Abstract
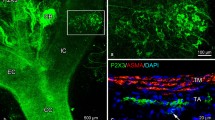
In the carotid body of laboratory rodents, adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP)-mediated transmission is regarded as critical for transmission from chemoreceptor type I cells to P2X3 purinoceptor-expressing sensory nerve endings. The present study investigated the distribution of P2X3-immunoreactive sensory nerve endings in the carotid body of the adult male Japanese monkey (Macaca fuscata) using multilabeling immunofluorescence. Immunoreactivity for P2X3 was detected in nerve endings associated with chemoreceptor type I cells immunoreactive for synaptophysin. Spherical or flattened terminal parts of P2X3-immunoreactive nerve endings were in close apposition to the perinuclear cytoplasm of synaptophysin-immunoreactive type I cells. Immunoreactivity for ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 2 (NTPDase2), which hydrolyzes extracellular ATP, was localized in the cell body and cytoplasmic processes of S100B-immunoreactive cells. NTPDase2-immunoreactive cells surrounded P2X3-immunoreactive terminal parts and synaptophysin-immunoreactive type I cells, but did not intrude into attachment surfaces between terminal parts and type I cells. These results suggest ATP-mediated transmission between type I cells and sensory nerve endings in the carotid body of the Japanese monkey, as well as those of rodents.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Al-Lami F, Murray RG (1968) Fine structure of the carotid body of Macaca mulata monkey. J Ultrastruct Res 24:465–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80049-8
Braun N, Sévigny J, Robson SC, Hammer K, Hanani M, Zimmermann H (2004) Association of the ecto-ATPase NTPDase2 with glial cells of the peripheral nervous system. Glia 45:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.10309
Buttigieg J, Nurse CA (2004) Detection of hypoxia-evoked ATP release from chemoreceptor cells of the rat carotid body. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.081
Capella C, Solcia E (1971) Optical and electron microscopical study of cytoplasmic granules in human carotid body, carotid body tumours and glomus jugulare tumours. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol 7:37–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02892077
Daly MB, Korner PI, Angell-James JE, Oliver JA (1978a) Cardiovascular and respiratory effects of carotid body stimulation in the monkey. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 5:511–524. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.1978.tb00704.x
Daly MB, Korner PI, Angell-James JE, Oliver JR (1978b) Cardiovascular-respiratory reflex interactions between carotid bodies and upper-airways receptors in the monkey. Am J Physiol 234:H293–H299. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.1978.234.3.H293
Gonzalez C, Almaraz L, Obeso A, Rigual R (1994) Carotid body chemoreceptors: from natural stimuli to sensory discharges. Physiol Rev 74:829–898. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1994.74.4.829
Hansen JT (1985) Ultrastructure of the primate carotid body: a morphometric study of the glomus cells and nerve endings in the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Neurocytol 14:13–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01150260
Iturriaga R, Alcayaga J (2004) Neurotransmission in the carotid body: transmitters and modulators between glomus cells and petrosal ganglion nerve terminals. Brain Res Rev 47:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.05.007
Kåhlin J, Mkrtchian S, Ebberyd A, Hammarstedt-Nordenvall L, Nordlander B, Yoshitake T, Kehr J, Prabhakar N, Poellinger L, Fagerlund MJ, Eriksson LI (2014) The human carotid body releases acetylcholine, ATP and cytokines during hypoxia. Exp Physiol 99:1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2014.078873
Lahiri S, Roy A, Baby SM, Hoshi T, Semenza GL, Prabhakar NR (2006) Oxygen sensing in the body. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 91:249–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2005.07.001
Lataro RM, Moraes DJA, Gava FN, Omoto ACM, Silva CAA, Brognara F, Alflen L, Brazão V, Colato RP, Prado JC, Ford AP, Salgado HC, Paton JFR (2023) P2X3 receptor antagonism attenuates the progression of heart failure. Nat Commun 14:1725. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37077-9
McDonald DM, Mitchell RA (1975) The innervations of glomus cells, ganglion cells and blood vessels in the rat carotid body: a quantitative ultrastructural analysis. J Neurocytol 4:177–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01098781
Nurse CA, Piskuric NA (2013) Signal processing at mammalian carotid body chemoreceptors. Semin Cell Dev Biol 24:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.09.006
Ortega-Sáenz P, Pardal R, Levitsky K, Villadiego J, Muñoz-Manchado AB, Durán R, Bonilla-Henao V, Arias-Mayenco I, Sobrino V, Ordóñez A, Oliver M, Toledo-Aral JJ, López-Barneo J (2013) Cellular properties and chemosensory responses of the human carotid body. J Physiol 591:6157–6173. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2013.263657
Otlyga D, Tsvetkova E, Junemann O, Saveliev S (2021) Immunohistochemical characteristics of the human carotid body in the antenatal and postnatal periods of development. Int J Mol Sci 22:8222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158222
Pijacka W, Moraes DJA, Ratcliffe LEK, Nightingale AK, Hart EC, da Silva MP, Machado BH, McBryde FD, Abdala AP, Ford AP, Paton JFR (2016) Purinergic receptors in the carotid body as a new drug target for controlling hypertension. Nat Med 22:1151–1159. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4173
Piskuric NA, Nurse CA (2013) Expanding role of ATP as a versatile messenger at carotid and aortic body chemoreceptors. J Physiol 591:415–422. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2012.234377
Salman S, Vollmer C, McClelland GB, Nurse CA (2017) Characterization of ectonucleotidase expression in the rat carotid body: regulation by chronic hypoxia. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 313:C274–C284. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00328.2016
Satoda T, Takahashi O, Uchida T, Mizuno N (1995) An anterograde-retrograde labeling study of the carotid sinus nerve of the Japanese monkey (Macaca fuscata). Neurosci Res 22:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-0102(95)00918-j
Yokoyama T, Saino T, Nakamuta N, Kusakabe T, Yamamoto Y (2016) Three-dimensional architectures of P2X2-/P2X3-immunoreactive afferent nerve terminals in the rat carotid body as revealed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Histochem Cell Biol 146:479–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1458-z
Yokoyama T, Yamamoto Y, Hirakawa M, Kato K, Saino T (2020) Vesicular nucleotide transporter-immunoreactive type I cells associated with P2X3-immunoreactive nerve endings in the rat carotid body. J Comp Neurol 528:1486–1501. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.24837
Zimmermann H (2001) Ecto-nucleotidases. In: Abbracchio MP, Williams M (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, Purinergic and pyrimidergic signalling, pp 209–250
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: TY, KN; Investigation: TY, MH, KM, TS; Methodology: TY. KN; Resources: KM, TS, KN; Validation: TY, MH, TS; Visualization: TY; Writing – original draft: TY; Writing – review & editing: TY, KN, TS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yokoyama, T., Hirakawa, M., Mochizuki, K. et al. Distribution of P2X3 purinoceptor-immunoreactive sensory nerve endings in the carotid body of Japanese macaque (Macaca fuscata). Anat Sci Int 99, 68–74 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-023-00735-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-023-00735-5