Abstract
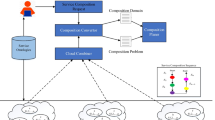
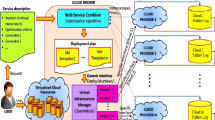
Cloud computing as a new computing paradigm has a great capacity for storing and accessing the remote data and services. Presently, many organizations decide to reduce the burden of local resources and support them by outsourcing the resources to the cloud. Typically, scalable resources are provided as services over the Internet. The way of choosing appropriate services in the cloud computing is done by determining the different Quality of Service (QoS) parameters to perform optimized resource allocation. Therefore, service composition as a developing approach combines the existing services to increase the number of cloud applications. Independent services can be integrated into complex composited services through service composition. In this paper, a new hybrid method is proposed for efficient service composition in the cloud computing. The agent-based method is also used to compose services by identifying the QoS parameters and the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is employed for selecting the best services based on fitness function. The simulation results have shown the performance of the method in terms of reducing the combined resources and waiting time.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almorsy M et al (2014) Adaptable, model-driven security engineering for SaaS cloud-based applications. Autom Softw Eng 21(2):187–224
AlRashidi M, El-Hawary M (2007) Hybrid particle swarm optimization approach for solving the discrete OPF problem considering the valve loading effects. Power Systems. IEEE Transac 22(4):2030–2038
Arvanitis S et al (2017) Why do firms adopt cloud computing? A comparative analysis based on South and North Europe firm data. Telemat Inform 34(7):1322–1332
Ashouraie M, Jafari Navimipour N (2015) Priority-based task scheduling on heterogeneous resources in the Expert Cloud. Kybernetes 44(10):1455–1471
Azad P, Navimipour JN (2017). An energy-aware task scheduling in cloud computing using a hybrid cultural and ant colony optimization algorithm. Int J Cloud Appl Comput 7(4)
Aznoli F, Navimipour NJ (2017) Cloud services recommendation: Reviewing the recent advances and suggesting the future research directions. J Netw Comput Appl 77:73–86
Behzadi S, Alesheikh AA (2013) Introducing a novel model of belief–desire–intention agent for urban land use planning. Eng Appl Artif Intell 26(9):2028–2044
Benmerzoug D et al. (2013). Agent interaction protocols in support of cloud services composition. In: International Conference on Industrial Applications of Holonic and Multi-Agent Systems, Springer
Buyya R, Ranjan R (2010) Special section: Federated resource management in grid and cloud computing systems. Future Gener Comput Syst 26(8):1189–1191
Canfora G et al. (2005). An approach for QoS-aware service composition based on genetic algorithms. Proceedings of the 7th annual conference on Genetic and evolutionary computation, ACM
Cao B et al. (2016). Querying similar process models based on the Hungarian Algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing
Chiregi M, Navimipour NJ (2016) A new method for trust and reputation evaluation in the cloud environments using the recommendations of opinion leaders’ entities and removing the effect of troll entities. Comput Hum Behav 60:280–292
Del Valle Y et al (2008) Particle swarm optimization: basic concepts, variants and applications in power systems. Evolutionary Computation. IEEE Transac 12(2):171–195
Dinesha H, Agrawal VK (2012). Multi-level authentication technique for accessing cloud services. Computing, Communication and Applications (ICCCA), 2012 International Conference on, IEEE
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proceedings of the sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science, MHS'95. IEEE
Elbeltagi E et al (2005) Comparison among five evolutionary-based optimization algorithms. Adv Eng Inf 19(1):43–53
Ferber J (1999). Multi-agent systems: an introduction to distributed artificial intelligence, Addison-Wesley Reading
Fethallah H et al. (2012). QoS-aware service selection based on swarm particle optimization. Information Technology and e-Services (ICITeS), 2012 International Conference on, IEEE
Guha T, Ludwig SA (2008). Comparison of service selection algorithms for grid services: Multiple objective particle swarm optimization and constraint satisfaction based service selection. Tools with Artificial Intelligence, 2008. ICTAI’08. 20th IEEE International Conference on, IEEE
Gupta B et al. (2016). Handbook of research on modern cryptographic solutions for computer and cyber security, IGI Global
Gutierrez-Garcia JO, Sim KM (2013) Agent-based Cloud service composition. Appl Intell 38(3):436–464
Iosup A et al. (2014). Iaas cloud benchmarking: approaches, challenges, and experience. In: Cloud Computing for Data-Intensive Applied, Springer, Berlin 83–104
Ivanović D, Carro M (2014). Transforming Service Compositions into Cloud-Friendly Actor Networks. In: International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing, Springer, Berlin
Jafari Navimipour N et al (2015) Expert Cloud: A Cloud-based framework to share the knowledge and skills of human resources. Comput Hum Behav 46(C):57–74
Jeong H-Y et al (2016) A service composition model based on user experience in Ubi-cloud comp. Telecommunication Syst 61(4):897–907
Jiuxin C et al. (2010). Efficient multi-objective services selection algorithm based on particle swarm optimization. Services Computing Conference (APSCC), 2010 IEEE Asia-Pacific, IEEE
Jula A et al (2014) Cloud computing service composition: A systematic literature review. Expert Syst Appl 41(8):3809–3824
Kang J, Sim KM (2012) A multiagent brokering protocol for supporting Grid resource discovery. Appl Intell 37(4):527–542
Kennedy J (2011) Particle swarm optimization. In: Sammut C, Webb GI (eds) Encyclopedia of machine learning. Springer, Boston, pp 760–766
Kiraz MS (2016) A comprehensive meta-analysis of cryptographic security mechanisms for cloud computing. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 7(5):731–760
Kofler K et al. (2009). A parallel branch and bound algorithm for workflow QoS optimization. Parallel Processing, 2009. ICPP’09. International Conference on, IEEE
Kurdi H et al (2015) A combinatorial optimization algorithm for multiple cloud service composition. Comput Electr Eng 42:107–113
Lai KR et al (2010) Learning opponent’s beliefs via fuzzy constraint-directed approach to make effective agent negotiation. Appl Intell 33(2):232–246
Li J et al (2015) A hybrid cloud approach for secure authorized deduplication. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 26(5):1206–1216
Liao J et al (2012) Service composition based on niching particle swarm optimization in service overlay networks. KSII Transac Internet Inf Syst 6(4):1106–1127
Lin M et al (2013) Dynamic right-sizing for power-proportional data centers. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 21(5):1378–1391
Ludwig SA, Schoene T (2011). Web service selection using particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithms. Nature Biol Inspired Computing (NaBIC), 2011 Third World Congress on, IEEE
Mell P, Grance T (2009) Draft NIST working definition of cloud computing. Referenced June 3rd 15:32
Mezgár I, Rauschecker U (2014) The challenge of networked enterprises for cloud computing interoperability. Comput Ind 65(4):657–674
Milani BA, Navimipour NJ (2016) A comprehensive review of the data replication techniques in the cloud environments: Major trends and future directions. J Netw Comput Appl 64:229–238
Murillo J et al (2011) Schedule coordination through egalitarian recurrent multi-unit combinatorial auctions. Appl Intell 34(1):47–63
Nathani A et al (2012) Policy based resource allocation in IaaS cloud. Future Gener Comput Syst 28(1):94–103
Navimipour NJ, Milani FS (2015) Task scheduling in the cloud computing based on the cuckoo search algorithm. Int J Model Opt 5(1):44
Navimipour NJ et al (2015) Expert Cloud: A Cloud-based framework to share the knowledge and skills of human resources. Comput Hum Behav 46:57–74
Navimipour NJ et al. (2017). Resources discovery in the cloud environments using collaborative filtering and ontology relations. Electron Commer Res Appl 26(Supplement C): 89–100
Öztürk P et al (2010) A multiagent framework for coordinated parallel problem solving. Appl Intell 33(2):132–143
Pooranian Z et al (2015) An efficient meta-heuristic algorithm for grid computing. J Combinatorial Opt 30(3):413–434
Proaño J et al (2017) Empirical modeling and simulation of an heterogeneous Cloud computing environment. Parallel Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parco.2017.11.004
Rao J, Su X (2004). A survey of automated web service composition methods. In: Semantic Web Services Web Process Composition Springer, Berlin: 43–54
Sellami M et al. (2013). PaaS-independent Provisioning and Management of Applications in the Cloud. In: 2013 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Cloud Computing, IEEE
Sheikholeslami F, Navimipour JN (2017). Service allocation in the cloud environments using multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on crowding distance. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation
Shi Y, Eberhart R (1998). A modified particle swarm optimizer. Evolutionary Computation Proceedings, 1998. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence., The 1998 IEEE International Conference on, IEEE
Singh A et al. (2015). A novel agent based autonomous and service composition framework for cost optimization of resource provisioning in cloud computing. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences
Stergiou C et al (2018) Secure integration of IoT and cloud computing. Future Gener Comput Syst 78:964–975
Tao F et al. (2008). Resource service composition and its optimal-selection based on particle swarm optimization in manufacturing grid system. Ind Inf IEEE Transac 4(4): 315–327
Tout H et al (2015) AOMD approach for context-adaptable and conflict-free web services composition. Comput Electr Eng 44:200–217
Verhaegen M et al. (2007). Filtering and system identification: an introduction to using Matlab software. Delft Univ Technol 68
Wakunuma K, Masika R (2017) Cloud computing, capabilities and intercultural ethics: Implications for Africa. Telecommun Policy 41(7):695–707
Wang W et al. (2013). Revenue maximization with dynamic auctions in IaaS cloud markets. Quality of Service (IWQoS), 2013 IEEE/ACM 21st International Symposium on, IEEE
Wang D et al (2015) A genetic-based approach to web service composition in geo-distributed cloud environment. Comput Electr Eng 43:129–141
Wang H et al (2016) A multi-agent reinforcement learning approach to dynamic service composition. Inf Sci 363:96–119
Wooldridge M (2009). An introduction to multiagent systems, Wiley, New Jersey
Xia H et al. (2009). Web service selection algorithm based on particle swarm optimization. Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, 2009. DASC’09. Eighth IEEE International Conference on, IEEE
Xie R et al. (2014). Diagnosing vulnerability patterns in cloud audit logs. In: High performance cloud auditing applications, Springer, Berlin: 119–146
Ye Z et al. (2011). Genetic algorithm based QoS-aware service compositions in cloud computing. In: International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications, Springer
Yu Q et al (2015) Ant colony optimization applied to web service compositions in cloud computing. Comput Electr Eng 41:18–27
Zeginis D et al (2013) A user-centric multi-PaaS application management solution for hybrid multi-Cloud scenarios. Scalable Comput 14(1):17–32
Zeng Z, Veeravalli B (2014) Optimal metadata replications and request balancing strategy on cloud data centers. J Parallel Distrib Comput 74(10):2934–2940
Zhao C-Y et al (2014) A hybrid algorithm combining ant colony algorithm and genetic algorithm for dynamic web service composition. Open Cybern Syst J 8:146–154
Zou G et al. (2010). AI planning and combinatorial optimization for web service composition in cloud computing. In: Proc international conference on cloud computing and virtualization
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naseri, A., Jafari Navimipour, N. A new agent-based method for QoS-aware cloud service composition using particle swarm optimization algorithm. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 10, 1851–1864 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0773-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0773-8