Abstract
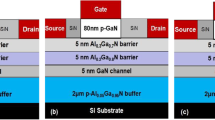
In this work, we have analysed the influence of passivation material such as Silicon dioxide (SiO2), Silicon Nitride (Si3N4), Aluminium oxide (Al2O3), Hafnium Silicon Oxide (HfSiO4), Yttrium Oxide (Y2O3), Hafnium Oxide (HfO2), Lanthanum Oxide (La2O3), and Titanium Oxide (TiO2) on the operational characteristics of gate field plate Al0.3Ga0.7 N/GaN/Al0.04Ga0.96 N Double Heterojunction (DH) HEMTs on silicon carbide substrate. The proposed DH-HEMT device structure having 0.25 μm gate length, 0.5 μm passivation thickness, 1 μm field plate length, and 3.2 μm gate to drain distance were used in numerical simulation. The off-state breakdown voltage (VBR), maximum transconductance (gm), ON resistance (RON), intrinsic capacitances (CGS and CGD), and cut-off frequency (fT) were investigated. From the analysis it was observed that the breakdown voltage (VBR) of the DH-HEMT is improved with high-k passivation layers, however, VBR does not increase for an increase in permittivity of different passivation material beyond a certain value. The La2O3 passivation DH-HEMT shows the highest breakdown voltage of 773 V than SiO2. Moreover, La2O3 yields better IDMAX, gm, and fT among the other passivation materials used in this work. The Al2O3 passivation layer DH-HEMT device shows 31 THz.V of JFoM, and a very low ON-resistance of 0.95 Ω.mm. From this analysis, the performance characteristics of various passivation layer material were observed and will be helpful for the selection of suitable passivation material for future GaN-based HEMT applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Adivarahan V, Gaevski ME, Islam MM, Zhang B, Deng Y, Khan MA (2008) Double-recessed high-frequency AlInGaN/InGaN/GaN metal–oxide double heterostructure field-effect transistors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 55(2):495–499. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2007.913001
Fletcher ASA, Nirmal D, Arivazhagan L, Murugapandiyan P et al (2022) A 28-GHz low-loss AlGaN/GaN HEMT for TX/RX switches in 5G base stations. J Electron Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09367-9
Natarajan R, Parthasarathy E (2021) Breakdown voltage enhancement of Al0.1Ga0.9N channel HEMT with recessed floating field plate. Silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01322-x
Shrestha NM, Li Y, Chen C-H, Sanyal I, Tarng J-H, Chyi J-I, Samukawa S (2020) Design and simulation of high performance lattice matched double barrier normally off AlInGaN/GaN HEMTs. IEEE J Electron Devices Soc 8:873–878. https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2020.3014252
Moon J-S, Wong J, Grabar B, Antcliffe M, Chen P, Arkun E, Khalaf I, Corrion A, Chappell J, Venkatesan N, Fay P (2020) 360 GHz fMAX graded-channel AlGaN/GaN HEMTs for mmW low-noise applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett 41:1173–1176. https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2020.3005337
Murugapandiyan P, Nirmal D, Hasan MdT, Varghese A, Ajayan J, Augustine Fletcher AS, Ramkumar N (2021) Influence of AlN passivation on thermal performance of AlGaN/GaN high-electron mobility transistors on sapphire substrate: A simulation study. Mater Sci Eng Vol B 273:115449, ISSN0921–5107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2021.115449
Wang R, Li G, Karbasian G, Guo J, Faria F, Hu Z, Yue Y, Verma J, Laboutin O, Cao Y, Johnson W, Snider G, Fay P, Jena D, Xing HG (2013) InGaN channel high-electron-mobility transistors with InAlGaN Barrier and fT/fmax of 260/220 GHz. Appl Phys Express 6:016503. https://doi.org/10.7567/APEX.6.016503
Sohel SH, Xie A, Beam E, Xue H, Razzak T, Bajaj S, Cao Y, Lee C, Lu W, Rajan S (2019) Polarization engineering of AlGaN/GaN HEMT with graded InGaN sub-channel for high-linearity X-band applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett 40(4):522–525. https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2019.2899100
Huang J, Ming L, Tang C-W, Lau K--M (2014) Lg = 100 nm T-shaped gate AlGaN/GaN HEMTs on Si substrates with non-planar source/drain regrowth of highly-doped n+-GaN layer by MOCVD. Chin Phys B 23:128102. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/23/12/128102
Fletcher ASA, Nirmal D, Ajayan J, Arivazhagan L (2020) An intensive study on assorted substrates suitable for high JFOM AlGaN/GaN HEMT. Silicon 13:1591–1598
Ankit Soni A, Shrivastava M (2020) Novel drain-connected field plate GaN HEMT designs for improved VBD–RON Trade-off and RF PA performance. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 67(4):1718–1725. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2020.2976636
Subramani NK, Julien C, Ahmad A, Jean C, Raphael S, Raymond Q (2017) Identification of GaN buffer traps in microwave power AlGaN/GaN HEMTs through low frequency S parameters measurements and TCAD-based physical device simulations. J Elect Dev Soc 5:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2017.2672685
Toprak A, Osmanoğlu S, Öztürk M, Yılmaz D, Cengiz Ö, Şen Ö, Bütün B, Özcan S, Özbay E (2018) Effect of gate structures on the DC and RF performance of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs. Semicond Sci Technol 33:125017DOI. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6641/aaebab
Hung T, Park PS, Krishnamoorthy S, Nath DN, Rajan S (2014) Interface charge engineering for enhancement-mode GaN MISHEMTs. IEEE Electron Device Lett 35(3):312–314. https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2013.2296659
Kolluri S, Keller S, DenBaars P, Mishra UK (2012) Microwave power performance N-Polar GaN MISHEMTs grown by MOCVD on SiC substrates using an Al2O3 etch-stop technology. IEEE Electron Device Lett 33(1):44–46. https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2011.2173458
Jiang H, Liu C, Ng KW, Lau KM, Lau KM (2018) High-performance AlGaN/GaN/Si power MOSHEMTs with ZrO2 gate dielectric. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 65(12):5337–5342. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2018.2874075
Liu C, Chor EF, Tan LS (2007) Enhanced device performance of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs using HfO2 high-k dielectric for surface passivation and gate oxide. Semicond Sci Technol 22:522–527. https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/22/5/011
Hanawa H, Onodera H, Nakajima A, Horio K (2014) Numerical analysis of breakdown voltage enhancement in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs with a High-k passivation layer. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 61(3):769–775. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2014.2298194
Roff C, Benedikt J, Tasker PJ, Wallis DJ, Hilton KP, Maclean JO, Hayes DG, Uren MJ, Martin T (2009) Analysis of DC–RF dispersion in AlGaN/GaN HFETs using RF waveform engineering. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 56(1):13–19. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2008.2008674
Ohno Y, Nakao T, Kishimoto S, Maezawa K, Mizutani T (2003) Effect of surface passivation on breakdown of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs. 2003 International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, San Diego, CA, USA, 169-170. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCS.2003.1239959
Brown DF et al (2013) High-speed enhancement-mode GaN power switch with regrown n+ GaN ohmic contacts and staircase field plates. IEEE Electron Device Lett 34(9):1118–1120. https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2013.2273172
Karmalkar S, Mishra UK (2001) Enhancement of breakdown voltage in AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistors using a field plate. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 48(8):1515–1521. https://doi.org/10.1109/16.936500
Ambacher O, Majewski J, Miskys C, Link A, Hermann M, Eickho M, Stutzmann M, Bernardini F, Fiorentini V, Tilak V et al (2002) Pyroelectric properties of Al (In) GaN/GaN hetero-and quantum well structures. J Phys Condens Matter 14:3399–3434
Inoue T et al (2008) Polarization engineering on buffer layer in GaN-based heterojunction FETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 55(2):483–488. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2007.912367
Li C, Li Z, Peng D, Ni J, Pan L, Zhang D (2015) Improvement of breakdown and current collapse characteristics of GaN HEMT with a polarization-graded AlGaN buffer,Semicond. Sci Technol 30:035007. https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/30/3/035007
Piprek J (2003) Semiconductor optoelectronic devices: introduction to physics and simulation. Academic, UCSB, p 22
Liu K, Li X (2020) Polarization properties of wurtzite III nitride indicate the principle of polarization engineering. Appl Phys :arXiv:1808.07211
Int SILVACO (2016) ATLAS User’s Manual; Device Simulation Software: Santa Clara, CA, USA. Available online: https://www.silvaco.com. Accessed 31 Dec 2021
Adachi S (2008) Properties of semiconductor alloys: Group-IV, III-V and II-VI semiconductors. Wiley, Chichester
Natarajan R (2022) Enhancement of blocking voltage in GaN HEMT using stacked passivation layer. Silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01646-8
Meneghesso G, Meneghini M, Zanoni E (2014) Breakdown mechanisms in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs: an overview. Jpn J App Phy 53:1–9
Binola K, Shobha R, Prajoon P, Mohankumar N, Nirmal D (2015) The influence of high-k passivation layer on breakdown voltage of schottky AlGaN/GaN HEMTs. J Microelectron 46:1387–1391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2015.04.006
Toshiki K, Shingo U, Yuki K, Kazushige H (2018) Enhancement of breakdown voltage in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs: field plate plus high-k passivation layer and high acceptor density in buffer layer. IEEE Trans Elect Dev 65(9):3848–3854. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2018.2857774
Robertson J (2004) High dielectric constant oxides. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 28:265–291. https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap:2004206
Luo Q, Yu Q (2012) Electric field modulation by introducing a HK dielectric film of tens of nanometers in AlGaN/GaN HEMT. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 4:936–939. https://doi.org/10.1166/nnl.2012.1406
Lee C-S, Hsu W-C, Chou B-Y, Liu H-Y, Yang C-L, Sun W-C, Wei S-Y, Yu S-M, Wu C-L (2015) Investigations of TiO2–AlGaN/GaN/Si-Passivated HFETs and MOS-HFETs using ultrasonic spray pyrolysis deposition. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 62(5):1460–1466. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2015.2414947
Bahat-Treidel E, Hilt O, Brunner F, Sidorov V, Würfl J, Tränkle G (2010) AlGaN/GaN/AlGaN DH-HEMTs Breakdown Voltage Enhancement Using Multiple Grating Field Plates (MGFPs). IEEE Trans Electron Devices 57(6):1208–1216. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2010.2045705
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai, India for providing the support and facility to carry out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the works in this paper have done together by Ramkumar Natarajan, Eswaran Parthasarathy and P. Murugapandiyan.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Conflicts of Interest/Competing Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest reported in this paper.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable as the manuscript does not contain any data from individual.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natarajan, R., Parthasarathy, E. & Murugapandiyan, P. Influence of High-k Passivation Layer on Gate Field Plate AlGaN/GaN/AlGaN Double Heterojunction HEMT. Silicon 14, 10437–10445 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-022-01746-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-022-01746-z