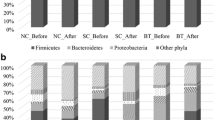
Abstract
In the present study, we evaluated how dietary administration of host-derived Pediococcus sp. Ab1 has an effect on the abalone gut microbiota using a culture-dependent method and 16S rRNA gene library analysis. The culturable lactic acid bacteria number in the probiotic sample was 105 higher than that in the non-probiotic sample, and we speculate that this significant increase was due to colonization of Ab1 into abalone gut. The result of a culture-dependent method showed that the proportion of Vibrio halioticoli clade, which is known to be a beneficial resident bacterium to abalone, was much higher in the probiotic sample than in the non-probiotic sample. 16S rRNA gene clone sequences revealed that gut microbiota in the probiotic sample was obviously diverse compared to the non-probiotic sample, probably due to improvement of the gut environment by Ab1 colonization. In addition, some beneficial bacteria–like sequences such as V. halioticoli were only found in the probiotic sample. These results suggest that the dietary administration of Ab1 to abalone gut has a great effect on modulation of not only culturable but also unculturable gut microbiota. Our results are useful for future investigations into understanding the effect of probiotics on gut microbiota.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nayak SK (2010) Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquacult Res 41:1553–1573
Erasmus JH, Cook PA, Coyne VE (1997) The role of bacteria in the digestion of seaweed by the abalone Haliotis midae. Aquaculture 155:377–386
Tanaka R, Sugimura I, Sawabe T, Yoshimizu M, Ezura Y (2003) Gut microflora of abalone Haliotis discus hannai in culture changes coincident with a change in diet. Fish Sci 69:951–958
Sawabe T, Sugimura I, Ohtsuka M, Nakano K, Tajima K, Ezura Y, Christen R (1998) Vibrio halioticoli sp. nov., a non-motile alginolytic marine bacterium isolated from the gut of the abalone Haliotis discus hannnai. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 48:573–580
Sawabe T, Setoguchi N, Inoue S, Tanaka R, Ootsubo M, Yoshimizu M, Ezura Y (2003) Acetic acid production of Vibrio halioticoli from alginate: a possible role for establishment of abalone—V. halioticoli association. Aquaculture 219:671–679
Tanaka R, Ootsubo M, Sawabe T, Ezura Y, Tajima K (2004) Biodiversity and in situ abundance of gut microflora of abalone (Haliotis discus hannai) determined by culture-independent techniques. Aquaculture 241:453–463
Huang ZB, Guo F, Zhao J, Li WD, Ke CH (2010) Molecular analysis of the intestinal bacterial flora in cage-cultured adult small abalone, Haliotis diversicolor. Aquacult Res 41:760–769
Farzanfar A (2006) The use of probiotics in shrimp aquaculture. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 48:149–158
Kesarcodi-Watson A, Kaspar H, Lategan MJ, Gibson L (2008) Probiotics in aquaculture: the need, principles and mechanisms of action and screening processes. Aquaculture 274:1–14
Prado S, Romalde JL, Barja JL (2010) Review of probiotics for use in bivalve hatcheries. Vet Microbiol 145:187–197
Merrifield DL, Dimitroglou A, Foey A, Davies SJ, Baker R, Bøgwald J, Castex M, Ringø E (2010) The current status and future focus of probiotic and prebiotic applications for salmonids. Aquaculture 302:1–18
Macey BM, Coyne VE (2005) Improved growth rate and disease resistance in farmed Haliotis midae through probiotic treatment. Aquaculture 245:249–261
Macey BM, Coyne VE (2006) Colonization of the gastrointestinal tract of the farmed South African abalone Haliotis midae by the probionts Vibrio midae SY9, Cryptococcus sp. SS1, and Debaryomyces hansenii AY1. Mar Biotechnol 8:246–259
Ten-Doeschate KI, Coyne VE (2008) Improved growth rate in farmed Haliotis midae through probiotic treatment. Aquaculture 284:174–179
Iehata S, Inagaki T, Okunishi S, Nakano M, Tanaka R, Maeda H (2009) Colonization and probiotic effects of lactic acid bacteria in the gut of the abalone Haliotis gigantea. Fish Sci 75:1285–1293
Silva-Aciares FR, Carvajal PO, Mejías CA, Riquelme CE (2011) Use of macroalgae supplemented with probiotics in the Haliotis rufescens (Swainson, 1822) culture in northern Chile. Aquacult Res 42:953–961
Ferguson RMW, Merrifield DL, Harper GM, Rawling MD, Mustafa S, Picchietti S, Balcazar JL, Davies SJ (2010) The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici on the gut microbiota and immune status of on-growing red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J Appl Microbiol 109:851–862
Sáenz de Rodrigáñez MA, Díaz-Rosales P, Chabrillón M, Smidt H, Arijo S, León-Rubio JM, Alarcón FJ, Balebona MC, Moriñigo MA, Cara JB, Moyano FJ (2009) Effect of dietary administration of probiotics on growth and intestine functionality of juvenile Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup 1858). Aquacult Nutri 15:177–185
Tapia-Paniagua ST, Chabrillón M, Díaz-Rosales P, de la Banda IG, Lobo C, Balebona MC, Moriñigo MA (2010) Intestinal microbiota diversity of the flat fish Solea senegalensis (Kaup, 1858) following probiotic administration. Microbial Ecol 60:310–319
Zhao J, Shi B, Jiang QR, Ke CH (2012) Changes in gut-associated flora and bacterial digestive enzymes during the development stages of abalone (Haliotis diversicolor). Aquaculture 338:147–153
Iehata S, Inagaki T, Okunishi S, Nakano M, Tanaka R, Maeda H (2010) Improved gut environment of abalone Haliotis gigantea through Pediococcus sp. Ab1 treatment. Aquaculture 305:59–65
Itoi S, Abe T, Washio S, Ikuno E, Kanomata Y, Sugita H (2008) Isolation of halotolerant Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis from intestinal tract of coastal fish. Int J Food Microbiol 121:116–121
Huber T, Faulkner G, Hugenholtz P (2004) Bellerophon: a program to detect chimeric sequences in multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 20:2317–2319
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Mullins TD, Britschgi TB, Krest RL, Giovannoni SJ (1995) Genetic comparisons reveal the same unknown bacterial lineages in Atlantic and Pacific bacterioplankton communities. Limnol Oceanogr 40:148–158
Ulrich W, Gotelli NJ (2007) Null model analysis of species nestedness patterns. Ecology 88:1824–1831
Castex M, Chim L, Pham D, Lemaire P, Wabete N, Nicolas JL, Schmidely P, Mariojouls C (2008) Probiotic P. acidilactici application in shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris culture subject to vibriosis in New Caledonia. Aquaculture 275:182–193
Castex M, Lemaire P, Wabete N, Chim L (2009) Effect of dietary probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici on antioxidant defences and oxidative stress status of shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris. Aquaculture 294:306–313
Merrifield DL, Bradley G, Harper GM, Baker RTM, Munn CB, Davies SJ (2011) Assessment of the effects of vegetative and lyophilized Pediococcus acidilactici on growth, feed utilization, intestinal colonization and health parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Aquacult Nutr 17:73–79
Dagá P, Feijoo G, Moreira MT, Costas D, Villanueva AG, Lema JM (2013) Bioencapsulated probiotics increased survival, growth and improved gut flora of turbot (Psetta maxima) larvae. Aquacult Int 21:337–345
Zokaeifar H, Balcázar JL, Saad CR, Kamarudin MS, Sijam K, Arshad A, Nejat N (2012) Effects of Bacillus subtilis on the growth performance, digestive enzymes, immune gene expression and disease resistance of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:683–689
Spanggaard B, Huber I, Nielsen J, Sick EB, Pipper CB, Martinussen T, Slierendrecht WJ, Gram L (2001) The probiotic potential against vibriosis of the indigenous microflora of rainbow trout. Environ Microbiol 3:755–765
Vaseeharan BARP, Ramasamy P (2003) Control of pathogenic Vibrio spp. by Bacillus subtilis BT23, a possible probiotic treatment for black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:83–87
Touraki M, Karamanlidou G, Karavida P, Chrysi K (2012) Evaluation of the probiotics Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus plantarum bioencapsulated in Artemia nauplii against vibriosis in European sea bass larvae (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2425–2433
Villamil L, Tafalla C, Figueras A, Novoa B (2002) Evaluation of immunomodulatory effects of lactic acid bacteria in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Clin Diagnos Lab Immunol 9:1318–1323
Sawabe T, Kita-Tsukamoto K, Thompson FL (2007) Inferring the evolutionary history of vibrios by means of multilocus sequence analysis. J Bacteriol 189:7932–7936
Sun YZ, Yang HL, Ma RL, Huang KP, Ye JD (2012) Culture-independent characterization of the autochthonous gut microbiota of grouper Epinephelus coioides following the administration of probiotic Enterococcus faecium. Aquacult Int 20:791–801
Sun YZ, Yang HL, Ma RL, Zhai SW (2012) Does dietary administration of Lactococcus lactis modulate the gut microbiota of grouper, Epinephelus coioides. J World Aquacult Soc 43:198–207
Yang HL, Sun YZ, Ma RL, Ye JD (2012) PCR-DGGE analysis of the autochthonous gut microbiota of grouper Epinephelus coioides following probiotic Bacillus clausii administration. Aquacult Res 43:489–497
Luis-Villaseñor IE, Castellanos-Cervantes T, Gomez-Gil B, Carrillo-García ÁE, Campa-Córdova ÁI, Ascencio F (2013) Probiotics in the intestinal tract of juvenile whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei: modulation of the bacterial community. World J Microbiol Biotech 29:257–265
Holben WE, Williams P, Saarinen M, Särkilahti LK, Apajalahti JHA (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of intestinal microflora indicates a novel Mycoplasma phylotype in farmed and wild salmon. Microbial Ecol 44:175–185
Bano N, DeRae SA, Bennett W, Vasquez L, Hollibaugh JT (2007) Dominance of Mycoplasma in the guts of the long-jawed mudsucker, Gillichthys mirabilis, from five California salt marshes. Environ Microbiol 9:2636–2641
Meziti A, Ramette A, Mente E, Kormas KA (2010) Temporal shifts of the Norway lobster (Nephrops norvegicus) gut bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:472–484
Macián MC, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Pujalte MJ, Garay E (2001) Vibrio agarivorans sp. nov., a novel agarolytic marine bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2031–2036
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Atsushi Hamabe at the Owase Aquaculture Center for kindly providing the abalone samples. This work was supported by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (no. 21780176) from the JSPS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iehata, S., Nakano, M., Tanaka, R. et al. Modulation of gut microbiota associated with abalone Haliotis gigantea by dietary administration of host-derived Pediococcus sp. Ab1. Fish Sci 80, 323–331 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-013-0691-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-013-0691-9