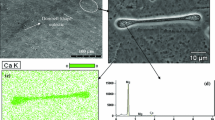
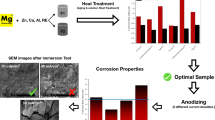
Abstract
The cooling gradient of Mg–3Zn–1Ca–0.5Sr alloy in cast ingots under different cooling methods (air cooling, warm-water cooling and ice–water-mixture cooling) was examined and the effect of cooling rate on the structure and corrosion properties was studied. The microstructure of the alloy was composed of α-Mg, Ca2Mg6Zn3 and Mg17Sr2 phases. As the solidification cooling rate increased, the grain was refined, Zn and Sr were less segregated, the distributions of Zn and Sr were more uniform, and corrosion rate was found to first increase and then decrease; this contradicts the findings of recent research. With cooling rate increasing, the number of corroded microcouples comprising second phase and α-Mg increases. More α-Mg participates in corrosion, leading to a layered and deep corrosion pit and an increased corrosion rate. However, as the microstructure became sufficiently dense, the corroded structure protected the deep α-Mg from participating in corrosion, thus reducing the corrosion rate.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang M, Deng WL, Yang XN, Wang YK, Zhang XY, Hang RQ, Deng KK. In vitro biodegradability of Mg–2Gd–xZn alloys with different Zn contents and solution treatments. Rare Met. 2019;38(7):620.
Cui T, Guan RG, Qin HM, Song FL. Study of the degradation behaviour of biomaterial Mg-4.0Zn-2.0Sr alloy in SBF. Adv Mater Res. 2015;1095:309.
Cui T, Guan RG, Qin HM. The microstructures and biocompatibility of a novel biomaterial Mg–4.0Zn–1.5Sr alloy sheet after aged treatment. Adv Sci Lett. 2013;19(4):1099.
Walker J, Shadanbaz S, Woodfield TB, Staiger MP, Dias GJ. Magnesium biomaterials for orthopedic application: a review from a biological perspective. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(6):1316.
Jang Y, Tan Z, Jurey C, Xu Z, Dong Z, Collins B, Yun Y. Understanding corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn–Ca alloys from subcutaneous mouse model: effect of Zn element concentration and plasma electrolytic oxidation. Mater Sci Eng, C. 2015;48:28.
Matias TB, Roche V, Nogueira RP, Asato GH, Kimunami CS, Bolfarini C, Botta WJ, Jorge AM. Mg–Zn–Ca amorphous alloys for application as temporary implant: effect of Zn content on the mechanical and corrosion properties. Mater Des. 2016;110:188.
Cai SH, Lei T, Li NF, Feng FF. Effects of Zn on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn alloys. Mater Sci Eng C. 2012;32(8):2570.
Chartrand P, Pelton AD. Critical evaluation and optimization of the thermodynamic properties and phase diagrams of the Al–Mg, Al–Sr, Mg–Sr, and Al–Mg–Sr systems. J Phase Equilibria. 1994;15(6):591.
Yin P, Li NF, Lei T, Liu L, Ouyang C. Effects of Ca on microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties and biocompatibility of Mg–Zn–Ca alloys. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(6):1365.
Torkian A, Faraji G, Pedram MS. Mechanical properties and in vivo biodegradability of Mg–Zr–Y–Nd–La magnesium alloy produced by a combined severe plastic deformation. Rare Met. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01353-9.
Persaud-Sharma D, Budiansky N, McGoron AJ. Biocompatibility assessment of novel bioresorbable alloys Mg–Zn–Se and Mg–Zn–Cu for endovascular applications: in vitro studies. J Biomimet Biomater Tissue Eng. 2013;17:25.
Cho SY, Chae SW, Choi KW, Seok HK, Kim YC, Jung JY, Assad M. Biocompatibility and strength retention of biodegradable Mg–Ca–Zn alloy bone implants. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(2):201.
Li D, Xue HS, Yang G, Zhang DF. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–6Zn–0.5Y magnesium alloy prepared with ultrasonic treatment. Rare Met. 2017;36(8):622.
Wang G, Guo CX, Pang SJ. Thermal stability, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of a Mg–Cu–Ag–Gd metallic glass with Nd addition. Rare Met. 2017;36(3):183.
Atrens A, Winzer N, Song GL, Dietzel W, Blawert C. Stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen diffusion in magnesium. Adv Eng Mater. 2006;8(8):749.
Bakhsheshi-Rad HR, Hamzah E, Farahany S, Staiger MP. The mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of quaternary Mg-6Zn-0.8Mn-xCa alloys. J Mater Eng Perform. 2015;24(2):598.
Wei L, Ke J, Prasadam I, Miron RJ, Lin S, Xiao Y, Zhang Y. A comparative study of Sr-incorporated mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds for regeneration of osteopenic bone defects. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(8):2089.
Bialkowski MM, Wierzbicki JG, Porter AT. Modeling of internal dose distributions during Sr-89 treatment of a patient with bone metastases. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 1997;12(5):355.
Landi E, Tampieri A, Celotti G, Sprio S, Sandri M, Logroscino G. Sr-substituted hydroxyapatites for osteoporotic bone replacement. Acta Biomater. 2007;3(6):961.
Cruz MAE, Tovani CB, Favarin BZ, Soares MPR, Fukada SY, Ciancaglini P, Ramos AP. Synthesis of Sr–morin complex and its in vitro response: decrease in osteoclast differentiation while sustaining osteoblast mineralization ability. J Mater Chem B. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB02045K.
Wu YH, He GP, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Li M, Wang XL, Li N, Li K, Zheng G, Zheng YF, Yin QS. Unique antitumor property of the Mg–Ca–Sr alloys with addition of Zn. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):21736.
Liu D, Liu Y, Huang Y, Song R, Chen M. Effects of solidification cooling rate on the corrosion resistance of Mg–Zn–Ca alloy. Prog Nat Sci: Mater Int. 2014;24(5):452.
Liu YH, Mao HK, Liu PY, Xu H. The effect of cooling rate on microstructure and mechanical properties on ZM5 magnesium alloy. Foundry. 2017;66(3):286.
Yamasaki M, Hashimoto K, Hagihara K, Kawamura Y. Multimodal microstructure evolution in wrought Mg–Zn–Y alloys with high strength and increased ductility. Mater Sci Forum. 2010;654–656:615.
Liu HM, Chen YG, Tang YB, Wei SH, Niu G. The microstructure, tensile properties, and creep behavior of as-cast Mg–(1–10)%Sn alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2007;440(1–2):122.
Zhang DF, Lan W, Ding DD, Zhang BP. Quantitative relationship between secondary dendrite arm spacing and solidification cooling rate of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Heat Treat Met. 2008;33(3):1.
Wasiur-Rahman S, Medraj M. Critical assessment and thermodynamic modeling of the binary Mg–Zn, Ca–Zn and ternary Mg–Ca–Zn systems. Intermetallics. 2009;17(10):847.
Song YW, Shan DY, Chen RS, Han EH. Corrosion characterization of Mg–8Li alloy in NaCl solution. Corros Sci. 2009;51(5):1087.
Song Y, Shan D, Han EH. Pitting corrosion of a rare earth Mg alloy GW93. J Mater Sci Technol. 2017;33(09):50.
Zhang X, Zhang K. Research progress on corrosion behavior and mechanism of magnesium alloy. Corros Scie Protect Technol. 2015;27(1):78.
Mostaed E, Vedani M, Hashempour M, Bestetti M. Influence of ECAP process on mechanical and corrosion properties of pure Mg and ZK60 magnesium alloy for biodegradable stent applications. Biomatter. 2014;4(1):e28283.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jiangsu Province Achievement Transformation Project (BA2017044). The authors acknowledge the staff at GRIMAT Engineering institute Co., Ltd. for their time and instrument use. Thanks to GRINM Analysis and Testing Center at for permitting us to use their electron microscope and to my teachers and classmates for their help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HN., Zhang, K., Li, XG. et al. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of bone-implanted Mg–Zn–Ca–Sr alloy under different cooling methods. Rare Met. 40, 643–650 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01368-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01368-7