Abstract
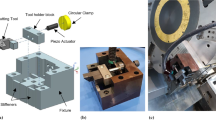
Tribology studies have recently shown the beneficial reduction in the friction coefficient of various mechanical components by application of surface texturing. This study presents a study of surface texturing using a piezoelectric tool holder actuator whereby the tool holder installed on a conventional computerized numerical controlled (CNC) machine lathe. The tool holder used in surface texturing a workpiece surface, yields average strokes up to 26 ?m and has a natural frequency of approximately 480 Hz. A piezo actuator of 15 μm maximum displacement was utilized, and a single parallel four-bar flexure hinge mechanism magnified the input displacement from the piezo actuator by an amplification ratio of 3:1. In this study, a piezo actuator that operated under the open-loop condition, in modulation frequency range from 100 Hz to 135 Hz, was imposed to cut into the workpiece surface to build a pattern of dimples. Moreover, the characteristics of the dimple-pattern topography were investigated by varying the spindle rotation rate between 30 rpm and 100 rpm at constant modulation frequency of 120 Hz. According to the experimental results, Al 6061-T6 and AISI 1045 were successfully textured by using the piezoelectric tool holder actuator. The results showed that the maximum errors of the dimple feature on Al 6061-T6 and AISI 1045 were approximately 10.14% and 47.97%, respectively, between the analysis and experimental results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- x(t):
-
tool position
- Vx(t):
-
tool velocity
- t:
-
time
- A:
-
amplitude of sinusoidal wave
- f m :
-
oscillation frequency
- f s :
-
spindle rotation frequency
- Δd:
-
wave’s peak-to-peak distance
- N:
-
spindle rotational speed
- D:
-
diameter of workpiece
- θ:
-
end-cutting angle of cutting tool
- d a :
-
length of dimple
- d b :
-
width of dimple
- L a :
-
distance of cutting direction
- L b :
-
distance of feed direction
- Neutral axis :
-
tool position without oscillation displacement
References
Pettersson, U. and Jacobson, S., “Tribological Texturing of Steel Surfaces with a Novel Diamond Embossing Tool Technique,” Tribology International, Vol. 39, No. 7, pp. 695–700, 2006.
Etsion, I., “State of the Art in Laser Surface Texturing,” Journal of Tribology, Vol. 127, No. 1, pp. 248–253, 2005.
Borghi, A., Gualtieri, E., Marchetto, D., Moretti, L., and Valeri, S., “Tribological Effects of Surface Texturing on Nitriding Steel for High-Performance Engine Applications,” Wear, Vol. 265, No. 7–8, pp. 1046–1051, 2008.
Zhou, R., Cao, J., Wang, Q. J., Meng, F., Zimowski, K., and Xia, Z. C., “Technology Effect of EDT Surface Texturing on Tribological Behavior of Aluminum Sheet,” Journal of Materials Processing Tech., Vol. 211, No. 10, pp. 1643–1649, 2011.
Wakuda, M., Yamauchi, Y., Kanzaki, S., and Yasuda, Y., “Effect of Surface Texturing on Friction Reduction Between Ceramic and Steel Materials under Lubricated Sliding Contact,” Wear, Vol. 254, No. 3–4, pp. 356–363, 2003.
Chen, J., Müller-Steinhagen, H., and Duffy, G. G., “Heat Transfer Enhancement in Dimpled Tubes,” Applied Thermal Engineering, Vol. 21, No. 5, pp. 535–547, 2001.
Vilhena, L. M., Sedlaèek, M., Podgornik, B., Vižintin, J., Babnik, A., and Možina, J., “Surface Texturing by Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser,” Tribology International, Vol. 42, No. 10, pp. 1496–1504, 2009.
Greco, A., Raphaelson, S., Ehmann, K., and Wang, Q. J., “Surface Texturing of Tribological Vibromechanical Texturing,” Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, Vol. 131, No. 6, pp. 1–8, 2009.
Etsion, I., Kligerman, Y., and Halperin, G., “Analytical and Experimental Investigation of Laser-Textured Mechanical Seal Faces,” Tribology Transactions, Vol. 42, No. 3, pp. 511–516, 1999.
Mann, J., Saldana, C., and Chandrasekar, S., “Metal Particulate Production by Modulation-Assisted Machining,” Scripta Materialia, Vol. 57, No. 10, pp. 909–912, 2007.
Byun, J. W., Shin, H. S., Kwon, M. H., Kim, B. H., and Chu, C. N., “Surface Texturing by Micro ECM for Friction Reduction,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 11, No. 5, pp. 747–753, 2010.
Kim, S. L. and Kim, G. M., “Micro-patterning on Roll Surface Using Photo-Lithography Processes,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 12, No. 5, pp. 763–768, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurniawan, R., Ko, T.J. A study of surface texturing using piezoelectric tool holder actuator on conventional CNC turning. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 14, 199–206 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-013-0028-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-013-0028-8