Abstract
Developing a novel bio-coagulant based on plant seeds using effective and affordable technique is an innovative way to advance bio-coagulant research in both developed and developing countries. This study investigates the potentiality and capacity of new bio-coagulants from Cucumeropsis mannii and Luffa acutangula seed proteins extract and purify for fecal sludge dewatering. A factorial design was made to obtain the best overall process optimization and improve the reaction between the coagulation/flocculation factors to provide suitable conditions for fecal sludge dewatering and concentrate a maximum of organic matter for biogas production. The experimental method identifies the potential parameters and the plant seed components that could interact based on different dosages used to optimize the treatment. To enhance the treatment, 10 mg/l of protein solution with a concentration of 10 g/l at pH 7.25 is considered a low-level dosage, and 20 mg/l of protein solution with a concentration of 20 g/l at pH 7.25 is considered a high-level dosage. The results have shown that the dosage of 20 mg/l of protein solution with a concentration of 20 g/l at pH 7.25 is optimal, with 99.17% turbidity, 99.58% COD and 99.13% ammonia nitrogen removal for C. mannii while L. acutangula seed proteins remove 97.67% turbidity, 98.49% COD and 98.7% ammonia nitrogen and recover 80% of water during fecal sludge dewatering.
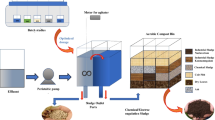
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Miller, G.W.: Integrated concepts in water reuse: managing global water needs. Desalination 187(1–3), 65–75 (2006)
Yimer, A., Dame, B.: Papaya seed extract as coagulant for potable water treatment in the case of Tulte River for the community of Yekuset district, Ethiopia. Environ. Chall. 4, 100198 (2021)
Azouz, M.: Alzheimer’s Disease Neurotoxic Peptides: Towards a Comprehension of Their Modes of Action on Model Membranes. Université de Montréal, Montreal (2019)
Rekha, B., Sumithra, S.: Natural plant seeds as an alternative coagulant in the treatment of mining effluent. Rekha Sumithra 6, 15–23 (2020)
Saleem, M., Bachmann, R.T.: A contemporary review on plant-based coagulants for applications in water treatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 72, 281–297 (2019)
Dezfooli, S.M., et al.: A simplified method for the purification of an intrinsically disordered coagulant protein from defatted Moringa oleifera seeds. Process Biochem. 51(8), 1085–1091 (2016)
Bhatia, S., Othman, Z., Ahmad, A.L.: Pretreatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) using Moringa oleifera seeds as natural coagulant. J. Hazard. Mater. 145(1–2), 120–126 (2007)
Muyibi, S.A., Evison, L.M.: Optimizing physical parameters affecting coagulation of turbid water with Morninga oleifera seeds. Water Res. 29(12), 2689–2695 (1995)
Lee, C.S., et al.: Optimisation of extraction and sludge dewatering efficiencies of bio-flocculants extracted from Abelmoschus esculentus (okra). J. Environ. Manage. 157, 320–325 (2015)
Betatache, H., et al.: Conditioning of sewage sludge by prickly pear cactus (Opuntia ficus Indica) juice. Ecol. Eng. 70, 465–469 (2014)
Sánchez-Martín, J., Beltrán-Heredia, J.: Nature is the answer: water and wastewater treatment by new natural-based agents. In: Advances in Water Treatment and Pollution Prevention, pp. 337–375. Springer (2012)
Miller, S.M., et al.: Toward understanding the efficacy and mechanism of Opuntia spp. as a natural coagulant for potential application in water treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42(12), 4274–4279 (2008)
Ramesh, P., Padmanaban, V., Sivacoumar, R.: Influence of homemade coagulants on the characteristics of surface water treatment: experimental study. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 4(12), 342–345 (2015)
Thakur, S.S., Choubey, S.: Use of Tannin based natural coagulants for water treatment: an alternative to inorganic chemicals. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 6(7), 3628–3634 (2014)
Govindan, V.: Coagulation studies on natural seed extracts. J Indian Waterworks Assoc. 37(2), 145 (2005)
Omer, R., et al.: Effect of guar gum (Cyamopsis tetragonolobus) powdered as natural coagulant aid with alum on drinking water treatment. ARPN J. Sci. Technol. 3, 1222–1228 (2013)
Schaefer, H., Renner, S.S.: A gift from the New World? The West African crop Cucumeropsis mannii and the American Posadaea sphaerocarpa (Cucurbitaceae) are the same species. Syst. Bot. 35(3), 534–540 (2010)
Kortse, P., Oladiran, A.: The effects of leaf colour at fruit harvest and fruit after-ripening duration on (Cucumeropsis mannii Naudin) seed quality. Extraction 3(2), 10 (2013)
Mbuli-Lingundi, Y., et al.: Chemical composition of seeds from Cucumeropsis mannii Naudin and their suitability as food. Zeitschrift fur Lebensmittel-untersuchung und-forschung 177(1), 37–40 (1983)
Houdegbe, C.A., Sogbohossou, O.E., Achigan-Dako, E.G.: Utilization and breeding perspective in the egusi gourd Melothria sphaerocarpa (Cogn.) H. Schaef. et SS Renner (syn: Cucumeropsis mannii Naudin). Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 63(3), 545–559 (2016)
Shendge, P.N., Belemkar, S.: Therapeutic potential of Luffa acutangula: a review on its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicological aspects. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1177 (2018)
Ogunbusola, E.M., Fagbemi, T.N., Osundahunsi, O.F.: Chemical and functional properties of full fat and defatted white melon (Cucumeropsis mannii) seed flours. J. Food Sci. Eng. 2(12), 691 (2012)
Ahmad, A., et al.: Exploring the extraction methods for plant-based coagulants and their future approaches. Sci. Total. Environ. 818, 151668 (2021)
Croteau, R., Kutchan, T.M., Lewis, N.G.: Natural products (secondary metabolites). Biochem. Mol. Biol. Plants 24, 1250–1319 (2000)
Hounsome, N., et al.: Plant metabolites and nutritional quality of vegetables. J. Food Sci. 73(4), R48–R65 (2008)
Liang, C., Garcia, R.A.: Protein-based flocculants and their applications. In: Sarker, M.I., Liu, L.S., Yadav, M.P., Yosief, H.O., Hussain, S.A. (eds.) Conversion of Renewable Biomass into Bioproducts, pp. 305–330. American Chemical Society, Washington (2021)
Baraniak, B., Świeca, M., Słowik, A.: Flocculants application for precipitation and separation of proteins from Lens culinaris cv. Tina. Acta Sci. Polonorum Technol. Alimentaria 8(2), 33–40 (2009)
Yamaguchi, N.U., et al.: A review of Moringa oleifera seeds in water treatment: trends and future challenges. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 147, 405–420 (2021)
Villaseñor-Basulto, D.L., et al.: Wastewater treatment using Moringa oleifera Lam seeds: a review. J. Water Proc. Eng. 23, 151–164 (2018)
Ghebremichael, K., Gunaratna, K., Dalhammar, G.: Single-step ion exchange purification of the coagulant protein from Moringa oleifera seed. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 70(5), 526–532 (2006)
Sánchez-Martín, J., Ghebremichael, K., Beltrán-Heredia, J.: Comparison of single-step and two-step purified coagulants from Moringa oleifera seed for turbidity and DOC removal. Biores. Technol. 101(15), 6259–6261 (2010)
William, H.: Official methods of analysis of AOAC international. AOAC Off. Method 985, 29 (2000)
Kansal, S.K., Kumari, A.: Potential of M. oleifera for the treatment of water and wastewater. Chem. Rev. 114(9), 4993–5010 (2014)
Okuda, T., et al.: Isolation and characterization of coagulant extracted from Moringa oleifera seed by salt solution. Water Res. 35(2), 405–410 (2001)
David, C., Narlawar, R., Arivazhagan, M.: Performance evaluation of Moringa oleifera seed extract (MOSE) in conjunction with chemical coagulants for treating distillery spent wash. Indian Chem. Eng. 58(3), 189–200 (2016)
Cescon, A., Jiang, J.-Q.: Filtration process and alternative filter media material in water treatment. Water 12(12), 3377 (2020)
Badifu, G., Ogunsua, A.: Chemical composition of kernels from some species of Cucurbitaceae grown in Nigeria. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 41(1), 35–44 (1991)
Rahman, I.M., et al.: Physicochemical properties of Moringa oleifera lam. seed oil of the indigenous-cultivar of Bangladesh. J. Food Lip. 16(4), 540–553 (2009)
Loukou, A., et al.: Macronutrient composition of three cucurbit species cultivated for seed consumption in Côte d’Ivoire. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 6(5), 10 (2007)
Anhwange, B., et al.: Chemical analysis of Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.), Cucumeropsis mannii (Naud.) and Telfairia occidentalis (Hook F.) seeds oils. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 265–268 (2010)
Abiodun, O., Adeleke, R.: Comparative studies on nutritional composition of four melon seeds varieties. Pak. J. Nutr. 9(9), 905–908 (2010)
Bae, Y., Foo, L., Karchesy, J.: GPC of natural procyanidin oligomers and polymers. Holzforschung 48(1), 4–6 (1994)
Huang, X., et al.: Molecular weight and protein binding affinity of Leucaena condensed tannins and their effects on in vitro fermentation parameters. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 159(3–4), 81–87 (2010)
Naumann, H., et al.: Molecular weight and protein-precipitating ability of condensed tannins from warm-season perennial legumes. J. Plant Interact. 9(1), 212–219 (2014)
Yarahmadi, M., et al.: Application of Moringa oleifera seed extract and poly aluminium chloride in water treatment. World Appl. Sci. J. 7(8), 962–967 (2009)
Chaudhuri, M., Khairuldin, P.: Coagulation-clarification of turbid coloured water by natural coagulant (Moringa oleifera) seed extract. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 8, 137–139 (2009)
Vilaseca, M., López-Grimau, V., Gutiérrez-Bouzán, C.: Valorization of waste obtained from oil extraction in Moringa oleifera seeds: coagulation of reactive dyes in textile effluents. Materials 7(9), 6569–6584 (2014)
Suhartini, S., Hidayat, N., Rosaliana, E.: Influence of powdered Moringa oleifera seeds and natural filter media on the characteristics of tapioca starch wastewater. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2(1), 1–11 (2013)
Francisco, J.P., et al.: Evaluation of the effect of the seed extract of Moringa oleifera Lam over the efficiency of organic filters in wastewater treatment of dairy cattle breeding. Eng. Agríc. 34, 143–152 (2014)
Santos, A.F., et al.: Isolation of a seed coagulant Moringa oleifera lectin. Proc. Biochem. 44(4), 504–508 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the National Key Research and Development Plan (2019YFC0408700) and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Research Development and technical assistance to RTTC-China Project (OPP1161151) and Reinvent the Toilet China Project: Innovative Toilet Solutions and Commercial Activities (OPP1157726)). The International Science and Technology Cooperation Base for Environment and Energy Technology of MOST supported this study.
Funding
The authors declare that they have no funds for this research that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare the following fund source, which may be considered as a potential conflict for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FAFJD: (Ph.D. student) conducted all the experiments and wrote the manuscript. ZL (Professor) revised the manuscript. XZ (Associate Professor) wrote and revised the manuscript. LZ: (Senior engineer) helped with experiment resources and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships, which may be considered as potential competing interests.
Ethical Approval
At this moment, I, Dima Francis Auguste Fleury Junior, consciously assure that for the manuscript: Plant Seed-Based Bio-coagulant Development and Application for Fecal Sludge Treatment and Biogas Production Improvement, the following is fulfilled: (1) This paper is the author’s original work, which has yet to be previously published elsewhere. (2) The paper is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. (3) The paper reflects the author's own research and analysis wholly and truthfully. (4) The paper properly credits the meaningful contributions of co-authors and co-researchers. (5) The results are appropriately placed in the prior and existing research context. (6) All sources used are correctly disclosed (correct citation). Copying of text must be indicated as such by using quotation marks and giving proper references. (7) All authors have been personally and actively involved in substantial work leading to the paper and will take public responsibility for its content. The violation of the Ethical Statement rules may result in severe consequences. To verify originality, your article may be checked by the originality detection software authenticate. I agree with the above statements and declare that this submission follows the policies of Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery as outlined in the Guide for Authors and in the Ethical Statement.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dima, F.A.F.J., Li, Z., Zhou, X. et al. Cucumeropsis mannii and Luffa acutangula Seed Proteins Analysis as a Novel Plant-Based Bio-coagulant: Fecal Sludge Treatment and Dewatering. Waste Biomass Valor (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02399-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02399-8