G (2015) The selection of transport and handling resources in logistics centers using multi-attributive border approximation area comparison (mabac). Expert Syst Appl 42(6):3016–3028
Pamucar D, Petrovic I, Cirovic G (2018) Modification of the best–worst and mabac methods: a novel approach based on interval-valued fuzzy-rough numbers. Expert Syst Appl 91:89–106
Peng X, Dai J (2018) Approaches to single-valued neutrosophic madm based on mabac, topsis and new similarity measure with score function. Neural Comput Appl 29(10):939–954
Qin Y, Liu Y, Abdullah S, Wei G (2021) Group decision support methodology based upon the multigranular generalized orthopair 2tuple linguistic information model. Int J Intell Syst 36(7):3367–3400
Qu S, Xu Y, Wu Z, Xu Z, Han Y (2020) An interval-valued bestcworst method with normal distribution for multi-criteria decision-making. Arab J Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05035-y
Rashid T, Faizi S, Zafar S (2019) Outranking method for intuitionistic 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic information model in group decision making. Soft Comput 23(15):6145–6155
Rezaei J (2015) Best–worst multi-criteria decision-making method. Omega 53:49–57
Rodrguez R, Lvaro Labella GT, Martínez L (2018) A large scale consensus reaching process managing group hesitation. Knowl Based Syst 159:86–97
Sklar A (1959) Fonctions de repartition a n dimensions et leurs marges. Université Paris 8:229–231
Tao Z, Bing H, Chen H (2018a) On intuitionistic fuzzy copula aggregation operators in multiple-attribute decision making. Cogn Comput 10:610–624
Tao Z, Han B, Zhou L, Chen H (2018b) The novel computational model of unbalanced linguistic variables based on archimedean copula. Int J Uncertain Fuzz 26(04):601–631
Tirkolaee EB, Mardani A, Dashtian Z, Soltani M, Weber GW (2020) A novel hybrid method using fuzzy decision making and multi-objective programming for sustainable-reliable supplier selection in two-echelon supply chain design. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119517
Wan SP (2013) 2-tuple linguistic hybrid arithmetic aggregation operators and application to multi-attribute group decision making. Knowl Based Syst 45:31–40
Wang L, Peng JJ, Wang JQ (2018) A multi-criteria decision-making framework for risk ranking of energy performance contracting project under picture fuzzy environment. J Clean Prod 191:105–118
Wang L, Wang Y, Pedrycz W (2019a) Hesitant 2-tuple linguistic bonferroni operators and their utilization in group decision making. Appl Soft Comput 77:653–664
Wang P, Wang J, Wei G, Wei C, Wei Y (2019b) The multi-attributive border approximation area comparison (mabac) for multiple attribute group decision making under 2-tuple linguistic neutrosophic environment. Informatica 30(4):799–818
Wu Y, Zhang Z, Kou G, Zhang H, Chao X, Li C, Dong Y, Herrera F (2020) Distributed linguistic representations in decision making: Taxonomy, key elements and applications, and challenges in data science and explainable artificial intelligence. Inform Fus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2020.08.018
Xu Z (2004) A method based on linguistic aggregation operators for group decision making with linguistic preference relations. Inf Sci 166(1C4):19–30
Xue YX, You JX, Lai XD, Liu HC (2016) An interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy mabac approach for material selection with incomplete weight information. Appl Soft Comput 38:703–713
Yuan R, Liu Y, Zheng P (2020) Complex q-rung orthopairfuzzy 2-tuple linguistic maclaurin symmetric mean operators and its application to emergency program selection. Int J Intell Syst 35(1):1749–1790
Yu W, Zhang Z, Zhong Q, Boros E (2021) Consensus reaching for magdm with multi-granular hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets: a minimum adjustment-based approach. Ann Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-019-03432-7
Zavadskas EK, Kaklauskas A, Sarka V (1994) The new method of multicriteria complex proportional assessment of projects. Technol Econ Dev Econ 1(3):131–139
Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhao X (2018) A new emergency decision support methodology based on multi-source knowledge in 2-tuple linguistic model. Knowl Based Syst 144:77–87
Zhang Z, Gao Y, Li Z (2020a) Consensus reaching for social network group decision making by considering leadership and bounded confidence. Knowl Based Syst 204:106240
Zhang S, Wei G, Fand Alsaadi T, Hayat WC, Zhang Z (2020b) Mabac method for multiple attribute group decision making under picture2-tuple linguistic environment. Soft Comput 24(8):5819–5829
Zhang Z, Yu W, Martínez L, Gao Y (2020c) Managing multigranular unbalanced hesitant fuzzy linguistic information in multiattribute large-scale group decision making: a linguistic distribution-based approach. IEEE T Fuzzy Syst 28(11):2875–2889
Acknowledgements
Authors thank the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions. This work is supported by the Application Basic Research Plan Project of Sichuan Province (No. 2021JY0108, 2019JDTD0015); Scientific Research Project of Neijiang Normal University under Grant 18TD08; Open Research Fund Program of Data Recovery Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Grant No. DRN2105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Qin, Y., Liu, F. et al. GIBWM-MABAC approach for MAGDM under multi-granularity intuitionistic 2-tuple linguistic information model. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 3405–3421 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03476-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03476-3