Abstract
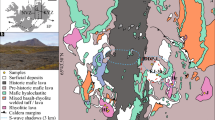
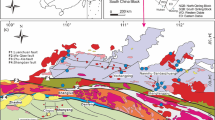
The Yanhu granitoids are located in the west segment of the Bangongco-Nujiang suture in the western Tibetan Plateau. The main rock types of the granitoids are diorite porphyry, quartz diorite, granodiorite, granite and granite porphyry. Here, their zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages and petrogeochemical data are reported. Three groups of magmatic events can be distinguished from the Yanhu area: group 1 includes samples AK01 and ZK01 of diorite porphyry, and sample D3658 of quartz diorite that yield mean zircon U-Pb ages of 121.0 ± 2.7 Ma, 116.6 ± 2.0 Ma and 116.0 ± 3.9 Ma, respectively; group 2 includes sample D0050 of diorite porphyry, samples D1393 and D3660 of granodiorite and sample D3065 of granite porphyry that yield mean zircon U-Pb ages of 104.9 ± 2.0 Ma, 105.4 ± 3.8 Ma, 104.2 ± 1.9 Ma and 104.2 ± 1.9 Ma, respectively; group 3 includes sample D3093 of granite that yields mean zircon U-Pb ages of 93.6 ± 1.5 Ma. The zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages suggest that the Yanhu granitoids were emplaced at 121.0–93.6 Ma, representing Cretaceous magmatism in the west segment of the Bangongco-Nujiang suture. The granitoids are composed of SiO2 (56.57 to 76.98 wt.%), Al2O3 (12.20 to 17.90 wt.%), Na2O (3.61 to 4.98 wt.%), K2O (2.06 to 4.71 wt.%) and CaO (0.27 to 5.74 wt.%). The Yanhu granitoids exhibit enrichment in LREE (light REE) and LILE (large ion lithophile elements) such as Rb, Th, U, Pb and K and depletion of HREE (heavy REE), P, Ti, Nb, Ta and Zr. Their A/CNK ratios of 0.85-1.06 are <1.1, implying that they are high-K, metaluminous-weakly peraluminous I-type granites. TheYanhu granitoids were generated mainly by partial melts of the meta-igneous lower crust and some arc-related materials. The Yanhu granitoids probably formed in VAG and syn-COLG tectonic settings related to the southward subduction of the Tethyan Ocean. Diorite porphyry and quartz diorite magmatism from 121.0 Ma to 116.0 Ma may be associated with the southward Bangongco–Nujiang Tethys oceanic crust subduction. Diorite porphyry, granodiorite, and granite porphyry magmatism from 105.4 Ma to 104.2 Ma may be associated with the rising asthenosphere induced by the slab breakoff. Granite magmatism from 93.6 Ma may be related to the crustal thickening induced by the final amalgamation of the Lhasa Terrane and the Qiangtang Terrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altherr, R., Holl, A., Hegner, E., Langer, C., Kreuzer, H. (2000) High-potassium, calc-alkaline I-type plutonism in the European Variscides: northern Vosges (France) and northern Schwarzwald (Germany). Lithos, v.50, pp.51–73.
Bonin, B. (2007) A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects. Lithos, v.97, pp.1–29.
Chappell, B.W., White, A.J.R. (1992). I-and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt. Geol. Soc. Amer. Spec. Paper, no.272, pp.1–26.
Chen, C.H., Lin, W., Lu, H.Y., et al. (2000). Cretaceous fractionated I-type granitoids and metaluminous A-type granites in SE China: the Late Yanshanian post-orogenic magmatism. Geol. Soc. Amer. Spec. Paper no.350, pp.195–205.
Collins, W.J., Beams, S.D., White, A.J.R. and Chappell, B.W. (1982) Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.80, pp.189–200.
Condie, K.C., Kröner, A. (2013) The bulding blocks of continental crust: evidence for a major change in the tectonic setting of continental growth at the end of the Archean. Gondwana Res., v.23, pp.394–402.
Fan, J.J., Li, C., Hu, P.Y., et al. (2013) The Characteristics of Zhonggang Ocean Island in Gaiz areaÿTibet: Evidence on the closure of the Nujiang Suture Zone-Bangong. China Guangzhou: University of Zhongshan Press (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Geng, Q.R., Sun, Z.M., Pan, G.T., et al. (2009) Origin of the Gangdise (Transhimalaya) Permian arc in southern Tibet: Stratigraphic and volcanic geochemical constraints. Island Arc, v.18(3), pp.467–487.
Hoskin, P.W.O., Schaltegger, U. (2003) The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev. Mineral. Geochem., v.53(1), pp.27–62. DOI: 10.2113/0530027.
Hsu, K.J., Pan, G.T., Sengor, A.M.C. (1995) Tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau: a working hypothesis based on the archipelago model of orogenesis. Internat. Geol. Rev., v.37(6), pp.473–508.
Jackson, S.E., Pearson, N.J., Griffin, W.L., et al. (2004) The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology. Chem. Geol., v.211, pp.47–69.
Kapp, P., Murphy, M.A., Yin, A., et al. (2003a) Mesozoic and Cenozoic gectonic evolution of the Shiquanhe area of western Tibet. Tectonics, v.22(4), pp.1029.
Kapp, P., Yin, A., Manning, C.E., et al. (2003b) Tectonic evolution of the Early Mesozoic blueschist-bearing Qiangtang metamorphic belt, central Tibet. Tectonics, v.22(4), pp.1043.
Li, J.X., Li, G.M., Qin, K.Z., et al. (2008) Geochemistry of porphyries and volcanic rocks and ore-forming geochronology of Duobuza gold-rich porphyry copper deposit in Bangonghu belt, Tibet: constraints on metallogenic tectonic settings. Acta Petrologica Sinica, v.24(3), pp.531–543 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Li, S.M., Zhu, D.C., Wang, Q., et al. (2014) Northward subduction of Bangong-Nujiang Tethys: insight from late Jurassic intrusive rocks from Bangong Tso in western Tibet. Lithos, v.205, pp.284–297.
Li, X.H., Li, Z.X., Li, W.X., Liu, Y., Yuan, C., Wei, G., Qi, C. (2007) U–Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic Island A-type granites from central Guangdong, SE China: a major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab? Lithos, v.96(1), pp.186–204.
Li, Y.L., He, J., Wang, C.S., et al. (2015) Cretaceous volcanic rocks in south Qiangtang terrane: products of northward subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean? Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.104, pp.69–83.
Liu, D.L., Shi, R.D., Ding, L., et al. (2015). Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic compositions of Mesozoic granitoids in southern Qiangtang, Tibet: implications for the subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean. Gondwana Res., http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2015.04.007
Liu, Y.S., Hu, Z.C., Gao, S., et al. (2008) In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geol., v.257(1-2), pp.34–43.
Liu, Y.S., Gao, S., Hu, Z.C. (2010a. Continental and oceanic crust recyclinginduced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Jour. Petrol., v.51 (1-2), pp.537–571.
Liu, Y.S., Hu, Z.C., Zong, K.Q. (2010b) Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chinese Sci. Bull., v.55(15), pp.1535–1546.
Ludwig, K.R. (2003) Using isoplot/EX, Version 3.0, a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel, Berkeley Geochronological Center Spec. Publ., no.4, 74p.
Matte, P., Tapponnier, P., Arnaud, N., et al. (1996) Tectonics of Western Tibet, between the Tarim and the Indus. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.142(3/4), pp.311–330
McCarron, J.J., Smellie, J.L. (1998) Tectonic implications of fore-arc magmatism and generation of high-magnesian andesites: Alexander Island, Antarctica. Jour. Geol. Soc., v.155, pp.269–280
Pan, G.T., Mo, X.X., Hou, Z.Q., et al. (2006) Spatial–temporal framework of the Gangdise Orogenic Belt and its evolution. Acta Petrol. Sinica, v.22, pp.521–533 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Patiño Douce, A.E. (1995) Experimental generation of hybrid silicic melts by reaction of high-Al basalt with metamorphic rocks. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.100, pp.15623–15639.
Patiño Douce, A.E. (1999) What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas? Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., v.168, pp.55–75.
Pearce JA, Harris NBW, Tindle A G (1984) Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Jour. Petrol., v.25, pp.956–983.
Qiu RZ, Zhou S, Demg JF, et al. (2004) Dating of gabbro in the Shemalagou ophiolite in the western segment of the Bangongco-Nujiang ophiolite belt, Tibet-With a discuss of the age of the Bangongco-Nujiang ophiolite belt. Geol. China, v.31(3), pp.262–268 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Qu, X.M., Wang, R.J., Xin, H.B., et al. (2009) Geochronology and geochemistry of igneous rocks related to the subduction of the Tethys oceanic plate along the Bangong Lake arc zone, the western Tibetan Plateau. Geochimica v.38(6), pp.523–535 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Qu, X.M., Wang, R.J., Xin, H.B., et al. (2012) Age and petrogenesis of A-type granites in the middle segment of the Bangonghu-Nujiang suture, Tibetan plateau. Lithos, v.146/147, pp.264–275
Rapp, R.P., Watson, E.B. (1995) Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8–32kbar: implications for continental growth and crust–mantle recycling. Journal of Petrology 36: 891–931
Ren, J.S., Xiao, L.W. (2004) Lifting the mysterious veil of the tectonics of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau by 1:250000 geological mapping. Geol. Bull. China, v.23(1), pp.1–11 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Rickwood, P.C. (1989) Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements. Lithos, v.22, pp.247–263
Streckeisen, A., Le Maitre, R.W. (1979) A chemical approximation to the modal QAPF classification of the igneous rocks. Neues Jb Mineral Abh, v.136, pp.169–206
Sui, Q.L., Wang, Q., Zhu, D.C., et al. (2013). Compositional diversity of ca. 110 Ma magmatism in the northern Lhasa Terrane, Tibet: implications for the magmatic origin and crustal growth in a continent–continent collision zone. Lithos, v.168–169, pp.144–159
Sun, S.S., McDonough, W.F. (1989) Chemical and isotope systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders, A.D. (Ed.), Magmatism in Ocean Basins: Geol. Soc. Publ, v.42, pp.313–345.
TRGSRG (2003) Tibet 1/250000 regional geological survey report in Geji (I44C004001) Geological Survey in Sichuan Province, Chengdu, (in Chinese).
Wang, Q., Zhu, D.C., Zhao, Z.D., et al. (2014) Origin of the ca. 90 Ma magnesia-rich volcanic rocks in SE Nyima, central Tibet: Products of lithospheric delamination beneath the Lhasa-Qiangtang collision zone. Lithos, v. 198199, pp.24–37.
Wang, W.L, Aitchison, J.C., Lo CH, et al. (2008) Geochemistry and geochronology of the amphibolites blocks in ophiolite melanges along Bangong-Nujiang suture, central Tibet. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.33(1/2), pp.122–138.
Wang, X.B., Bao, P.S., Deng, W.M. (1987) Tectonic revolution of Himalaya lithosphere: Xizang ophiolite. Beijing geological publishing house, pp.138–214 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Wang, Z.H., Wang, Y.S., Xie, Y.H., et al. (2005) The Tarenben oceanic-island basalts in the middle part of the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone and their geological implications. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, v.25(1/2), pp.153–162 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Whalen JB, Currie KL, Chappell BW (1987) A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib Mineral Petrol v.95, pp.407–419.
Wiedenbeck, M., Alle, P, Corfu, F., et al. (1995). Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace-element and REE analyses. Geostand Newsl no.19, pp.1–23
Wolf, M.B., Wyllie, P.J. (1994) Dehydration-melting of amphibolite at 10 kbar: the effects of temperature and time. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.115, pp.369–383.
Wu, F.Y., Jahn, B.M., Wilde, S.A., et al. (2003a) Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (I): geochronology and petrogenesis. Lithos, v.66(3): pp.241–273.
Wu, F.Y., Jahn, B.M., Wilde, S.A., et al. (2003b) Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (II): isotopic geochemistry and implications for crustal growth in the Phanerozoic. Lithos, v.67(3), pp.191–204.
Wu, F.Y., Li, X.H., Yang, J.H., et al. (2007). Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites. Acta Petrol. Sin., no.23, pp.1217–1238 (in Chinese).
Wu, H., Li, C., Hu, P.Y., et al. (2013) The discovery of Qushenla volcanic rocks in Tasepule area of Nyima Country, Tibet, and its geological significance. Geol. Bull. China, v.32(7), pp.1014–1026 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Wu, Z.H., Ye, P.S., Hu, D.G., et al. (2003). Crust Deformation and Tectonic-Geonomorphic Evolution of the Central Tibet Plateau. Geological Publishing House, Beijing. 292 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Ye, M.F., Li, X.H., Li, W.X., Liu, Y., Li, Z.X. (2007) SHRIMP zircon U–Pb geochronological and whole-rock geochemical evidence for a nearly Neoproterozoic Sibaoan magmatic arc along the southeastern margin of the Yangtze Block. Gondwana Res., v.12, pp.144–156.
Yin A, Harrison TM (2000) Geologic evolution of the Himalayan–Tibetan orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 28: 211–280.
Yuan, H.L., Gao, S., Liu, X.M., et al. (2004) Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Res, v.28(3), pp.353–370.
Zhang, K.J., Zhang, Y.X., Tang, X.C., Xia, B. (2012) Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution and growth of the Tibetan plateau prior to the Indo-Asian collision. Earth Sci. Rev., v.114(3), pp.36–249.
Zhang, Y.X., Zhang K.J., Li B., et al. (2007) Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology and petrogenesis of the plagiogranites from the Lagkor Lake ophiolite, Gerze, Tibet, China. Chinese Sci. Bull., v.52(5), pp.651–659.
Zhu, D.C., Li, S.M., Peter, A. Cawood, et al. (2015). Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in central Tibet by divergent double subduction. Lithos, DOI/10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.023.
Zhu, D.C., Mo, X.X., Niu, Y.L., et al. (2009a) Geochemical investigation of Early Cretaceous igneous rocks along an east-west traverse throughout the central Lhasa Terrane, Tibet. Chemical Geol., v.268: pp.298–312.
Zhu, D.C., Mo, X.X., Wang, L.Q., et al. (2009b) Petrogenesis of highly fractionated I-type granites in the Zayu area of eastern Gangdese, Tibet: constraints from zircon U–Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes. Sci. China, Ser. D Earth Sci., v.52(9), pp.1223–1239.
Zhu, D.C., Zhao, Z.D., Niu, Y.L., et al. (2011) The Lhasa Terrane: Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.301, pp.241–255.
Zhu, D.C., Zhao, Z.D., Niu, Y.L., et al. (2013) The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Gondwana Res., v.23, pp.1429–1454.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mi, W., Kong, X., Zhang, D. et al. Zircon LA-ICP-MS dating and geochemical characteristics of I-type granitoids from the Yanhu area, west segment of the Bangongco-Nujiang suture (western Tibet): Petrogenesis and implications for the southward subduction of the Tethyan Ocean. J Geol Soc India 90, 335–346 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0722-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0722-8