Abstract
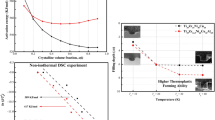
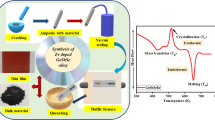
Both thermoplastic formability and electrical conductivity of Al–Ni–Y metallic glass with 12 different compositions have been investigated in the present study with an aim to apply as a functional material, i.e. as a binder of Ag powders in Ag paste for silicon solar cell. The thermoplastic formability is basically influenced by thermal stability and fragility of supercooled liquid which can be reflected by the temperature range for the supercooled liquid region (ΔTx) and the difference in specific heat between the frozen glass state and the supercooled liquid state (ΔCp). The measured ΔTx and ΔCp values show a strong composition dependence. However, the composition showing the highest ΔTx and ΔCp does not correspond to the composition with the highest amount of Ni and Y. It is considered that higher ΔTx and ΔCp may be related to enhancement of icosahedral SRO near Tg during cooling. On the other hand, electrical resistivity varies with the change of Al contents as well as with the change of the volume fraction of each phase after crystallization. The composition range with the optimum combination of thermoplastic formability and electrical conductivity in Al–Ni–Y system located inside the composition triangle whose vertices compositions are Al87Ni3Y10, Al85Ni5Y10, and Al86Ni5Y9.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Wiest, G. Duan, M.D. Demetriou, L.A. Wiest, A. Peck, G. Kaltenboeck, B. Wiest, W.L. Johnson, Acta Mater. 56, 2625 (2008)
G. Kumar, A. Desai, J. Schroers, Adv. Mater. 23, 461 (2011)
M. Carmo, R.C. Sekol, S. Ding, G. Kumar, J. Schroers, A.D. Taylor, ACS Nano 5, 2979 (2011)
R.C. Sekol, G. Kumar, M. Carmo, F. Gittleson, N. Hardesty-Dyck, S. Mukherjee, J. Schroers, A.D. Taylor, Small 9, 2081 (2013)
S.Y. Kim, S.J. Kim, S.S. Jee, J.M. Park, K.H. Park, S.C. Park, E.A. Cho, J.H. Lee, I.Y. Song, S.M. Lee, I.T. Han, K.R. Lim, W.T. Kim, J.C. Park, J. Eckert, D.H. Kim, E.S. Lee, Sci. Rep. 3, 2185 (2013)
K.C. Kim, K.R. Lim, E.S. Lee, W.T. Kim, A. Gebert, J. Eckert, D.H. Kim, Corros. Sci. 77, 1 (2013)
A. Inoue, Prog. Mater. Sci. 43, 365 (1998)
A. Peker, W.L. Johnson, Appl. Phys. Lett. 64, 2342 (1993)
H.W. Kui, A.L. Greer, D. Turnbull, Appl. Phys. Lett. 45, 615 (1984)
W.N. Myung, K.H. Parkxs, D.H. Jang, L. Battezzati, T. Zhang, A. Inoue, T. Masumoto, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 226, 406 (1997)
S.H. Hong, J.T. Kim, H.J. Park, Y.S. Kim, Y.S. Na, K.R. Lim, J.K. Lee, J.H. Lee, W.M. Wang, J.M. Park, K.B. Kim, Sci. Adv. Mater. 8, 1989 (2016)
S.H. Hong, J.T. Kim, S.C. Mun, Y.S. Kim, H.J. Park, Y.S. Na, K.R. Lim, J.M. Park, K.B. Kim, Intermetallics 91, 90 (2017)
C.A. Angell, Science 267, 1924 (1995)
X. Li, X. Bian, L. Hu, Y. Wu, J. Guo, J. Zhang, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 103540 (2007)
A. Takeuchi, A. Inoue, Mater. Trans. JIM 41, 1372 (2000)
X. Li, X. Bian, L. Hu, Phys. Lett. A 374, 3784 (2010)
J. Ding, Y.Q. Cheng, H. Sheng, E. Ma, Phys. Rev. B 85, 060201(R) (2012)
Q. Wang, C.T. Liu, Y. Yang, Y.D. Dong, J. Lu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 215505 (2011)
S.O. Kasap, Principles of Electronic Materials and Devices, 3rd edn. (McGraw Hill, New York, 2006)
V. Raghavan, JPEDAV 31, 57 (2010)
V.C. Sricastava, S.N. Ojha, Bull. Mater. Sci. 28, 125 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Na, M.Y., Park, S.H., Kim, K.C. et al. Optimum Combination of Thermoplastic Formability and Electrical Conductivity in Al–Ni–Y Metallic Glass. Met. Mater. Int. 24, 1256–1261 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0130-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0130-7