Abstract
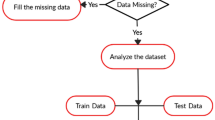
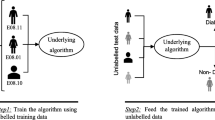
In predictive modelling it is important to use any feature selection methods as irrelevant features when used with powerful classifiers can lead to over-fitting and thus create models which fail to perform as good as when these features are not used. Particularly it is important in case of disease datasets where various features or attributes are available through the patients’ medical records and many features in these datasets may not be relevant to the diagnosis of some specific disease. Wrong models in this case can be disastrous and lead to wrong diagnosis, and maybe in extreme cases lead to loss of life. To this end, we have used a wrapper based feature selection model for the said purpose. In recent years, Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm (GOA) has proved its superiority over other optimization algorithms in different research areas. In this paper, we propose an improved version of GOA, called (LAGOA), which uses Learning Automata (LA) for adjusting the parameters of GOA in an adaptive way, and two-phase mutation for enhancing exploitation capability of the algorithm. LA is used for adjusting the parameter values of each grasshopper in the population individually. In two-phase mutation the first phase reduces the number of selected features while preserving high classification accuracy, while the second phase adds relevant features which increase the classification accuracy. Proposed method has been applied to Breast Cancer (Wisconsin), Breast Cancer (Diagnosis), Statlog (Heart), Lung Cancer, SpectF Heart and Hepatitis datasets taken from UCI Machine Learning Repository. Experimental results confirm its superiority over state-of-the-art methods considered here for comparison.



























Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable for this submission.
Code availability
Not applicable for this submission.
Notes
References
Abdel-Basset M, El-Shahat D, El-henawy I, de Albuquerque V, Mirjalili S (2020) A new fusion of grey wolf optimizer algorithm with a two-phase mutation for feature selection. Expert Syst Appl 139:112824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112824, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417419305263
Alirezanejad M, Enayatifar R, Motameni H, Nematzadeh H (2020) Gsa-la: gravitational search algorithm based on learning automata. J Exper Theor Artif Intell 2020:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/0952813X.2020.1725650
Baliarsingh SK, Vipsita S, Muhammad K, Bakshi S (2019) Analysis of high-dimensional biomedical data using an evolutionary multi-objective emperor penguin optimizer. Swarm Evolution Comput 48:262–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2019.04.010, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2210650219301580
Cestnik G, Konenenko I, Bratko I (1987) Assistant-86: a knowledge-elicitation tool for sophisticated users. In: IBratko & NLavrac (Eds) Progress in machine learning. Sigma Press, London, pp 31–45
Chattopadhyay S (2017) A neuro-fuzzy approach for the diagnosis of depression. Appl Comput Informatics 13(1):10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aci.2014.01.001, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2210832714000027
Chen Y, Wang Y, Cao L, Jin Q (2018) An effective feature selection scheme for healthcare data classification using binary particle swarm optimization. In: 2018 9th international conference on information technology in medicine and education (ITME), pp 703–707
Cuevas E, Echavarría A, Zaldívar D, Pérez-Cisneros M (2013) A novel evolutionary algorithm inspired by the states of matter for template matching. Expert Syst Appl 40(16):6359–6373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.05.055, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417413003539
Das H, Naik B, Behera H, Jaiswal S, Mahato P, Rout M (2020) Biomedical data analysis using neuro-fuzzy model with post-feature reduction. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2020.01.007, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319157819311656
De Cicco P, Catani M, Gasperi V, Sibilano M, Quaglietta M, Savini I (2019) Nutrition and breast cancer: a literature review on prevention, treatment and recurrence. Nutrients 11:1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071514
Dua D, Graff C (2017) UCI machine learning repository. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: MHS’95, proceedings of the sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science, pp 39–43
Enayatifar R, Yousefi M, Abdullah AH, Darus AN (2013) Lahs: A novel harmony search algorithm based on learning automata. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18(12):3481–3497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2013.04.028, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1007570413002001
Geem ZW (2005) Harmony search in water pump switching problem. In: Wang L, Chen K, Ong YS (eds) Advances in natural computation. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 751–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/11539902_92
Ghosh KK, Ahmed S, Singh PK, Geem ZW, Sarkar R (2020a) Improved binary sailfish optimizer based on adaptive \(\beta\)-hill climbing for feature selection. IEEE Access 2020:1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2991543
Ghosh KK, Singh PK, Hong J, Geem ZW, Sarkar R (2020b) Binary social mimic optimization algorithm with x-shaped transfer function for feature selection. IEEE Access 8:97890–97906. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2996611
Ghosh S, Biswas S, Sarkar D, Sarkar PP (2014) A novel neuro-fuzzy classification technique for data mining. Egypt Informatics J 15(3):129–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eij.2014.08.001, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1110866514000292
Gupta R, Mohan I, Narula J (2016) Trends in coronary heart disease epidemiology in India, hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease in Low and Middle Income Countries. Ann Glob Health 82(2):307–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aogh.2016.04.002, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214999616300297
Harimoorthy K, Thangavelu M (2020) Multi-disease prediction model using improved svm-radial bias technique in healthcare monitoring system. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01652-0
Hashemi A, Meybodi M (2011) A note on the learning automata based algorithms for adaptive parameter selection in PSO. Appl Soft Comput 11(1):689–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2009.12.030
Hichem H, Elkamel M, Rafik M, Mesaaoud MT, Ouahiba C (2019) A new binary grasshopper optimization algorithm for feature selection problem. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 2019:5
Hong Z, Yang J (1991) Optimal discriminant plane for a small number of samples and design method of classifier on the plane. Pattern Recogn 24(4):317–324
Horn G, Oommen BJ (2010) Solving multiconstraint assignment problems using learning automata. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybern) 40(1):6–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2009.2032528
Hsu C, Manogaran G, Panchatcharam P, Vivekanandan S (2018) A new approach for prediction of lung carcinoma using back propagation neural network with decision tree classifiers. In: 2018 IEEE 8th international symposium on cloud and service computing (SC2), pp 111–115
Hu B, Dai Y, Su Y, Moore P, Zhang X, Mao C, Chen J, Xu L (2018) Feature selection for optimized high-dimensional biomedical data using an improved shuffled frog leaping algorithm. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 15(6):1765–1773
Janghel RR, Shukla A, Verma K (2016) Soft computing based expert system for hepatitis and liver disorders. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on engineering and technology (ICETECH), pp 740–744
Jayaraman V, Sultana HP (2019) Artificial gravitational cuckoo search algorithm along with particle bee optimized associative memory neural network for feature selection in heart disease classification. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01193-6
Kadam V, Jadhav S, Vijayakumar K (2019) Breast cancer diagnosis using feature ensemble learning based on stacked sparse autoencoders and softmax regression. J Med Syst 2019:43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1397-z
Khuriwal N, Mishra N (2018) Breast cancer diagnosis using adaptive voting ensemble machine learning algorithm. In: 2018 IEEMA Engineer Infinite Conference (eTechNxT), pp 1–5
Kira K, Rendell L (1992) The feature selection problem: traditional methods and a new algorithm. In: 10th National Conf on Artificial Intelligence, Cambridge: MIT Press, pp 129–134
Kulkarni S, Mishra G, Dusane R (2019) Determinants of compliance to breast cancer screening and referral in low socio-economic regions of urban India. Int J Prevent Med 10(1):84. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_335_17, http://www.ijpvmjournal.net/article.asp?issn=2008-7802;year=2019;volume=10;issue=1;spage=84;epage=84;aulast=Kulkarni;t=6
Kumar M, Kumar R, Kaur P (2019) A healthcare monitoring system using random forest and internet of things (iot). Multimedia Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7327-8
Kumar P, Thakur R (2020) Liver disorder detection using variable- neighbor weighted fuzzy k nearest neighbor approach. Multimedia Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-07978-3
Kurgan L, Cios K, Tadeusiewicz R, Ogiela M, Goodenday L (2001) Knowledge discovery approach to automated cardiac spect diagnosis. Artif Intell Med 23(2):149–169
Lin Y, Wang L, Zhong Y, Zhang C (2016) Control scaling factor of cuckoo search algorithm using learning automata. Int J Comput Sci Math 7:476. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJCSM.2016.080088
Lopez FG, Torres MG, Batista BM, Perez JAM, Moreno-Vega JM (2006) Solving feature subset selection problem by a parallel scatter search, feature Cluster on Scatter Search Methods for Optimization. Eur J Oper Res 169(2):477–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2004.08.010
Mafarja M, Aljarah I, Faris H, Hammouri AI, Al-Zoubi AM, Mirjalili S (2019) Binary grasshopper optimisation algorithm approaches for feature selection problems. Expert Syst Appl 117:267–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.09.015
Malakar S, Ghosh M, Bhowmik S, Sarkar R, Nasipuri M (2020) A ga based hierarchical feature selection approach for handwritten word recognition. Neural Comput Appl 32(7):2533–2552
Mangasarian OL, Wolberg WH (1990) Cancer diagnosis via linear programming. SIAM News 23(5):1–18
Mitchell M (1996) An introduction to genetic algorithms. MIT Press, Cambridge
Mojtaba Ahmadieh Khanesar, Mohammad Teshnehlab, Mahdi Aliyari Shoorehdeli (2007) A novel binary particle swarm optimization. In: 2007 Mediterranean Conference on Control Automation, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/MED.2007.4433821
Murty NVR, Babu PMSP (2017) A critical study of classification algorithms for lungcancer disease detection and diagnosis. Int J Comput Intell Res 13:1041–1048
Nagpal S, Arora S, Dey S, Shreya, (2017) Feature selection using gravitational search algorithm for biomedical data. Procedia Comput Sci 115:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.09.133, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877050917319610 (7th International Conference on Advances in Computing & Communications, ICACC-2017, 22-24 August 2017, Cochin, India)
Narendra KS, Thathachar MAL (1974) Learning automata—a survey. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet SMC 4(4):323–334. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1974.5408453
Nguyen T, Khosravi A, Creighton D, Nahavandi S (2015) Classification of healthcare data using genetic fuzzy logic system and wavelets. Expert Syst Appl 42(4):2184–2197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.10.027, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417414006514
Prakash PNS, Rajkumar N (2020) Improved local fisher discriminant analysis based dimensionality reduction for cancer disease prediction. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02542-6
Ramana BV, Kumar Boddu RS (2019) Performance comparison of classification algorithms on medical datasets. In: 2019 IEEE 9th annual computing and communication workshop and conference (CCWC), pp 0140–0145
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S (2009) Gsa: A gravitational search algorithm, special Section on High Order Fuzzy Sets. Inf Sci 179(13):2232–2248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2009.03.004, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025509001200
Rastegar R, Meybodi MR, Badie K (2004) A new discrete binary particle swarm optimization based on learning automata. In: 2004 International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, 2004. Proceedings., pp 456–462. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLA.2004.1383550
Reddy D (2019) Elimination of viral hepatitis: evolution and india’s response. Indian J Public Health 63:275. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijph.IJPH_581_19
Sandhiya S, Palani U (2020) An effective disease prediction system using incremental feature selection and temporal convolutional neural network. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01910-6
Saqlain S, Shah F, Ramzan MS, Khan I, Ashraf M, Ghani A, Awais M (2018) Fisher score and matthews correlation coefficient-based feature subset selection for heart disease diagnosis using support vector machines. Knowl Inf Syst 2018:58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-018-1185-y
Saremi S, Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2017) Grasshopper optimisation algorithm: theory and application. Adv Eng Softw 105:30–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.01.004
Sarkar S, Ghosh M, Chatterjee A, Malakar S, Sarkar R (2018) An advanced particle swarm optimization based feature selection method for tri-script handwritten digit recognition. In: International conference on computational intelligence, communications, and business analytics, Springer, pp 82–94
Shankar A, Saini D, Dubey A, Roy S, Bharati S, Singh N, Khanna M, Prasad C, Singh M, Kumar S, Sirohi B, Seth T, Rinki M, Mohan A, Guleria R, Rath G (2019) Feasibility of lung cancer screening in developing countries: challenges, opportunities and way forward. Transl Lung Cancer Res 8:S106–S121. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr.2019.03.03
Shihabudheen K, Pillai G (2018) Recent advances in neuro-fuzzy system: a survey. Knowl Based Syst 152:136–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.04.014, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950705118301825
Street WN, Wolberg WH, Mangasarian OL (1993) Nuclear feature extraction for breast tumor diagnosis. In: Acharya RS, Goldgof DB (eds) Biomedical image processing and biomedical visualization, international society for optics and photonics, SPIE, vol 1905, pp 861–870. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.148698
Thanga Selvi R, Muthulakshmi I (2020) An optimal artificial neural network based big data application for heart disease diagnosis and classification model. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02181-x
Wilt C, Thayer J, Ruml W (2010) A comparison of greedy search algorithms
Xue B, Zhang M, Browne WN, Yao X (2016) A survey on evolutionary computation approaches to feature selection. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 20(4):606–626
Yagiura M, Ibaraki T (2001) On metaheuristic algorithms for combinatorial optimization problems. Syst Comput Jpn 32(3):33–55. https://doi.org/10.1002/1520-684X(200103)32:3%3c33::AID-SCJ4%3e3.0.CO;2-P
Yang X, Suash Deb (2009) Cuckoo search via lévy flights. In: 2009 World Congress on Nature Biologically Inspired Computing (NaBIC), pp 210–214
Yang XS (2010a) Firefly algorithm, stochastic test functions and design optimisation. Int J Bio-inspired Comput 2010:2. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBIC.2010.032124
Yang XS (2010b) A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12538-6_6
Yang XS (2012) Flower pollination algorithm for global optimization. In: Durand-Lose J, Jonoska N (eds) Unconventional computation and natural computation. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 240–249
Yu L, Liu H (2004) Eficient feature selection via analysis of relevance and redundancy. J Mach Learn Res 5:1205–1224
Funding
All the authors declare that they have not received any kind of funding from any agencies
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest or competing interests
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors
Informed consent
Not applicable for this submission
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dey, C., Bose, R., Ghosh, K.K. et al. LAGOA: Learning automata based grasshopper optimization algorithm for feature selection in disease datasets. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 13, 3175–3194 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03155-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03155-3