Abstract
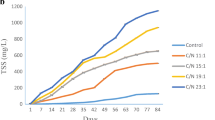
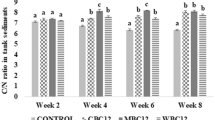
A 120-day evaluation was performed to determine the impacts of various carbon source supplements on the water grade and production of bottom- and filter-feeding carp inside a minimum-water-exchange system. The outcomes revealed that the overall ammonia nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, total inorganic nitrogen, and orthophosphate concentrations in every one of the carbon source treatments were significantly less (P < 0.05) than the control. The net production of silver carp and bighead carp in the molasses treatment was significantly higher (P < 0.05) than that in the control. The total feed conversion rates of the fish in the molasses and the mixed carbon source treatments were significantly lower (P < 0.05) than in the control, while the total protein efficiency ratio values in the corn starch, molasses, and mixed carbon source treatments were significantly higher (P < 0.05) than those in the control. The bioflocs significantly (P < 0.05) impacted the muscle makeup of crude protein, crude fat, and ash of mirror carp. The current examination showed that the increased generation and feed used in mirror, silver, and bighead carp may be reached with an enhanced water grade when different carbon sources were added, while the use of molasses, an organic carbon source, was optimal compared to the other carbon sources due to its low price and good effect.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand P, Kumar S, Panigrahi A, Ghoshal T, Dayal J, Biswas G, Sundaray J, De D, Raja R, Deo A, Pillai S, Ravichandran P (2013) Effects of C:N ratio and substrate integration on periphyton biomass, microbial dynamics and growth of Penaeus monodon juveniles. Aquacult Int 21:511–524
Anand P, Kohli M, Kumar S, Sundaray J, Roy S, Venkateshwarlu G, Sinha A, Pailan G (2014) Effect of dietary supplementation of biofloc on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities in Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 418–419:108–115
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis. In: Horwitz W (ed) Association of Official Analytical Chemists. AOAC International, OMA, Washington, DC
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of the water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Asaduzzaman M, Wahab M, Verdegem M, Huque S, Salam M, Azim M (2008) C/N ratio control and substrate addition for periphyton development jointly enhance freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii production in ponds. Aquaculture 280:117–123
Avnimelech Y (1999) Carbon/nitrogen ratio as a control element in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 176:227–235
Avnimelech Y (2007) Feeding with microbial flocs by tilapia in minimal discharge bio-flocs technology ponds. Aquaculture 264:140–147
Avnimelech Y (2012) Biofloc technology—a practical guide book, 2d edn. The World Aquaculture Society, Baton Rouge
Avnimelech Y, Kochba M (2009) Evaluation of nitrogen uptake and excretion by tilapia in bio floc tanks, using N-15 tracing. Aquaculture 287:163–168
Avnimelech Y, Ritvo G (2003) Shrimp and fish pond soils: processes and management. Aquaculture 220:549–567
Azim M, Little D (2008) The biofloc technology (BFT) in indoor tanks: water quality, biofloc composition, and growth and welfare of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 283:29–35
Ballester E, Abreu P, Cavalli R, Emerenciano M, Abreu L, Wasielesky W (2010) Effect of practical diets with different protein levels on the performance of Farfantepenaeus paulensis juveniles nursed in a zero exchange suspended microbial flocs intensive system. Aquacult Nutr 16:163–172
Barbieri R, Ostrensky A (2002) Camarões Marinhos-Engorda. Viçosa, Brasil, p 370
Cohen J, Samocha T, Fox J, Gandy R, Lawrence A (2005) Characterization of water quality factors during intensive raceway production of juvenile L. vannamei using limited discharge and biosecure management tools. Aquacult Eng 32:425–442
Curtin L (1993) Molasses—general considerations. Molasses in animal nutrition. National Feed Ingredients Association, West Des Moines
Davenport J, Black K, Burnell G, Cross T, Culloty S, Ekaratne S, Furness B, Mulcahy M, Thetmeyer H (2003) Aquaculture, the ecological issues. Blackwell, Oxford
Dong S, Li D, Bing X, Shi Q, Wang F (1992) Suction volume and filtering efficiency of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix Val.) and bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis Rich.). J Fish Biol 41:833–840
Ebeling J, Timmons M, Bisogni J (2006) Engineering analysis of the stoichiometry of photoautotrophic, autotrophic, and heterotrophic removal of ammonia-nitrogen in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 257:346–358
Ekasari J, Crab R, Verstraete W (2010) Primary nutritional content of bioflocs cultured with different organic carbon sources and salinity. J Biosci 17:125
Fukushima M, Takamura N, Sun L, Nakagawa M, Matsushige K, Xies P (1999) Changes in the plankton community following introduction of filter-feeding planktivorous fish. Freshw Biol 42:719–735
Furtado P, Poersch L, Wasielesky J (2011) Effect of calcium hydroxide, carbonate and sodium bicarbonate on water quality and zootechnical performance of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei reared in bio-flocs technology (BFT) systems. Aquaculture 321:130–135
Gross A, Boyd C, Wood C (2000) Nitrogen transformations and balance in channel catfish ponds. Aquacult Eng 24:1–14
Hargreaves J (2006) Photosynthetic suspended-growth systems in aquaculture. Aquacult Eng 34:344–363
Izquierdo M, Forster I, Divakaran S, Conquest L, Decamp O (2006) Effect of green and clear water and lipid source on survival, growth and biochemical composition of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult Nutr 12:192–202
Jimenez A, Borja R, Martin A (2004) A comparative kinetic valuation of the anaerobic digestion of untreated molasses and molasses previously fermented with Penicillium decumbens in batch reactors. Biochem Eng J 18(2):121–132
Ju Z, Forster I, Conquest L, Dominy W, Kuo W, Horgen F (2008) Determination of microbial community structures of shrimp floc cultures by biomarkers and analysis of floc amino acid profiles. Aquacult Res 39:118–133
Ke Z, Xie P, Guo L, Liu Y, Yang H (2007) In situ study on the control of toxic Microcystis blooms using phytoplanktivorous fish in the subtropical Lake Taihu of China: a large fish pen experiment. Aquaculture 265:127–138
Li D, Yang H, Wang J, Lu J, Tian X, Liu G (1998) A device of land-based experimental enclosure used in ponds. J Ocean Univ Qingdao 28:199–204 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Little D, Murray J, Azim M, Leschen W, Grady K, Young J, Watterson A (2008) Warm-water fish production in the UK: limits to green growth? Trends Food Sci Technol 19:255–264
Lyons M, Dobbs F (2012) Differential utilization of carbon substrates by aggregate-associated and water-associated heterotrophic bacterial communities. Hydrobiologia 686(1):181–193
McIntosh B, Samocha T, Jones E, Lawrence A, McKee D, Horowitz S, Horowitz A (2000) The effect of a bacterial supplement on the high-density culturing of Litopenaeus vannamei with low protein diet on outdoor tank system and no water exchange. Aquacult Eng 21:215–227
NASS (2005) Agricultural prices, 2004 summary. A. S. Board, USDA, Washington, DC
Quan Z, Jin Y, Yin C, Lee J, Lee S (2005) Hydrolyzed molasses as an external carbon source in biological nitrogen removal. Bioresou Technol 96(15):1690–1695
Rahman M, Nagelkerke L, Verdegem M, Wahab M, Verreth J (2008) Relationships among water quality, food resources, fish diet and fish growth in polyculture ponds: a multivariate approach. Aquaculture 275:108–115
Tacon A, Cody J, Conquest L, Divakaran S, Forster I, Decamp O (2002) Effect of culture system on the nutrition and growth performance of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) fed different diets. Aquacult Nutr 8:121–137
Ugalde U, Castrillo J (2002) Single cell proteins from fungi and yeasts. In: Arora D, Khachatourians G (eds) Agriculture and food production, vol 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 360
Wang J, Li D, Dong S, Wang K, Tian X (1998) Experimental studies on polyculture in closed shrimp ponds: I. Intensive polyculture of Chinese shrimp (Penaeus chinensis) with tilapia hybrids. Aquaculture 163:11–27
Xie P, Liu J (2001) Practical success of biomanipulation using filter-feeding fish to control cyanobacteria blooms. Sci World 1:337–356
Xu W, Pan L (2012) Effects of bioflocs on growth performance, digestive enzyme activity and body composition of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei in zero-water exchange tanks manipulating C/N ratio in feed. Aquaculture 356–357:147–152
Xu Y, Zhang X, Zheng X, Kuang Y, Lu C, Cao D, Yin S, Li C, Sun X (2013) Studies on quantitative trait loci related to superoxide dismutase in mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquacult Res 44:1860–1871
Zhao Z, Xu Q, Luo L, Wang C, Li J, Wang L (2014) Effect of feed C/N ratio promoted bioflocs on water quality and production performance of bottom and filter feeder carp in minimum-water exchanged pond polyculture system. Aquaculture 434:442–448
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (No. 2016HY-ZD0602), CAFS (No. 2016HY-JC02-03), an earmarked fund of the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-45), and the National Science and Technology Support Program (2012BAD25B00). The authors declare that they have no competing interests related to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Luo, L., Wang, C. et al. Effects of organic carbon addition on water quality and growth performance of bottom- and filter-feeding carp in a minimum-water-exchange pond polyculture system. Fish Sci 84, 681–689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-018-1204-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-018-1204-7