Abstract
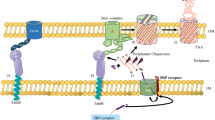
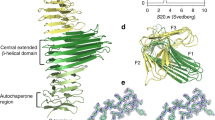
Haemophilus influenzae adhesin (Hia) belongs to the trimeric autotransporter family, and it mediates the adherence of these bacteria to the epithelial cells of host organisms. Hia is composed of the passenger domain, which is a virulence factor, and the translocator domain, which anchors the passenger domain into the outer membrane. The Hia transmembrane domain forms a transmembrane β-barrel of 12 β-strands, four of which are provided from each subunit. The β-barrel has a pore that is traversed by three α-helices, one of which is provided from each subunit. This domain has a unique arginine arrangement inside the β-barrel. The side chains of the arginine residues protrude from the β-strands of three subunits toward the center of the barrel and are close to each other. Mutation of this arginine residue revealed the importance of the electrostatic repulsion between the three arginines. Electrostatic repulsion is considered to prevent misfolding and/or misassembly. The arginine clusters at the interface were found in several proteins and might generally play an important role in the assembly of the oligomer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki E, Sato D, Fujiwara K, Ikeguchi M (2017) Electrostatic repulsion between unique arginine residues is essential for the efficient in vitro assembly of the transmembrane domain of a trimeric autotransporter. Biochemistry 56:2139–2148. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b01130
Barlow DJ, Thornton JM (1983) Ion-pairs in proteins. J Mol Biol 168:867–885
Chauhan N et al (2019) Insights into the autotransport process of a trimeric autotransporter, Yersinia Adhesin A (YadA). Mol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14195
Dai W, Wu A, Ma L, Li YX, Jiang T, Li YY (2016) A novel index of protein-protein interface propensity improves interface residue recognition. BMC Syst Biol 10:112. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12918-016-0351-7
Duarte JM, Biyani N, Baskaran K, Capitani G (2013) An analysis of oligomerization interfaces in transmembrane proteins. BMC Struct Biol 13:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6807-13-21
Fan E, Chauhan N, Udatha DB, Leo JC, Linke D (2016) Type V secretion systems in bacteria. Microbiol Spectr 4. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0009-2015
Ganser BK, Li S, Klishko VY, Finch JT, Sundquist WI (1999) Assembly and analysis of conical models for the HIV-1 core. Science 283:80–83
Ganser-Pornillos BK, von Schwedler UK, Stray KM, Aiken C, Sundquist WI (2004) Assembly properties of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 CA protein. J Virol 78:2545–2552. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.78.5.2545-2552.2004
Grijpstra J, Arenas J, Rutten L, Tommassen J (2013) Autotransporter secretion: varying on a theme. Res Microbiol 164:562–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2013.03.010
Harms MJ, Schlessman JL, Sue GR, Garcia-Moreno E B (2011) Arginine residues at internal positions in a protein are always charged. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:18954–18959. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1104808108
Isom DG, Cannon BR, Castaneda CA, Robinson A, Garcia-Moreno B (2008) High tolerance for ionizable residues in the hydrophobic interior of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:17784–17788. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805113105
Isom DG, Castaneda CA, Cannon BR, Velu PD, Garcia-Moreno EB (2010) Charges in the hydrophobic interior of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:16096–16100. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1004213107
Isom DG, Castaneda CA, Cannon BR, Garcia-Moreno E B (2011) Large shifts in pKa values of lysine residues buried inside a protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:5260–5265. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1010750108
Jahn TR, Radford SE (2005) The Yin and Yang of protein folding. FEBS J 272:5962–5970. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.05021.x
Jurrus E et al (2018) Improvements to the APBS biomolecular solvation software suite protein science : a publication of the. Protein Soc 27:112–128. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3280
Leo JC, Grin I, Linke D (2012) Type V secretion: mechanism(s) of autotransport through the bacterial outer membrane. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 367:1088–1101. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2011.0208
Li S, Hill CP, Sundquist WI, Finch JT (2000) Image reconstructions of helical assemblies of the HIV-1 CA protein. Nature 407:409–413. https://doi.org/10.1038/35030177
Ma B-G, Goncearenco A, Berezovsky IN (2010) Thermophilic adaptation of protein complexes inferred from proteomic homology modeling. Structure 18:819–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2010.04.004
Magalhaes A, Maigret B, Hoflack J, Gomes JN, Scheraga HA (1994) Contribution of unusual arginine-arginine short-range interactions to stabilization and recognition in proteins. J Protein Chem 13:195–215
Mason PE, Neilson GW, Dempsey CE, Barnes AC, Cruickshank JM (2003) The hydration structure of guanidinium and thiocyanate ions: implications for protein stability in aqueous solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:4557–4561. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0735920100
Meng G, Surana NK, St Geme JW 3rd, Waksman G (2006) Structure of the outer membrane translocator domain of the Haemophilus influenzae Hia trimeric autotransporter. EMBO J 25:2297–2304. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601132
Meng G, St Geme JW 3rd, Waksman G (2008) Repetitive architecture of the Haemophilus influenzae Hia trimeric autotransporter. J Mol Biol 384:824–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.085
Mikula KM, Leo JC, Lyskowski A, Kedracka-Krok S, Pirog A, Goldman A (2012) The translocation domain in trimeric autotransporter adhesins is necessary and sufficient for trimerization and autotransportation. J Bacteriol 194:827–838. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.05322-11
Neves MA, Yeager M, Abagyan R (2012) Unusual arginine formations in protein function and assembly: rings, strings, and stacks. J Phys Chem B 116:7006–7013. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp3009699
Noinaj N et al (2013) Structural insight into the biogenesis of beta-barrel membrane proteins. Nature 501:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12521
Noinaj N, Kuszak AJ, Balusek C, Gumbart JC, Buchanan SK (2014) Lateral opening and exit pore formation are required for BamA function. Structure 22:1055–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.05.008
Noinaj N, Gumbart JC, Buchanan SK (2017) The beta-barrel assembly machinery in motion. Nat Rev Microbiol 15:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.191
O'Neil PK, Rollauer SE, Noinaj N, Buchanan SK (2015) Fitting the pieces of the beta-barrel assembly machinery complex. Biochemistry 54:6303–6311. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00852
Richardson JS, Richardson DC (2002) Natural β-sheet proteins use negative design to avoid edge-to-edge aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:2754–2759. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.052706099
Rollauer SE, Sooreshjani MA, Noinaj N, Buchanan SK (2015) Outer membrane protein biogenesis in gram-negative bacteria. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 370. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0023
Sato D, Takebe S, Kurobe A, Ohtomo H, Fujiwara K, Ikeguchi M (2016) Electrostatic repulsion during ferritin assembly and its screening by ions. Biochemistry 55:482–488. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01197
Shahid SA, Bardiaux B, Franks WT, Krabben L, Habeck M, van Rossum BJ, Linke D (2012) Membrane-protein structure determination by solid-state NMR spectroscopy of microcrystals. Nat Methods 9:1212–1217. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2248
Sikdar R, Peterson JH, Anderson DE, Bernstein HD (2017) Folding of a bacterial integral outer membrane protein is initiated in the periplasm. Nat Commun 8:1309. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01246-4
Stites WE, Gittis AG, Lattman EE, Shortle D (1991) In a staphylococcal nuclease mutant the side-chain of a lysine replacing valine 66 is fully buried in the hydrophobic core. J Mol Biol 221:7–14
Surana NK, Cutter D, Barenkamp SJ, St Geme JW 3rd (2004) The Haemophilus influenzae Hia autotransporter contains an unusually short trimeric translocator domain. J Biol Chem 279:14679–14685. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M311496200
Szczesny P, Lupas A (2008) Domain annotation of trimeric autotransporter adhesins—daTAA. Bioinformatics 24:1251–1256. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btn118
Yan C, Wu F, Jernigan RL, Dobbs D, Honavar V (2007) Characterization of protein–protein interfaces. Protein J 27:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-007-9108-x
Yeo HJ, Cotter SE, Laarmann S, Juehne T, St Geme JW 3rd, Waksman G (2004) Structural basis for host recognition by the Haemophilus influenzae Hia autotransporter. EMBO J 23:1245–1256. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600142
Yoo J, Cui Q (2008) Does arginine remain protonated in the lipid membrane? Insights from microscopic pKa calculations. Biophys J 94:L61–L63. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.107.122945
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Eriko Aoki declares that she has no conflict of interest. Masamichi Ikeguchi declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of a Special Issue dedicated to the “2018 Joint Conference of the Asian Biophysics Association and Australian Society for Biophysics” edited by Kuniaki Nagayama, Raymond Norton, Kyeong Kyu Kim, Hiroyuki Noji, Till Böcking, and Andrew Battle.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoki, E., Ikeguchi, M. In vitro assembly of Haemophilus influenzae adhesin transmembrane domain and studies on the electrostatic repulsion at the interface. Biophys Rev 11, 303–309 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-019-00535-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-019-00535-0