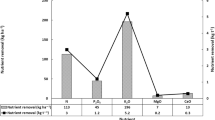
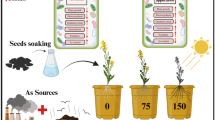
Abstract
Silicon (Si) combined with foliar spraying of salicylic acid (SA) can affect the absorption of this beneficial element. A study with Si non-accumulators plants (soybean and bean) observed that SA foliar spraying improved leaf absorption. However, this effect is unknown in peanut (Arachis hypogaea), a Si non-accumulator species. The aim of the present study was to assess the effect of applying Si to the leaves or roots, associated with foliar applications of SA, on Si absorption and dry weight production of peanut plants. An experiment was conducted with IAC OL4 peanut cultivars in pots filled with 6 L of sand. A randomized block design was used, in a 3 × 3 factorial scheme, as follows: Si application via leaves and roots in the form of monosilicic acid and the control (no Si) and three foliar applications of salicylic acid (0; 0.05; 0.15 mM), with five repetitions. The Si was supplied via nutrient solution (root) and leaves throughout the experiment, with three spraying treatments: at the end of the vegetative stage, onset of flowering and at the start of pod formation. The SA foliar sprayings were performed together with Si. Foliar silicon application was superior to its root counterpart at all SA concentrations. The greatest Si accumulation for root application was observed at a concentration of 0.05 mM of SA. Shoot dry weight and root dry weight production increased with Si. SA application, at a concentration of 0.05 mM, especially when associated with foliar Si, favored Si absorption and dry weight production in peanut plants. Foliar spraying of Si with the addition of salicylic acid is a new strategy for silicon supplementation in Si non-accumulators.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Etesami H, Jeong BR (2018) Silicon (Si): review and future prospects on the action mechanisms in alleviating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:881–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2017.09.063
Prado R de M (2020) Nutrição de plantas [Plant nutrition], 2a ed. Editora Unesp, São Paulo
Takahashi E, Ma JF, Miyake Y (1990) The possibility of silicon as an essential element for higher plants. Comments Agric Food Chem 2:99–102
Carneiro JMT, Oliveira LA, Rossete ALRM, Abreu Júnior CH, Bendassolli JA (2010) Accumulation and translocation of silicon in rice and bean plants using the 30 si stable isotope. J Plant Nutr 33:1374–1383. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2010.484097
Ma JF, Miyake Y, Takahashi E (2001) Chapter 2 silicon as a beneficial element for crop plants. Stud Plant Sci 8:17–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-3420(01)80006-9
Ma JF, Yamaji N (2008) Functions and transport of silicon in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:3049–3057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-7580-x
Nikolic M, Nikolic N, Liang Y, Kirkby EA, Römheld V (2007) Germanium-68 as an adequate tracer for silicon transport in plants. Characterization of silicon uptake in different crop species. Plant Physiol 143:495–503. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.090845
Yamaji N, Ma JF (2007) Spatial distribution and temporal variation of the rice silicon transporter Lsi1. Plant Physiol 143:1306–1313. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.093005
Mehrabanjoubani P, Abdolzadeh A, Sadeghipour HR, Aghdasi M (2015) Silicon affects transcellular and apoplastic uptake of some nutrients in plants. Pedosphere 25:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60004-2
Shi G, Cai Q, Liu C, Wu L (2010) Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in peanut plants in relation to cadmium distribution and stimulation of antioxidative enzymes. Plant Growth Regul 61:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-010-9447-z
Shen X, Xiao X, Dong Z, Chen Y (2014) Silicon effects on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of peanut under aluminum stress. Acta Physiol Plant 36:3063–3069. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1676-8
Dong Z, Li Y, Xiao X, Chen Y, Shen X (2018) Silicon effect on growth, nutrient uptake, and yield of peanut ( Arachis hypogaea L.) under aluminum stress. J Plant Nutr 41:2001–2008. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2018.1485163
Crusciol CAC, Soratto RP, Castro GSA, Costa CHMD, Ferrari Neto J (2013) Foliar application of stabilized silicic acid on soybean, common bean, and peanut. Rev Ciência Agronômica 44:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1806-66902013000200025
Barros TC, De Mello PR, Garcia Roque C, Barzotto GR, Wassolowski CR (2018) Silicon and salicylic acid promote different responses in legume plants. J Plant Nutr 41:2116–2125. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2018.1497177
Laane H-M (2018) The effects of foliar sprays with different silicon compounds. Plants 7:45. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants7020045
Birchall JD (1995) The essentiality of silicon in biology. Chem Soc Rev 24:351. https://doi.org/10.1039/cs9952400351
Epstein E, Bloom AJ (2006) Nutrição Mineral de Plantas: principios e perspectivas [Mineral plant nutrition: principles and perspectives]. Planta, Londrina
Choppin GR, Pathak P, Thakur P (2008) Polymerization and complexation behavior of silicic acid: a review. Main Gr Met Chem 31:53–71
Khan W, Prithiviraj B, Smith DL (2003) Photosynthetic responses of corn and soybean to foliar application of salicylates. J Plant Physiol 160:485–492. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00865
Khan MIR, Fatma M, Per TS, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Salicylic acid-induced abiotic stress tolerance and underlying mechanisms in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:462. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00462
Nazar R, Iqbal N, Syeed S, Khan NA (2011) Salicylic acid alleviates decreases in photosynthesis under salt stress by enhancing nitrogen and sulfur assimilation and antioxidant metabolism differentially in two mungbean cultivars. J Plant Physiol 168:807–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPLPH.2010.11.001
Hayat Q, Hayat S, Irfan M, Ahmad A (2010) Effect of exogenous salicylic acid under changing environment: a review. Environ Exp Bot 68:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVEXPBOT.2009.08.005
Deus ACF, de Mello PR, Alvarez RCF, Oliveira RLL, Felisberto G (2019) Role of silicon and salicylic acid in the mitigation of nitrogen deficiency stress in rice plants. Silicon 12:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00195-5
Prasad PVV, Boote KJ, Allen LH, Thomas JMG (2003) Super-optimal temperatures are detrimental to peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) reproductive processes and yield at both ambient and elevated carbon dioxide. Glob Chang Biol 9:1775–1787. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00708.x
D’souza AA, Shegokar R (2016) Polyethylene glycol (PEG): a versatile polymer for pharmaceutical applications. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 13:1257–1275
Savvas D, Ntatsi G (2015) Biostimulant activity of silicon in horticulture. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 196:66–81
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circ Calif Agric Exp Stn 347
Ferreira DF (2014) Sisvar: a guide for its bootstrap procedures in multiple comparisons. Ciência e Agrotecnologia 38:109–113
Mitani N, Ma JF (2005) Uptake system of silicon in different plant species. J Exp Bot 56:1255–1261. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri121
Dayanandan P, Kaufman PB, Franklin CI (1983) Detection of silica in plants. Am J Bot 70:1079–1084. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1983.tb07909.x
Ma JF, Yanaji N, Mitani-Ueno N (2011) Transport of silicon from roots to panicles in plants. Proc Japan Acad Ser B 87:377–385. https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.87.377
Wiese H, Nikolic M, Romheld V (2007) Silicon in plant nutrition – effects on zinc, manganese and boron leaf concentrations ans compartmentation. In: Sttelmacher B, Horst WJ (eds) The apoplast of higher plants: compartment of storage, transport and reaction. Springer, London, pp 33–47
de Queiroz DL, Camargo JMM, Dedecek RA, Oliveira EBD, Zanol KMR, Melido RCN (2018) Absorção e translocação de silício em mudas de Eucalyptus camaldulensis [Absorption and translocation of silicon in Eucalyptus camaldulensis seedlings]. Ciência Florest 28:632. https://doi.org/10.5902/1980509832053
Ma JF, Yamaji N (2006) Silicon uptake and accumulation in higher plantas. Trends Plant Sci 11:392–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2006.06.007
Souza Junior JP, Prado RM, Sarah MMS, Felisberto G (2019) Silicon mitigates boron deficiency and toxicity in cotton cultivated in nutrient solution. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 182:805–814. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201800398
Barros TC, de Mello PR, Roque CG, Arf MV, Vilela RG (2019) Silicon and salicylic acid in the physiology and yield of cotton. J Plant Nutr 42:458–465. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2019.1567765
Javanmardi J, Akbari N (2016) Salicylic acid at different plant growth stages affects secondary metabolites and phisico-chemical parameters of greenhouse tomato. Adv Hortic Sci 30:151–157. https://doi.org/10.13128/ahs-20277
Nivedithadevi D, Somasundaram R, Pannerselvam R (2012) Effect of abscisic acid, paclobutrazol and salicylic acid on the growth and pigment variation in Solanum trilobatum (L). Int J drug Dev Res 4:236–246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Souza Junior, J.P., Frazão, J.J., de Morais, T.C.B. et al. Foliar Spraying of Silicon Associated with Salicylic Acid Increases Silicon Absorption and Peanut Growth. Silicon 13, 1269–1275 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00517-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00517-y