Abstract
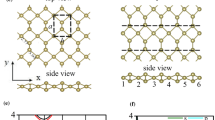
First-principles calculations are performed to determine the effects of zirconium doping on structural, electronic and optical properties of zinc oxide nanotubes. Dielectric tensor is derived within the random phase approximation and optical properties are calculated for both parallel and perpendicular electric field polarizations with respect to nanotube axis. Results show that for all impurity concentrations, the formation energy is negative; hence all doped systems are stable. Energy gap of zirconium-doped single walled zinc oxide nanotube is smaller than their pristine zinc oxide nanotube. Our results show that pristine zinc oxide nanotube is a direct gap semiconductor, while it is an indirect gap when zirconium is doped into zinc oxide nanotube. In Zn1−xZrxOs, the absorption edge has red shift to that of pure zinc oxide nanotube and is located at the visible region. Our results show optical anisotropy of pristine and zirconium-doped zinc oxide nanotube.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y Li, X Zhao and W Fan J. Phys. Chem. C 115 3552 (2011)
X Wang, W P Careg and S. Yee Sens. Actuators B 28 63 (1995)
Y Ohaya, M Ueda and Y Takahashi Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35 4738 (1996)
Y Natsume Thin Solid Films 372 30 (2000)
G K Paul, S Bandyapadhyay and S K Sen Phys. Stat. Sol. A 191 509 (2002)
Z K Tang, G K L Wong, P Yu, M Kawasaki, A Ohtomo and H koinuma Appl. Phys. Lett. 72 3270 (1998)
S Shionoya and W M Yen Phosphor Handbook (Boca Raton: CRC Press) (1999)
B O Regan and M Gratzel Nature 353 737 (1991)
M H Huang et al. Science 292 1897 (2001)
M S Arnold, P Avouris, Z W Pan and Z L Wang J. Phys. Chem. B 107 659 (2003)
G C Yi, C Wang and W I Park Semicond. Sci. Technol. 20 22 (2005)
Z L Wang Mater Today 7 26 (2004)
X Zhang, Y Zhang, J Xu, Z Wang, X Chen and D Yu Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 123111 (2005)
C Rath, S Singh, P Mallick, D Pandey, N P Lalla and N C Mishra Indian J. Phys. 83 415 (2009)
J Manam, S Das and A Isaac Indian J. Phys. 83 1407 (2009)
G Mandal and T Ganguly Indian J. Phys. 85 1229 (2011)
J J S Wu, C Liu, C T Wu, K H Chen and L C Chen Appl. Phys. Lett. 81 1312 (2002)
X H Zhang et al. J. Phys. Chem. B 107 10114 (2003)
Y J Xing et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 1689 (2003)
Z C Tu and X Hu Phys. Rev. B 74 035434 (2006)
A L He, X Q Wang, Y Q Fan and Y P Feng J. Appl. Phys. 108 084308 (2010)
R Moradian and M Shahrokhi Phys. E 44 1760 (2012)
R Moradian and M Shahrokhi J. Phys. Chem. Solids 74 1063 (2013)
M j K Yadav, M Ghosh, R Biswas, A K Raychaudhuri and A Mookerjee Phys. Rev. B 76 195450 (2007)
F Wang, B Liu, Z Zhang and S Yuan Phys. E 41 879 (2009)
F Wang et al. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254 6983 (2008)
M Lv, X Xiu, Z Pang, Y Dai and S Han Appl. Surf. Sci. 252 5687 (2006)
S B Qadri et al. Thin Solid Films 750 377 (2000)
V Gokulakrishnan, S Parthiban, K Jeganathan and K Ramamurthi Appl. Surf. Sci. 257 9068 (2011)
J Zhang and et al Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6 587 (2011)
P Blaha, D Singh, P I Sorantin and K Schwarz Phys. Rev. B 46 1321 (1992)
P Blaha and K Schwarz WIEN2k University of Technology Austria, http://www.wien2k.at/,Vienna. (2002)
J P Perdew, K Burke and M Ernzerhof Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865 (1996)
M Lv et al. Thin Solid Films 516 2017 (2008)
V Walle and C G Neugebauer J. Appl. Phys. 95 3851 (2004)
F Wooten Optical Properties of Solids (New York: Academic Press) (1972)
C Ambrosch-Draxl and J O Sofo Comput. Phys. Commun. 175 1 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahrokhi, M., Moradian, R. Structural, electronic and optical properties of Zn1−xZrxO nanotubes: first principles study. Indian J Phys 89, 249–256 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-014-0567-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-014-0567-6