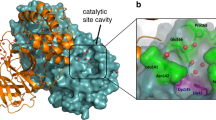
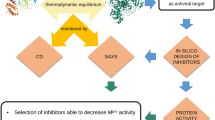
Abstract
In the process of the development of structural biology, both the size and the complexity of the determined macromolecular structures have grown significantly. As a result, the range of application areas for the results of structural studies of biological macromolecules has expanded. Significant progress in the development of structural biology methods has been largely achieved through the use of synchrotron radiation. Modern sources of synchrotron radiation allow to conduct high-performance structural studies with high temporal and spatial resolution. Thus, modern techniques make it possible to obtain not only static structures, but also to study dynamic processes, which play a key role in understanding biological mechanisms. One of the key directions in the development of structural research is the drug design based on the structures of biomolecules. Synchrotron radiation offers insights into the three-dimensional time-resolved structure of individual viral proteins and their complexes at atomic resolution. The rapid and accurate determination of protein structures is crucial for understanding viral pathogenicity and designing targeted therapeutics. Through the application of experimental techniques, including X-ray crystallography and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), it is possible to elucidate the structural details of SARS-CoV-2 virion containing 4 structural, 16 nonstructural proteins (nsp), and several accessory proteins. The most studied potential targets for vaccines and drugs are the structural spike (S) protein, which is responsible for entering the host cell, as well as nonstructural proteins essential for replication and transcription, such as main protease (Mpro), papain-like protease (PLpro), and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). This article provides a brief overview of structural analysis techniques, with focus on synchrotron radiation-based methods applied to the analysis of SARS-CoV-2 proteins.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Aatif M, Muteeb G, Alsultan A et al (2021) Dieckol and its derivatives as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (UK strain: VUI 202012/01): a computational study. Mar Drugs 19:242. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050242
Akdel M, DE Pires V, Pardo EP et al (2022) A structural biology community assessment of AlphaFold2 applications. Nat Struct Mol Biol 29:1056–1067. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-022-00849-w
Almehdi AM, Khoder G, Alchakee AS et al (2021) SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: pathogenesis, vaccines, and potential therapies. Infection 49:855–876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-021-01677-8
Als-Nielsen J, McMorrow D (2011) X-rays and their interaction with matter. In: Elements of modern X-ray physics, 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons, pp 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119998365.ch1
Arafet K, Serrano-Aparicio N, Lodola A et al (2021) Mechanism of inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 M pro by N3 peptidyl Michael acceptor explained by QM/MM simulations and design of new derivatives with tunable chemical reactivity. Chem Sci 12:1433–1444. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC06195F
Arnal RD, Millane RP (2022) Ab initio reconstruction from one-dimensional crystal diffraction data. Acta Crystallogr A Found Adv 78:249–261. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053273322001942
Avelar M, Pedraza-González L, Sinicropi A, Flores-Morales V (2023) Triterpene derivatives as potential inhibitors of the RBD spike protein from SARS-CoV-2: an in silico approach. Molecules 28:2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052333
Baek M, Baker D (2022) Deep learning and protein structure modeling. Nat Methods 19:13–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01360-8
Bai Z, Cao Y, Liu W, Li J (2021) The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and its role in viral structure, biological functions, and a potential target for drug or vaccine mitigation. Viruses 13:1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061115
Bai B, Belovodskiy A, Hena M et al (2022) Peptidomimetic α-acyloxymethylketone warheads with six-membered lactam P1 glutamine mimic: SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibition, coronavirus antiviral activity, and in vitro biological stability. J Med Chem 65:2905–2925. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00616
Baker JD, Uhrich RL, Kraemer GC et al (2021) A drug repurposing screen identifies hepatitis C antivirals as inhibitors of the SARS-CoV2 main protease. PLoS One 16:e0245962. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245962
Barends TRM, Stauch B, Cherezov V, Schlichting I (2022) Serial femtosecond crystallography. Nat Rev Methods Prim 2:59. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-022-00141-7
Baumgärtel H (1981) BESSY - Der Berliner Elektronenspeicherring. Nachr Chem Tech Lab 29:440–444. https://doi.org/10.1002/nadc.19810290706
Berman HM (2000) The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.235
Bhowmick S, Jing T, Wang W et al (2022) In silico protein folding prediction of COVID-19 mutations and variants. Biomolecules 12:1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111665
Bielecki J, Maia FRNC, Mancuso AP (2020) Perspectives on single particle imaging with X rays at the advent of high repetition rate X-ray free electron laser sources. Struct Dyn 7:040901. https://doi.org/10.1063/4.0000024
Boldon L, Laliberte F, Liu L (2015) Review of the fundamental theories behind small angle X-ray scattering, molecular dynamics simulations, and relevant integrated application. Nano Rev 6:25661. https://doi.org/10.3402/nano.v6.25661
Brosey CA, Tainer JA (2019) Evolving SAXS versatility: solution X-ray scattering for macromolecular architecture, functional landscapes, and integrative structural biology. Curr Opin Struct Biol 58:197–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.04.004
Buel GR, Walters KJ (2022) Can AlphaFold2 predict the impact of missense mutations on structure? Nat Struct Mol Biol 29:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-021-00714-2
Bukhtiyarov AV, Bukhtiyarov VI, Zhuravlev AN et al (2022) Synchrotron radiation facility “Siberian Circular Photon Source” (SRF SKIF). Crystallogr Rep 67:690–711. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063774522050029
Byer AS, Pei X, Patterson MG, Ando N (2023) Small-angle X-ray scattering studies of enzymes. Curr Opin Chem Biol 72:102232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102232
Casasanta MA, Jonaid GM, Kaylor L et al (2023) Structural insights of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein: implications for the inner-workings of rapid antigen tests. Microsc Microanal 29:649–657. https://doi.org/10.1093/micmic/ozac036
Chakraborty C, Bhattacharya M, Sharma AR, Mallik B (2022) Omicron (B.1.1.529) - a new heavily mutated variant: mapped location and probable properties of its mutations with an emphasis on S-glycoprotein. Int J Biol Macromol 219:980–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.254
Cho HS, Schotte F, Stadnytskyi V, Anfinrud P (2021) Time-resolved X-ray scattering studies of proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 70:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2021.05.002
Cohen AE (2021) A new era of synchrotron-enabled macromolecular crystallography. Nat Methods 18:433–434. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01146-y
Da Vela S, Svergun DI (2020) Methods, development and applications of small-angle X-ray scattering to characterize biological macromolecules in solution. Curr Res Struct Biol 2:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crstbi.2020.08.004
de la Mora E, Coquelle N, Bury CS et al (2020) Radiation damage and dose limits in serial synchrotron crystallography at cryo- and room temperatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci 117:4142–4151. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1821522117
Dodson E (2021) Introduction to molecular replacement: a time perspective. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 77:867–879. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798321004368
Dong S, Sun J, Mao Z et al (2020) A guideline for homology modeling of the proteins from newly discovered betacoronavirus, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). J Med Virol 92:1542–1548. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25768
Ekici ÖD, Götz MG, James KE et al (2004) Aza-peptide Michael acceptors: a new class of inhibitors specific for caspases and other clan CD cysteine proteases. J Med Chem 47:1889–1892. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm049938j
Fischer M (2021) Macromolecular room temperature crystallography. Q Rev Biophys 54:e1. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033583520000128
Foos N, Rizk M, Nanao MH (2022) Single-support serial isomorphous replacement phasing. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 78:716–724. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798322003977
Fu L, Ye F, Feng Y et al (2020) Both boceprevir and GC376 efficaciously inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by targeting its main protease. Nat Commun 11:4417. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18233-x
Gao X, Qin B, Chen P et al (2021) Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease. Acta Pharm Sin B 11:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.08.014
Gomes PSFC, Gomes DEB, Bernardi RC (2022) Protein structure prediction in the era of AI: challenges and limitations when applying to in silico force spectroscopy. Front Bioinform 2:983306. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbinf.2022.983306
Gore S, Sanz García E, Hendrickx PMS et al (2017) Validation of structures in the Protein Data Bank. Structure 25:1916–1927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.10.009
Gorkhali R, Koirala P, Rijal S et al (2021) Structure and function of major SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV proteins. Bioinform Biol Insights 15:117793222110258. https://doi.org/10.1177/11779322211025876
Gräwert TW, Svergun DI (2020) Structural modeling using solution small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). J Mol Biol 432:3078–3092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.01.030
Guo L, Zafar F, Moeen N et al (2022) Ultra-large-scale screening of natural compounds and free energy calculations revealed potential inhibitors for the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2. Molecules 27:7317. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217317
Hameduh T, Haddad Y, Adam V, Heger Z (2020) Homology modeling in the time of collective and artificial intelligence. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 18:3494–3506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2020.11.007
Hardenbrook NJ, Zhang P (2022) A structural view of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and its assembly. Curr Opin Virol 52:123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.011
He Z, Ye F, Zhang C et al (2022) A comparison of remdesivir versus gold cluster in COVID-19 animal model: a better therapeutic outcome of gold cluster. Nano Today 44:101468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2022.101468
Hendrickson WA, Ogata CM (1997) Phase determination from multiwavelength anomalous diffraction measurements. Methods Enzymol 276:494–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(97)76074-9
Hillen HS, Kokic G, Farnung L et al (2020) Structure of replicating SARS-CoV-2 polymerase. Nature 584:154–156. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2368-8
Hu Y, Cheng K, He L et al (2021) NMR-based methods for protein analysis. Anal Chem 93:1866–1879. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03830
Hu Q, Xiong Y, Zhu G-H et al (2022) The SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro): structure, function, and emerging therapies for COVID-19. MedComm (Beijing) 3:e151. https://doi.org/10.1002/mco2.151
Ionescu MI (2020) An overview of the crystallized structures of the SARS-CoV-2. Protein J 39:600–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-020-09933-w
Jamison DA, Anand Narayanan S, Trovão NS et al (2022) A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, part 1: intracellular overdrive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur J Hum Genet 30:889–898. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-022-01108-8
Jin Z, Du X, Xu Y et al (2020) Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature 582:289–293. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2223-y
Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A et al (2021) Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596:583–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2
Kilim O, Mentes A, Pál B et al (2023) SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain deep mutational AlphaFold2 structures. Sci Data 10:134. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-023-02035-z
Kim Y, Nam KH (2022) Pink-beam serial synchrotron crystallography at Pohang light source II. Crystals (Basel) 12:1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12111637
Kim AK, Porter LL (2021) Functional and regulatory roles of fold-switching proteins. Structure 29:6–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2020.10.006
Kingston RL, Millane RP (2022) A general method for directly phasing diffraction data from high-solvent-content protein crystals. IUCrJ 9:648–665. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052252522006996
Kirian RA, White TA, Holton JM et al (2011) Structure-factor analysis of femtosecond microdiffraction patterns from protein nanocrystals. Acta Crystallogr A 67:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108767310050981
Kneller DW, Phillips G, O’Neill HM et al (2020) Structural plasticity of SARS-CoV-2 3CL Mpro active site cavity revealed by room temperature X-ray crystallography. Nat Commun 11:3202. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16954-7
Koelmel W, Kuper J, Kisker C (2021) Cesium based phasing of macromolecules: a general easy to use approach for solving the phase problem. Sci Rep 11:17038. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95186-1
Kursula P (2021) Small-angle X-ray scattering for the proteomics community: current overview and future potential. Expert Rev Proteomics 18:415–422. https://doi.org/10.1080/14789450.2021.1951242
Lam TT-Y, Jia N, Zhang Y-W et al (2020) Identifying SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins. Nature 583:282–285. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2169-0
Lane TJ (2023) Protein structure prediction has reached the single-structure frontier. Nat Methods 20:170–173. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-022-01760-4
Lawrence JM, Orlans J, Evans G et al (2020) High-throughput in situ experimental phasing. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 76:790–801. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798320009109
Lee J, Kenward C, Worrall LJ et al (2022a) X-ray crystallographic characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease polyprotein cleavage sites essential for viral processing and maturation. Nat Commun 13:5196. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32854-4
Lee RK-L, Li T-N, Chang S-Y et al (2022b) Identification of entry inhibitors against delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2. Int J Mol Sci 23:4050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23074050
Li M, Ren Y, Aw ZQ et al (2022) Broadly neutralizing and protective nanobodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.1, BA.2, and BA.4/5 and diverse sarbecoviruses. Nat Commun 13:7957. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35642-2
Ma S, Damfo S, Lou J et al (2022) Two ligand-binding sites on SARS-CoV-2 non-structural protein 1 revealed by fragment-based X-ray screening. Int J Mol Sci 23:12448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012448
Mahal A, Duan M, Zinad DS et al (2021) Recent progress in chemical approaches for the development of novel neuraminidase inhibitors. RSC Adv 11:1804–1840. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA07283D
Martiel I, Müller-Werkmeister HM, Cohen AE (2019) Strategies for sample delivery for femtosecond crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 75:160–177. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798318017953
Martínez-Flores D, Zepeda-Cervantes J, Cruz-Reséndiz A et al (2021) SARS-CoV-2 vaccines based on the spike glycoprotein and implications of new viral variants. Front Immunol 12:701501. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.701501
Martin-Garcia JM (2021) Protein dynamics and time resolved protein crystallography at synchrotron radiation sources: past, present and future. Crystals (Basel) 11:521. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11050521
McCoy AJ (2007) Solving structures of protein complexes by molecular replacement with Phaser. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 63:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444906045975
McCoy AJ, Sammito MD, Read RJ (2022) Implications of AlphaFold 2 for crystallographic phasing by molecular replacement. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 78:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798321012122
Medina A, Jiménez E, Caballero I et al (2022) Verification: model-free phasing with enhanced predicted models in ARCIMBOLDO_SHREDDER. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 78:1283–1293. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798322009706
Meents A, Wiedorn MO, Srajer V et al (2017) Pink-beam serial crystallography. Nat Commun 8:1281. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01417-3
Mehrabi P, Bücker R, Bourenkov G et al (2021) Serial femtosecond and serial synchrotron crystallography can yield data of equivalent quality: a systematic comparison. Sci Adv 7:eabf1380. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abf1380
Mironov V, Shchugoreva IA, Artyushenko PV et al (2022) Structure‐ and interaction‐based design of anti‐SARS‐CoV‐2 aptamers. Chemistry 28:e202104481. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202104481
Miyashita O, Joti Y (2017) X-ray free electron laser single-particle analysis for biological systems. Curr Opin Struct Biol 43:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2017.03.014
Mody V, Ho J, Wills S et al (2021) Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents. Commun Biol 4:93. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01577-x
Morgan AJ, Ayyer K, Barty A et al (2019) Ab initio phasing of the diffraction of crystals with translational disorder. Acta Crystallogr A Found Adv 75:25–40. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053273318015395
Mou T-C, Zeng B, Doukov TI, Sprang SR (2022) Application of sulfur SAD to small crystals with a large asymmetric unit and anomalous substructure. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 78:1021–1031. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798322005848
Muhammed MT, Aki-Yalcin E (2019) Homology modeling in drug discovery: overview, current applications, and future perspectives. Chem Biol Drug Des 93:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.13388
Munro IH (1997) Synchrotron radiation research in the UK. J Synchrotron Radiat 4:344–358. https://doi.org/10.1107/S090904959701176X
Nam KH (2020) Approach of serial crystallography. Crystals (Basel) 10:854. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100854
Nam KH (2022) Serial X-ray crystallography. Crystals (Basel) 12:99. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12010099
Newman JA, Douangamath A, Yadzani S et al (2021) Structure, mechanism and crystallographic fragment screening of the SARS-CoV-2 NSP13 helicase. Nat Commun 12:4848. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25166-6
Osipiuk J, Azizi S-A, Dvorkin S et al (2021) Structure of papain-like protease from SARS-CoV-2 and its complexes with non-covalent inhibitors. Nat Commun 12:743. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21060-3
Ou J, Lan W, Wu X et al (2022) Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Omicron diverse spike gene mutations identifies multiple inter-variant recombination events. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:138. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-00992-2
Outeiral C, Nissley DA, Deane CM (2022) Current structure predictors are not learning the physics of protein folding. Bioinformatics 38:1881–1887. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btab881
Pearce NM, Krojer T, Bradley AR et al (2017) A multi-crystal method for extracting obscured crystallographic states from conventionally uninterpretable electron density. Nat Commun 8:15123. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15123
Pearson AR, Mehrabi P (2020) Serial synchrotron crystallography for time-resolved structural biology. Curr Opin Struct Biol 65:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2020.06.019
Peng Q, Peng R, Yuan B et al (2020) Structural and biochemical characterization of the nsp12-nsp7-nsp8 core polymerase complex from SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep 31:107774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107774
Pereira J, Simpkin AJ, Hartmann MD et al (2021) High-accuracy protein structure prediction in <scp>CASP14</scp>. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinforma 89:1687–1699. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.26171
Petrosino M, Stellato F, Chiaraluce R et al (2021) Zn-induced interactions between SARS-CoV-2 orf7a and BST2/Tetherin. ChemistryOpen 10:1133–1141. https://doi.org/10.1002/open.202100217
Putnam CD, Hammel M, Hura GL, Tainer JA (2007) X-ray solution scattering (SAXS) combined with crystallography and computation: defining accurate macromolecular structures, conformations and assemblies in solution. Q Rev Biophys 40:191–285. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033583507004635
Rambo RP, Tainer JA (2013) Super-resolution in solution X-ray scattering and its applications to structural systems biology. Annu Rev Biophys 42:415–441. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130301
Robertson JC, Nassar R, Liu C et al (2019) NMR-assisted protein structure prediction with MELDxMD. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinforma 87:1333–1340. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.25788
Rodríguez DD, Grosse C, Himmel S et al (2009) Crystallographic ab initio protein structure solution below atomic resolution. Nat Methods 6:651–653. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1365
Różycki B, Boura E (2022) Conformational ensemble of the full-length SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein based on molecular simulations and SAXS data. Biophys Chem 288:106843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2022.106843
Russi S, González A, Kenner LR et al (2017) Conformational variation of proteins at room temperature is not dominated by radiation damage. J Synchrotron Radiat 24:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600577516017343
Sanchez-Cano C, Alvarez-Puebla RA, Abendroth JM et al (2021) X-ray-based techniques to study the nano–bio interface. ACS Nano 15:3754–3807. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c09563
Sanders B, Pokhrel S, Labbe A et al (2022) Potent and selective covalent inhibition of the papain-like protease from SARS-CoV-2. Res Sq. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-906621/v1
Schlichting I, Goody RS (1997) Triggering methods in crystallographic enzyme kinetics. Methods Enzymol 277:467–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(97)77026-5
Schmidt A, Teeter M, Weckert E, Lamzin VS (2011) Crystal structure of small protein crambin at 0.48 Å resolution. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 67:424–428. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309110052607
Seffernick JT, Lindert S (2020) Hybrid methods for combined experimental and computational determination of protein structure. J Chem Phys 153:240901. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0026025
Shabalin IG, Porebski PJ, Minor W (2018) Refining the macromolecular model – achieving the best agreement with the data from X-ray diffraction experiment. Crystallogr Rev 24:236–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/0889311X.2018.1521805
Shang J, Ye G, Shi K et al (2020) Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 581:221–224. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y
Shi W, Cai Y, Zhu H et al (2023) Cryo-EM structure of SARS-CoV-2 postfusion spike in membrane. Nature 619:403–409. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06273-4
Śledź P, Caflisch A (2018) Protein structure-based drug design: from docking to molecular dynamics. Curr Opin Struct Biol 48:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2017.10.010
Sugiki T, Yamaguchi Y, Fujiwara T et al (2020) In-cell NMR as a sensitive tool to monitor physiological condition of Escherichia coli. Sci Rep 10:2466. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59076-2
Terwilliger TC, Poon BK, Afonine PV et al (2022) Improved AlphaFold modeling with implicit experimental information. Nat Methods 19:1376–1382. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-022-01645-6
Theillet F-X, Luchinat E (2022) In-cell NMR: why and how? Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 132–133:1–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnmrs.2022.04.002
Truong JQ, Nguyen S, Bruning JB, Shearwin KE (2021) Simplified heavy-atom derivatization of protein structures via co-crystallization with the MAD tetragon tetrabromoterephthalic acid. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 77:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X21004052
Wang J (2015) Estimation of the quality of refined protein crystal structures. Protein Sci 24:661–669. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2639
Wang R, Zhang Q, Ge J et al (2021) Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations reveals neutralization escape mechanisms and the ability to use ACE2 receptors from additional species. Immunity 54:1611-1621.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.06.003
Webb B, Viswanath S, Bonomi M et al (2018) Integrative structure modeling with the integrative modeling platform. Protein Sci 27:245–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3311
Weber IT, Wang Y-F, Harrison RW (2021) HIV protease: historical perspective and current research. Viruses 13:839. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050839
Wierbowski SD, Liang S, Liu Y et al (2021) A 3D structural SARS-CoV-2–human interactome to explore genetic and drug perturbations. Nat Methods 18:1477–1488. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01318-w
Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS et al (2020) Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 367:1260–1263. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb2507
Yang Z, Zeng X, Zhao Y, Chen R (2023) AlphaFold2 and its applications in the fields of biology and medicine. Signal Transduct Target Ther 8:115. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01381-z
Ye G, Liu B, Li F (2022) Cryo-EM structure of a SARS-CoV-2 Omicron spike protein ectodomain. Nat Commun 13:1214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28882-9
Yousef M, Abdelkader T, El-Bahnasy K (2019) Performance comparison of ab initio protein structure prediction methods. Ain Shams Eng J 10:713–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2019.03.004
Yuan Y, Tam MF, Simplaceanu V, Ho C (2015) New look at hemoglobin allostery. Chem Rev 115:1702–1724. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500495x
Yun H-Y, Lee J, Kim H et al (2018) Structural study reveals the temperature-dependent conformational flexibility of Tk-PTP, a protein tyrosine phosphatase from Thermococcus kodakaraensis KOD1. PLoS One 13:e0197635. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197635
Zhang L, Lin D, Sun X et al (2020) Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved α-ketoamide inhibitors. Science 368:409–412. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb3405
Zhu L, Chen X, Abola EE et al (2020) Serial crystallography for structure-based drug discovery. Trends Pharmacol Sci 41:830–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2020.08.009
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (agreement №075-15-2021-1355).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The first draft of the manuscript was written by M.K., and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. A.R. led the work and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kosenko, M., Onkhonova, G., Susloparov, I. et al. SARS-CoV-2 proteins structural studies using synchrotron radiation. Biophys Rev 15, 1185–1194 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-023-01153-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-023-01153-7