Abstract
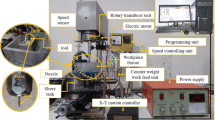
Due to significant increase in the incidence of cardiovascular disease, the development of medical devices to treat thrombosis has recently been of great concern. In order to develop a rotational tool to remove vascular blood clots, it is especially important to understand the tribological behavior of the tool inside a vessel to effectively remove blood clots without any damage to the vessel. In this work, the grinding behaviors of different tools were experimentally investigated using clotted blood samples from cattle. Three tools of different shapes were designed and tested. We found that an elliptical design tool with four stainless steel blades (0.25 mm-thickness) yielded the smallest clot particles. In experiments using two other tools with stainless steel and fluoro carbon wires, stainless steel generated small particles more efficiently than fluoro carbon. Particle size decreased as the contact length of the tool edges and the rotational velocity of the tool increased. It is expected that the results of this work may be used to design superior devices for a variety of medical applications related to clot removal in blood vessels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matthew, D. R., Jennifer, B. L., Cornelis, V. V., Donald, P. G. and Kenneth, G. M., “Blood Clotting in Minimally Altered Whole Blood,” Blood, Vol. 88, No. 9, pp. 3432–3445, 1996.
Rauch, U., Osende, J. I., Fuster, V., Badimon, J. J., Fayad, Z. and Chesebro, J. H., “Thrombus Formation on Atherosclerotic Plaques: Pathogenesis and Clinical Consequences,” Ann. Intern. Med., Vol. 134, No. 3, pp. 224–238, 2001.
Zubkov, Y. N., Nikiforov, B. M. and Shustin, V. A., “Balloon Catheter Technique for Dilatation of Constricted Cerebral Arteries After Aneurysmal SAH,” Acta Neurochirurgica, Vol. 70, No. 1–2, pp. 65–79, 1984.
Vicenzi, M. N., Meislitzer, T., Heitzinger, B., Halaj, M., Fleisher, L. A. and Metzler, H., “Coronary artery stenting and non-cardiac surgery–a prospective outcome study,” Br. J. Anaesth., Vol. 96, No. 6, pp. 686–693, 2006.
Marks, M. P., Marcellus, M., Norbash, A. M., Steinberg, G. K., Tong, D. and Albers, G. W., “Outcome of angioplasty for atherosclerotic intracranial stenosis,” Stroke, Vol. 30, No. 5, pp. 1065–1069, 1999.
Marks, M. P., Marcellus, M. L., Do, H. M., Schraedley-Desmond, P. K., Steinberg, G. K., Tong, D. C. and Albers, G. W., “Intracranial angioplasty without stenting for symptomatic atherosclerotic stenosis: long-term follow-up,” Am. J. Neuroradiol., Vol. 26, No. 3, pp. 525–530, 2005.
Mori, T., Fukuoka, M., Kazita, K. and Mori, K., “Follow-up study after intracranial percutaneous transluminal cerebral balloon angioplasty,” Am. J. Neuroradiol., Vol. 19, No. 8, pp. 1525–1533, 1998.
Arko, F. R., Davis, C. M., Murphy, E. H., Smith, S. T., Timaran, C. H., Modrall, J. G., Valentine, R. J. and Clagett, G. P., “Aggressive percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy of deep venous thrombosis: early clinical results,” Arch. Surg., Vol. 142, No. 6, pp. 513–519, 2007.
Bertrand, M. E., Lablanche, J. M., Leroy, F., Bauters, C., Jaegere, P. D., Serruys, P. W., Meyer, J., Dietz, U. and Erbel, R., “Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Rotary Ablation with Rotablator (European Experience),” Am. J. Cardiol., Vol. 69, No. 5, pp. 470–474, 1992.
Anand, S. S., Yusuf, S., Pogue, J., Weitz, J. I. and Flather, M., “Long-Term Oral Anticoagulant Therapy in Patients With Unstable Angina or Suspected Non-Q-Wave Myocardial Infarction: Organization to Assess Strategies for Ischemic Syndromes (OASIS) Pilot Study Results,” Circulation, Vol. 98, No. 11, pp. 1064–1070, 1998.
Vogel, P. M., Bansal, V. and Marshall, M. W., “Thrombosed Hemodialysis Grafts: Lyse and Wait with Tissue Plasminogen Activator or Urokinase Compared to Mechanical Thrombolysis with the Arrow-Trerotola Percutaneous Thrombolytic Device,” J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol., Vol. 12, No. 10, pp. 1157–1165, 2001.
Davis, G. B., Dowd, C. F., Bookstein, J. J., Maroney, T. P., Lang, E. V. and Halasz, N., “Thrombosed dialysis grafts: efficacy of intrathrombic deposition of concentrated urokinase, clot maceration, and angioplasty,” Am. J. Roentgenol., Vol. 149, No. 1, pp. 177–181, 1987.
Kerber, C. W., Barr, J. D., Berger, R. M. and Chopko, B. W., “Snare Retrieval of Intracranial Thrombus in Patients with Acute Stroke,” J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol., Vol. 13, No. 12, pp. 1269–1274, 2002.
Savrasov, G. V. and Skvortsov, S. P., “Modern Surgical Devices for Treating Thromboses: Current Status and Prospects,” Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 34, No. 4, pp. 173–179, 2000.
Mower, W. R., Quiõnes, W. J. and Gambhir, S. S., “Effect of intraluminal thrombus on abdominal aortic aneurysm wall stress,” J. Vasc. Surg., Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 602–608, 1997.
Di Martino, E., Mantero, S., Inzoli, I., Melissano, G., Astore, D., Chiesa, R. and Fumero, R., “Biomechanics of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the presence of endoluminal thrombus: Experimental characterisation and structural static computational analysis,” Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg., Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 290–299, 1998.
Riha, P., Wang, X., Liao, R. and Stoltz, J. F., “Elasticity and fracture strain of whole blood clots,” Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc., Vol. 21, No. 1, pp. 45–49, 1999.
Anand, M., Rajagopal, K. and Rajagopal, K. R., “A Model for the Formation and Lysis of Blood Clots,” Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb., Vol. 34, No. 2–3, pp. 109–120, 2005.
Mackman, N., “Triggers, targets and treatments for thrombosis,” Nature, Vol. 451, No. 7181, pp. 914–918, 2008.
Collet, J. P., Shuman, H., Ledger, R. E., Lee, S. T. and Weisel, J. W., “The elasticity of an individual fibrin fiber in a clot,” PNAS, Vol. 102, No. 26, pp. 9133–9137, 2005.
Kim, Y. T., Park, S. J. and Lee, S. J., “Micro/Meso-scale Shapes Machining by Micro EDM Process,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 6, No. 2, pp. 5–11, 2005.
Kim, H. T., Yang, H. J. and Kim, S. C., “Control Method for the Tool Path Aspherical Surface Grinding and Polishing,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 7, No. 4, pp. 51–56, 2006.
Isobe, H., Hara, K., Kyusojin, A., Okada, M. and Yoshihara, H., “Ultrasonically Assisted Grinding for Mirror Surface Finishing of Dies with Electroplated Diamond Tools,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 38–43, 2007.
Alagumurthi, N., Palaniradja, K. and Soundararajan, V., “Cylindrical Grinding — A Review on Surface Integrity,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 8, No. 3, pp. 24–44, 2007.
Lin, T., Lee, J. W. and Bohez, E. L. J., “A new accurate curvature matching and optimal tool based five-axis machining algorithm,” Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, Vol. 23, No. 10, pp. 2624–2634, 2009.
Wei, J., Zhang, Q., Xu, Z. and Lyu, S. K., “Study on Precision Grinding of Screw Rotors using CBN Wheel,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 11, No. 5, pp. 651–658, 2010.
Jang, K. S., Kang, T. W., Lee, K. S., Kim, C. and Kim, T. W., “The effect of change in width on stress distribution along the curved segments of stents,” Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, Vol. 24, No. 6, pp. 1265–1271, 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, CL., Kim, YT., Lee, KS. et al. Development of rotary tool for removal of intravascular blood clots. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 13, 413–419 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0053-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0053-z